Diencephalon, Brain Stem and Cranial Nerves
advertisement

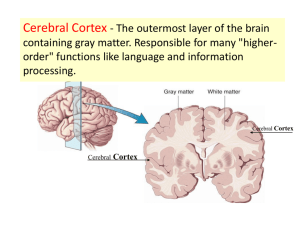
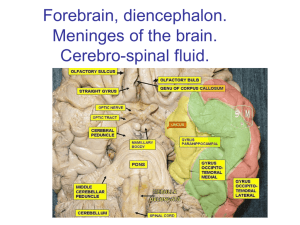
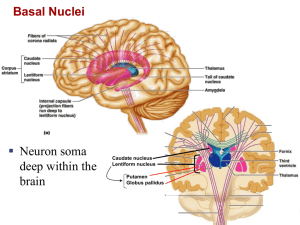
Diencephalon, Brain Stem and Cranial Nerves Day 5 Pages: 242-246 Diencephalon • Located between the cerebral hemispheres and above midbrain • Composed largely of gray matter • Surrounds 3rd ventricle • Includes: – – – – – – – – Thalamus Hypothalamus Optic tracts Optic chiasma Infundibulum Posterior pituitary gland Mammillary bodies Pineal gland Parts to Diencephalon • Optic tracts/optic chiasma – Formed by optic nerve fibers crossing over each other • Infundibulum – Behind optic chiasma, attachment for pituitary gland • Posterior pituitary gland – Hangs from floor of hypothalamus • Mammillary Bodies – Two rounded structures behind infundibulum • Pineal gland – Cone shaped structure attached to upper portion of diencephalon Thalamus • Bulge into 3rd ventricle • Central relay station for all sensory impulses except smell (ascending fibers) • Channels impulses to appropriate regions of cortex for interpretation • Can communicate with cerebral cortex by means of descending fibers Hypothalamus • Located below thalamus and forms floor of 3rd ventricle • Maintains homeostasis and links endocrine to nervous system • Regulates: – – – – – Heart rate and arterial BP Body Temp. H2O and electrolyte balance Control of hunger and body weight Control movements and glandular secretions of stomach and intestines – Production of neurosecretory substances and stimulation of pituitary gland to secrete hormones – Sleep and wakefulness Other functions of Diencephalon • Limbic System – Comprised of parts of: cerebral cortex, frontal and temporal lobes, hypothalamus, thalamus basal ganglia and other deep masses called nuclei • Controls emotional experiences and expressions • Can modify the way a person acts – Fear, anger, pleasure, and sorrow • Guides persons behavior towards a likely increase in survival. Brain Stem • Bundle of nervous tissue that connects cerebrum to spinal cord. • Consists of three parts – Midbrain – Pons – Medulla Oblongata Midbrain • Located at the top between diencephalon and pons • Contain corticospinal tracts which are the main motor pathways between cerebrum and lower parts of nervous system • Contains several masses of gray matter that serve as reflex centers. Pons • Rounded bulge on underside of brain stem • Dorsal side relays impulses to and from M.O and cerebrum. • Ventral side transmits impulses to cerebrum and cerebellum. • Also relays sensory impulses from PNS to higher brain centers Medulla Oblongata • End of brain stem • All ascending and descending nerve fibers pass through MO • Controls vital visceral activites – Cardiac center • Alters heart rate – Vasomotor Center • Constricting and dilating of blood vessels – Respiratory Center • Regulate rate, rhythm, and depth of breathing • Also responsible for coughing, sneezing, swallowing and vomiting. Reticular Formation • Found throughout the brain stem • Network of nerve fibers • Responsible for taking sensory impulses and activating cerebral cortex into a state of wakefulness • Decreased activity in reticular formation is known as sleep. • Comatose state: – Point at which the reticular formation is injured and cannot be aroused even with strong stimulation. Cerebellum • Large mass of tissue located below occipital bone. • Divided into two hemispheres • Surrounded by cerebral cortex • Communicates with CNS by three pairs of nerve tracts – Cerebellar peduncles Cellebellar Peduncles • Inferior – Brings sensory information concerning position of limbs, joints, and other body parts • Middle – Transmits signals from the cerebral cortex to the cerebrellum concerning desired positions of these parts. After interpretation/analysis, sends pulses on to 3rd pair • Superior – Incorporated into motor impulses that get sent down brainstem to move body in desired way. Cerebellum • Reflex center for integrating sensory information concerning position of body parts and coordination of skeletal muscle movements • Maintains posture • Damage/Injury – Tremors – Inaccurate movements of voluntary muscles – Loss of muscle tone – Reeling walk – Loss of equilibrium Review • What are the major functions of the thalamus? The hypothalamus? • How may the limbic system influence behavior? • List the structures of the brain stem. • What vital reflex centers are located in the brain stem? • What is the function of the reticular formation? • Where is the cerebellum located? • What are the major functions of the cerebellum?