Kingdom Fungi
advertisement

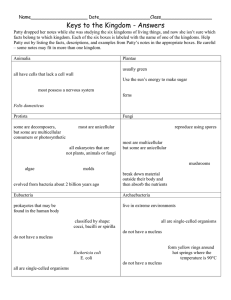
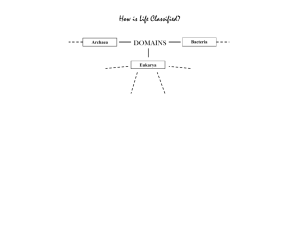
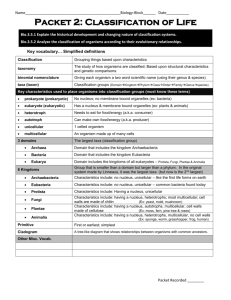
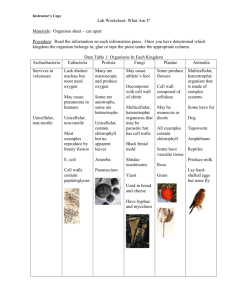
Classifying Living Things •Classifying means grouping together according to •Grouped according to common characteristics (TAXONOMY) •Classification system developed by Carolus Linnaeus (1707-1778) •Largest group of a classification is called a DOMAIN •All living things are grouped into SIX KINGDOMS System of Classification Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus Species Six Kingdoms Archaea • Bacteria • Protista • Fungi • Plantae • Animalia • Kingdom Archaea • • • • • • Smallest of Living Things One-celled (Unicellular) No cell nucleus (Prokaryote) Cell wall lacks PEPTIDOGLYCAN No cell organelles Live in extreme environments (boiling mud, hot ocean vents, salty ponds) • Example: halophile Bacteria • • • • • • Unicellular organisms No nucleus ( PROKARYOTE) Cell wall containing PEPTIDOGLYCAN Reproduce by binary fission Cause human disease and food spoilage Example: E. coli, salmonella, Kingdom Protista • • • • • • • SOME Multicellular BUT mostly Unicellular Have a nucleus (EUKARYOTES) Plant like producers (AUTOTROPH) Animal like consumers (HETEROTROPH) Have cell organelles Have no cell wall Example: Algae and Amoeba Kingdom Fungi • • • • • SOME Unicellular but MOSTLY Multicellular Have a nucleus (EUKARYOTIC) Have cell organelles Have cell walls containing CHITIN Examples: Yeast and mushrooms Kingdom Plantae • • • • • • • Multicellular Have a nucleus (EUKARYOTIC) Have cell organelles Have a cell membrane Have a cell wall CONTAINING CELLULOSE Producers (AUTOTROPHS) Examples: Pine trees, dogwood trees Kingdom Animalia • • • • • • • Have a nucleus (EUKARYOTES) Multicellular Have cell organelles No cell walls Have cell membrane Consumers (HETEROTROPHS) Examples: Frog, starfish, eagle RULES For Writing Scientific Names • • • • Binomial Nomenclature Uses two Latin Words First word (Genus) starts with upper case letter Second word (Species) starts with lower case letter • Must be italicized or underlined • Example: Quercus rubra (Red Oak)