W_59_Training and Le..
advertisement

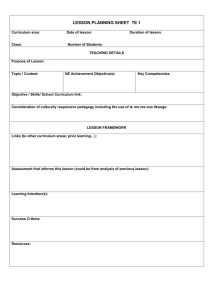
Training And Leading On Purpose: The Art Of Intentional Facilitation Presenter: Nora Gerber, UC Davis Instructor Center for Human Services UC Davis Extension human@ucde.ucdavis.edu Training And Leading On Purpose: The Art Of Intentional Facilitation This workshop is intended for AGENCY LEADERS -those who Lead Learning Sessions (workshops/ meetings/ public presentations): Trainers Managers Supervisors Mentors & Coaches Training And Leading On Purpose: The Art Of Intentional Facilitation Have you ever noticed that we often tend to “see the light” and remember things a bit differently? Think to yourself for a minute: In what ways might this reality complicate your ability to deliver information? What challenges does it present? Training And Leading On Purpose: The Art Of Intentional Facilitation Have you ever noticed that we often tend to “see the light” and remember things a bit differently? What strategies could you use to ensure that your learners begin to focus their thinking in your intended direction… to meet your planned training outcomes? TARGETING THE PLANNED OUTCOMES WORKSHOP PURPOSE STATEMENT To promote the employment of processing prompts when training or leading a meeting, as a tool for facilitating comprehension and transfer of learning. TARGETING THE PLANNED OUTCOMES GLOBAL GOALS OF THE WORKSHOP • To introduce the strategy of Intentional Facilitation • To provide options for promoting the processing of information • To suggest sample prompts & questions based on the intended outcome focus of the material TARGETING THE PLANNED OUTCOMES OBSERVABLE OBJECTIVES Learners will • take targeted and designated notes as directed while they listen and view • practice processing information using 4 different options • document examples of prompts that would be relevant to their content presentations Explain to someone nearby why you need all 4 -what’s the usefulness to you, the trainer, of each? TARGETING YOUR OUTCOMES COMPETENCIES Professional Standards to reach Responding to management request; policy change; PURPOSE = BIG PICTURE A Purpose Statement is an answer to the question, “Why?” “Why am I conducting this training?” new forms… General VS Global Goals Observable Observable Objectives What you hope to accomplish Starts with “to” What they will be doing Starts with a verb NOBLE, YET DIFFICULT TO OBSERVE BEHAVIORS OBSERVABLE BEHAVIORS Best Practice = design has Purpose, Goals, & Objectives Deciding how to choose materials /content Determines the reinforcement activities THE EFFICIENT TRAINER FOCUSES ON HOW THEY WANT IT ALL TO COME OUT – THE OUTCOMES This is where the “Intentional” part comes in. You know the change you want to see as a result of the training/ meeting/ presentation. Craft your processing prompts to lead the learner directly and intentionally toward your planned outcomes. TODAY: MODELING 4 OPTIONS AND 4 FOCUS TOPICS 4 OPTIONS-- Mix them up; Match to your planned Outcomes Meta-cognition Table-Team-Talk Pair Sharing Whole Class Discussion 4 likely FOCUS TOPICS -Selected per your Outcomes Personalization Mission/ Values Business Processes Problem Solving IT’S NOT YOUR JOB TO “COVER THE MATERIAL” BLAHBLAHBLAH “Cover The Material” PLEASE MAKE A NOTE IT IS YOUR JOB TO ENHANCE WORKPLACE BEHAVIOR TO ILLUSTRATE… PRACTICE Take a moment to talk silently to yourself… then make a response note on the lines to the right… What do you tend to do when you are feeling like you have too much material to cover and not enough time to cover it? Which training/ presentation methods do you tend to employ when in this situation? TO ILLUSTRATE… PRACTICE Option: Meta-cognition Take a moment to talk silently to yourself… then make a response note on the lines to the right… Focus: Personalization & Problem to Solve What do you tend to do when you are feeling like you have too much material to cover and not