Erosion by Rivers
advertisement

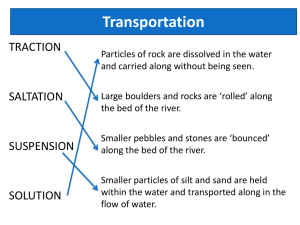
Water Erosion Runoff and Erosion • Moving water is a major agent of the erosion that has shaped Earth’s land surface. • When it rains, some water sinks into ground and other evaporates or is taken up by plants. • Moving water or water moving over Earth is called runoff. Amount of Runoff • • • • • • Depends on 5 factors: 1. Amt of rain 2. vegetation- more plants=less runoff 3. type of soil- some absorb more 4. shape of land- slope or flat 5. how people use the land- paved areas do not absorb water. Also, when farmers cut down crops, it creates more runoff. MORE RUNOFF MEANS MORE EROSION Rills and Gullies • As the runoff travels, it forms tiny grooves in the soil called rills. • As many rills flow into one another, they grow larger, forming gullieslarge grooves or channels in the soil that carries runoff after a rainstorm. Streams and Rivers • Gullies join together to form a larger channel called a stream (channel where water is continually flowing down a slope.) • Streams rarely dry up. Small streams are called creeks or brooks. • A large stream is called a river. Tributaries • Stream or river that flows into a larger river. • Ex: Missouri and Ohio rivers are tributaries of the Mississippi River. • A drainage basin or watershed is the area from which a river and its tributaries collect their water. Quick Check • 1. What is a tributary? • 2. What is a watershed/drainage basin? • Of these items, which one(s) are NOT part of a watershed/drainage basin? Rivers, oceans, streams, rills, gullies Valleys • Through erosion, a river creates valleys, waterfalls, flood plains, meanders, and oxbow lakes. • Steep slopes along a river erode rapidly, forming a deep V- shaped valley. • Rivers create a V-shaped valley. • Glaciers create a Ushaped valley. A. Waterfalls • 1. Waterfall- softer rock is below harder rock. The softer rock erodes first and the water drops off. Flood plain • Lower down on its course, the river spreads out and erodes the land, forming a wide river valley called a flood plain. • A river overflows into the floodplain during floods. Check up 1.How is a waterfall formed? 2.What creates a V-Shaped valley? U-shaped valley? B. MEANDERS • 1. Meander- a curve in a river. • 2. River curves around an obstacle (tree or rock) • 3. It erodes the outer bank and deposits on the inner bank. • 4. Over time, the meander becomes more curved. Meander Meander C. Oxbow Lake • 1. Oxbow Lake- meander that has been cut off from a river. • 2. May form when river floods and deposits sediments at the end of the meander. • 3. Eventually, the meander is cut off from the river forming an oxbow lake. (looks like a horseshoe lake). Oxbow lake diagram Oxbow Lake and almost an oxbow lake Teach Time • Explain to your neighbor what a meander is and how it forms. • Explain to your neighbor what an oxbow lake is and how it forms. III. DEPOSITS BY RIVERS • A. Alluvial Fan- wide, sloping deposit of sediment formed where a stream leaves a mtn. range.(Shaped like a fan). III. DEPOSITS BY RIVERS B. Delta-Sediment deposited where a river flows into an ocean or lake. It builds up a landform called a delta. Teach Time • Compare and contrasts alluvial fans and deltas. • Draw a diagram to show the differences btwn alluvial fans and deltas. C. Soil on Flood Plains 1. River floods over land near it and deposits new sediment. 2. The new soil is FERTILE and great for growing things. IV. Groundwater Erosion 1. Groundwater- Water that is UNDERGROUND. 2. Precipitation (rain, snow) soaks into cracks of soil and rock and goes underground. 3. Groundwater erodes the land through chemical weathering. 4. Water combines with Carbon dioxide to form carbonic acid which breaks down limestone. 5. Limestone erodes away and leaves a hole underground called a cave or cavern. Karst Topography • If the roof of a cave collapses because of the erosion of the underlying limestone, the result is a depression called a sinkhole. • This type of landscape is called karst topography. A. Cave Formations 1. Cave formations occur when water drips leaving behind calcite. 2. Stalactites- A deposit of calcite HANGING from the roof of a cave. 3. Stalagmite- Slow dripping builds up calcite in a cone-shape from the cave floor. Stalactites and Stalagmites Erosion- Rivers Deltas