HAND
advertisement

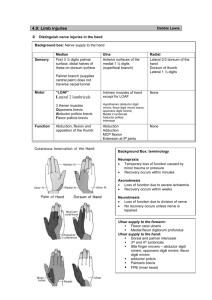
DEPARTMENT OF ANATOMY UPPER LIMB Hand The hand is the region of the upper limb distal to the wrist joint. It is subdivided into three parts: 1. Wrist 2.Metacarpus 3.Digits (five fingers including the thumb). The hand has an anterior surface (palm) and a dorsal surface (dorsum of hand). The carpal tunnel is formed anteriorly at the wrist by a deep arch formed by the carpal bones and the flexor retinaculum. The base of the carpal arch is formed medially by the pisiform and the hook of the hamate and laterally by the tubercles of the scaphoid and trapezium. flexor retinaculum is a thick connective tissue ligament that bridges the space between the medial and lateral sides of the base of the arch and converts the carpal arch into the carpal tunnel. Four tendons of the flexor digitorum profundus Four tendons of the flexor digitorum superficialis One tendon of the flexor pollicis longus Median nerve Carpal tunnel syndrome is an entrapment syndrome caused by pressure on the median nerve within the carpal tunnel. Carpal Tunnel syndrome Common in computer professionals. Due to constant dorsiflexion of wrist while typing the keyboard 8 The palmar aponeurosis is a triangular-shaped condensation of deep fascia that covers the palm and is anchored to the skin in distal regions. The apex of the triangle is continuous with the palmaris longus tendon. Dupuytren contracture is a disease of the palmar fascia resulting in progressive shortening, thickening, and fibrosis of the palmar fascia and aponeurosis. 1. Hypothenar compartment 2. Thenar compartment 3. Central compartment 4. Adductor compartment 5.Interosseous compartment The intrinsic muscles of the hand are located in five compartments All of the intrinsic muscles of the hand are innervated by the deep branch of the ulnar nerve except for the three thenar and two lateral lumbrical muscles, which are innervated by the median nerve. Abductor Pollicis Brevis Abducts thumb Opponens Pollicis Flexor Pollicis Brevis To oppose thumb Flexes thumb Abductor Digit Minimi Flexor Digiti Minimi Brevis Opponens Digiti Minimi Abducts digit 5 Flexes proximal phalanx of digit 5 bringing digit 5 into opposition with the thumb Action: Improves grip Action: Adducts thumb towards middle digit Extension: extensor pollicis longus, extensor pollicis brevis Flexion: flexor pollicis longus and flexor pollicis brevis Abduction: abductor pollicis longus and abductor pollicis brevis. Adduction: adductor pollicis Opposition: opponens pollicis. Lumbricals 1 and 2 Flex digits at metacarpophalangeal joints and extends interphalangeal joints Lumbricals 3 and 4 Flex digits at metacarpophalangeal joints and extends interphalangeal joints Dorsal interossei 1-4 Abducts digits from axial line and act with lumbricals to flex metacarpo-phalangeal joints and extends interphalangeal joints Palmar interossei 1-3 Adducts toward axial line & assist lumbriaclas in flexing the same joints as above Action of Dorsal Interossei : DAB : Abduction Little finger and thumb have no Dorsal interossei muscle Action of Palmar interossei : PAD :Adduction Middle finger and thumb have no palmar interossei muscle Blood supply to the hand is by the radial and ulnar arteries, which form two interconnected vascular arches (superficial and deep) in the palm. Superficial palmar arch: Ulnar artery+ palmar branch of radial artery Deep palmar arch: Deep palmar branch of ulnar artery+ radial artery To test for adequate anastomoses between the radial and ulnar arteries, compress both the radial and ulnar arteries at the wrist, then release pressure from one or the other, and determine the filling pattern of the hand. The hand is supplied by the ulnar, median, and radial nerves. Immediately distal to the pisiform, ulnar nerve divides into a deep branch, which is mainly motor and a superficial branch, which is mainly sensory. Deep branch: supplies the hypothenar interossei, adductor pollicis, and the two medial lumbricals. Superficial branch: supply skin on the palmar surface of the little finger and the medial half of the ring finger The ulnar nerve is most commonly injured at two sites: 1. Elbow 2. wrist Clawing of the hand: Metacarpophalangeal joints of the fingers are hyperextended and the interphalangeal joints are flexed. Compression of the ulnar nerve may occur at the wrist where it passes between the pisiform and the hook of the hamate. The median nerve is the most important sensory nerve in the hand because it innervates skin on the thumb, index and middle fingers, and lateral side of the ring finger. Branches: 1. Recurrent branch: innervates the three thenar muscles 2. Palmar digital nerves: In addition to skin, the digital nerves supply the lateral two lumbrical muscles Refers to a deformity in which thumb movements are limited to flexion and extension of the thumb in the plane of the palm. Severance of median nerve paralyzes the thenar muscles and the thumb loses much of its usefulness. The only part of the radial nerve that enters the hand is the superficial branch. Innervates skin over the dorsolateral aspect of the palm and the dorsal aspects of the lateral three and one-half digits distally to approximately the terminal interphalangeal joints. A 21 year old girl is brought to the emergency department with a puncture wound on the palmar side of her left index finger. Preservation of which of the following movements of her index finger will confirm the functional integrity of the flexor digitorum profundus muscle? A. Flexion of the metacarpophalangeal joint B. Adduction C. Abduction D. Flexion of the distal interphalangeal joint E. Flexion of the proximal interphalangeal joint A 53-year-old African American man involved in a motor vehicle accident sustains a severe mid-shaft fracture of the right humerus. Vitals are Temp-100.0F, BP120/88mm/Hg, pulse- 118/min, and RR- 14/min. Examination reveals wrist drop and no ulnar or radial pulses in the right arm. Examination reveals decreased sensation over the dorsal aspect of the lateral 3½ digits. The rest of the physical exam is otherwise unremarkable. What nerve is most likely injured given the findings in this patient? A.Axillary nerve B.Musculocutaneous nerve C.Median nerve D.Radial nerve E.Ulnar nerve The figure below represents cutaneous innervation of wrist and hand. The area A in the figure represents which Nerve? 1.Superficial branch of radial nerve 2.Anterior interosseous nerve 3.Palmar branch of median nerve 4.Palmar branch of ulnar nerve 5.Lateral cutaneous nerve of fore arm