enough time to cover it? Which training/ presentation methods do you tend to employ when in this situation? TO ILLUSTRATE… PRACTICE OPTION: Pair Share FOCUS: Problem to Solve TURN TO ONE SMART PERSON SEATED NEAR YOU Share your notes and thoughts; you have 2 minutes between you Share What happens to you, as a learner, when the Trainer employs your “too much material… too little time” method? How effective is it? What might be more effective for you, as a learner? THE CYCLE OF LEARNING WHAT? NOW WHAT? How /When/ Where will I apply this? What’s my Action Plan? Content/ Activity Data/ Material SO WHAT? What’s In It For Me? How does it impact me/ my life/ my job/ my work with families? “Covering The Material” Usually = the “WHAT” only Covering the material is yada-yada-data-dump-dumpdump EFFECTIVE TRAINING ALSO ADDRESSES THE “SO WHAT?” Cognitive/ Head Psychomotor/ Hands NOW WHAT? How /When/ Where will I apply this? What’s my Action Plan? WHAT? Content/ Activity Data/ Material Affective/ Heart SO WHAT? What’s In It For Me? How does it impact me/ my life/ my job/ my work with families? TRAINING TRUISM: “You can change people’s minds with new information; but they will only remember the information and / or change their behavior when they feel the need to remember and / or change.” Tap the affective domain MAKE A NOTE – FILLING IN THE KEY WORDS Training is an organized, structured activity, designed to produce specific learning for improving performance. Training: A visible process; an event Learning: An inferred process, recognized by changes in behavior TRAINING CAN INDUCE LEARNING IN THE BEST DESIGNED AND DELIVERED WORLD, “TRAINING” INDUCES “LEARNING”! INTENTIONAL FACILITATION TOL PROMPT: Turn to ONE smart person near you and put this Learning Point into your own words, so you own it and grow dendrites to store it where you can retrieve it when needed. Go back as far as “Cover The “It’s not your job…” Material” FYI: This is Option: Pair Share/ Focus: Personalization More to come on these soon LEFT RIGHT Content in Context TO MOVE THE LEARNER FROM “AWARENESS OF…” TO “ABLE TO…,” GIVE THEM A JOB TO DO WHICH ENCOURAGES THE LEARNER TO BUILD A BRIDGE BETWEEN LEFT RIGHT BRAIN HEMISPHERE FUNCTIONS Logical Sequential Verbal Linear Analytical Content Rational Explicit Any lecture/ handout/ text Data Facts manual/ screen shot/ information Rules Regulations Non-Verbal Visual Spacial Context Creative Example/ story/ anecdote/ case Holistic Intuitive study / picture experience/ Humorous exercise BIG Picture processing prompt WHOLE BRAIN -FRIENDLY TRAINING VERBAL INFORMATION is generally processed analytically = LEFT BRAIN VISUAL INFORMATION is generally processed in holistically = RIGHT BRAIN Content: words (printed and spoken) with Context: graphics or stories or examples or real-job challenges or processing prompts promotes whole brain learning RETENTION RATES AFTER 60 DAYS 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 TELL Primarily LEFT Brain Input TELL + SHOW TELL+ SHOW+ DO Involves more LEFT + RIGHT/ WHOLE BRAIN Input/ processing PROCESSING PRACTICE OPPORTUNITY REGARDING WHOLE-BRAIN-BRIDGING DELIVERY… OPTION #1 = Metacognition -thinking about what I am thinking… THINK silently and independently for a minute. If asked to explain this concept to someone (presume they are fairly bright), how would you phrase this important training concept in your own words? PROCESSING PRACTICE OPPORTUNITY REGARDING WHOLE-BRAIN-BRIDGING DELIVER… OPTION # 2) Pair Share -- processing my thinking out loud, clarifying, adding value to my understanding… Share with ONE other person for a minute. Explain this concept to someone (presume they are fairly bright). How would you phrase this important training concept in your own words? PROCESSING PRACTICE OPPORTUNITY REGARDING WHOLE-BRAIN-BRIDGING DELIVER… OPTION # 3) Table Talk / 4 on the Floor -creaming for our best shot/ adding value to our mutual understanding Form small groups of 4 and no more. Whoever thinks they’ve got it, start talking; others chime in and add value. Explain this concept in your own words PROCESSING PRACTICE OPPORTUNITY REGARDING WHOLE-BRAIN-BRIDGING DELIVER… Option #4) Whole Class Discussion If your team agrees on an explanation, promote a spokesperson to enlighten us all -- the trainer may be adding value to what is shared Explain this concept in your own words SO WHAT? WHAT DOES THIS MEAN TO ME WHEN I PLAN AND DELIVER TRAINING? Think (privately) about the questions above. Take a hike over the bridge from from CONTENT (whole-brain-friendly training) to CONTEXT (your workshops/ meetings) In what ways do YOU facilitate helping the learner to bridge what you are training to their own workplace application? WHAT, IF ANYTHING DO YOU INTENTIONALLY DO? MIX IT UP / MATCH IT UP It takes time to go through all 4 options, + we came back to Metacognition again in the end. Select all 4 when the topic is complex or requires change/ involves resistance/ has the potential for a big impact. Mix it up to keep it interesting. Match it up to your planned Outcomes A TRAINER OR LEADER OR PRESENTER WHO WANTS TO BE MOST EFFECTIVE… NOT EVEREVEREVER DOES JUST READ THE SLIDES / HANDOUTS/ LECTURE WORD FOR WORD • THIS IS DEADLY • IT IS NOT EFFECTIVE/ EFFICIENT. • IT’S BORING • IT’S INSULTING TO MOST ADULT LEARNERS. • IT’S A WASTE OF EVERYONE’S TIME. THE LEARNER’S MIND IS LIKE A BANK OF FILE CABINETS All new knowledge is attached to what we already know. We have what we know filed away -using our own filing system PRINCIPLES OF COGNITION THAT IMPACT CURRICULUM DEVELOPMENT Everything that is ever learned and remembered is organized into a congruent system & attached to what we already know. HUH? Make a note. What is it? THE LEARNER’S MIND IS LIKE A BANK OF FILE CABINETS When introduced to new information, the learner searches the file cabinets and asks, “What’s that like? What do I already know about that and what does this add? Change? THE LEARNER’S MIND IS LIKE A BANK OF FILE CABINETS HELP LEARNERS OPEN THE RIGHT FOLDER BEFORE YOU DUMP DATA INTO THEIR IN-BASKET Put the information into a meaninful context by telling them what they are expected to DO with the information—BEFORE you deliver it. The key is to: Ask the best question Send them to a relevant file folder of their mind Place the material/ problem/ information in the right context TRAINING TRUISM: Trainees are LEARNING what they are DOING. “Give them a job to do” Old Proverb: Show me and I see; Tell me and I hear; Involve me and I learn. This Is A Powerful Transfer Of Learning Training Technique Frame questions and processing prompts designed to promote critical thinking, phrased to guide the participants toward achieving the intended workshop or meeting outcomes… then give them a minute to think… ACTIVITIES VS. PROCESSING PROMPTS ACTIVITIES = • generally result in a product/ response • take 30 +/1 minutes • involve some props and pieces ACTIVITIES VS. PROCESSING PROMPTS PROCESSING PROMPTS • require only words + brains + a little time • engage all learners’ minds on the topic • guide them to remember/ “own” the material • allow the learner to reflect upon the importance / relevance of the material so they decide they DO want to remember/ apply it on the job • make retrieval more likely in the workplace USE INTENTIONAL FACILITATION: PROCESSING PROMPTS… WHEN TRAINING MATERIAL THEY NEED TO REMEMBER WITHOUT READING “AT” THEM LINE FOR LINE & SLIDE FOR SLIDE 4 OPTIONS FOR PROCESSING THE INFORMATION Metacognition Thinking about what I am thinking • Always begin here • Engaging all brains • Searching my data banks for what I already know about this information 4 OPTIONS FOR PROCESSING THE INFORMATION MIX IT UP / MATCH IT UP Pair Share/ Co-Worker Confirmation Turn to ONE partner/ peer/ neighbor • Share and compare • Clarify their thinking by processing out loud • Receive feedback and value added from a peer 4 OPTIONS FOR PROCESSING THE INFORMATION Table-Team Talk • Cluster as a small group (4-6 max) • Discuss as a small group • Whoever has something to say starts talking; others chime in • They clarify + add value to each other’s ideas • They “cream” for the best thinking Training Truism: The more the training matches the way (we want them to) do business, the more likely the transfer of learning ANOTHER PRACTICE OPPORTUNITY OPTION: METACOGNITION THEN TABLE TEAM TALK Think to yourself for 30 seconds, then cluster into a team of 4 and discuss: FOCUS: BUSINESS PROCESSES In what ways are the first three options: 1) Metacognition 2) Pair sharing/ Co-worker Confirmation 3) Table-Team Talk LIKE the way we want them to be doing business in the workplace? 4 OPTIONS FOR PROCESSING THE INFORMATION Whole Class Discussion • The floor is open for questions/ comments • Participants ask questions/ respond to what has been asked/ said • The Trainer asks/ responds • Most of the conversation is between the Trainer and… one or all SELECTING THE FOCUS OF THE PROMPTS FOCUS the attention where you want the participants to FOCUS, based on your planned OUTCOMES. BE INTENTIONAL ABOUT HOW YOU PHRASE THE QUESTION/ PROMPT Decide WHERE do you want them to end up in their minds about this information? GUIDE them to go there by your processing prompt SELECTING THE FOCUS OF THE PROMPTS HERE ARE 4 COMMON AREAS OF FOCUS: • PERSONALIZATION/ BUY IN • AGENCY VALUES/ MISSION/ COMPASSION FOR CUSTOMERS & CO-WORKERS • BUSINESS PROCESSES • A PROBLEM TO SOLVE SELECTING THE FOCUS OF THE PROMPTS Is your goal to achieve Buy in? Commitment? Ownership of the information -as if it is THEIR idea? Employ PERSONALIZATION prompts Examples: • In what ways do you believe this is true? • How might this impact you/ the way you do business? • Which parts will be easy for you? • Which might present a challenge for you? SELECTING THE FOCUS OF THE PROMPTS Is your goal to get them to honor agency Mission & Values or demonstrate compassion with customers and co-workers Employ MISSION/ VALUES prompts Examples: • In what ways will this information / behavior benefit families in the system? • In what ways does this help us meet our Mission? • In what ways does this match your personal values? In what ways might it be in conflict, if at all? • In what ways is it the right thing to do? SELECTING THE FOCUS OF THE PROMPTS Is your goal to promote a better way of doing business?To be in compliance? Employ BUSINESS PROCESSES prompts Examples: • Which comes first, second, etc. • Where in the whole picture of our work does this fit? • How does this relate to the law? To agency policy? • What support is available to you…? SELECTING THE FOCUS OF THE PROMPTS Is your goal to help the participants figure out how to solve a particular type of problem? Employ PROBLEM TO SOLVE prompts Examples: • How would you use this information/ tool/ skill/ idea to help families? • How will doing this fix the problem of…? • What have you done in the past to solve similar problems? NAVIGATING THE SYSTEM: WHERE TO GO WHEN THEY ACTUALLY NEED TO KNOW <<<<<<< We are living and working in the information age NAVIGATING THE SYSTEM: WHERE TO GO WHEN THEY ACTUALLY NEED TO KNOW Show them how to navigate the system by using… • post-its/ dividers • table of contents/ indexes • search engines/ websites • executive summaries • job aids/ desk guides • templates • “how to fix it” lists + note and share (shout out) YOUR Bright Ideas -What DO YOU DO to help Participants navigate…? We are living and working in the information age KEY POINT SUMMARY (CLOSURE STRAGEGY) I learned… I feel… I was surprised… I’m wondering… I re-discovered… I appreciated… I… THANK YOU Center for Human Services UC Davis Extension University of California, Davis 1632 Da Vinci Court Davis, CA 95618 (530) 757-8643 Phone (530) 754-5104 Fax www.humanservices.ucdavis.edu human@ucde.ucdavis.edu