Nondisjunction
advertisement
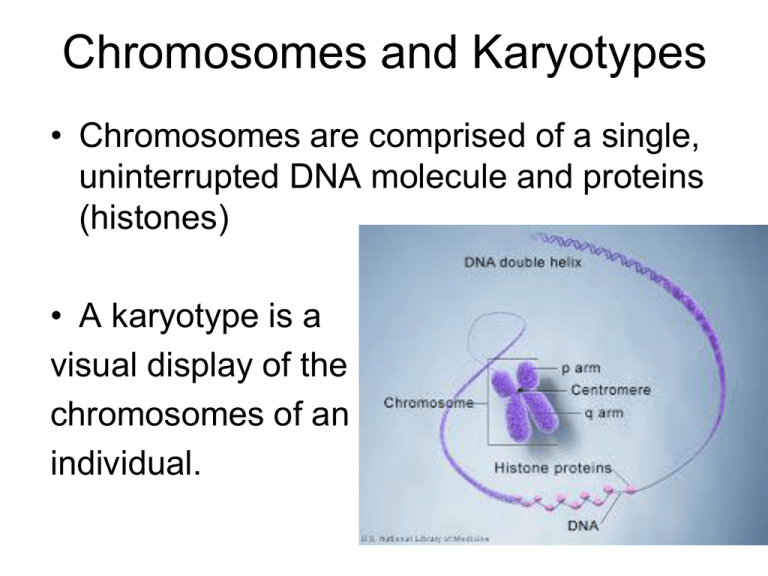
Chromosomes and Karyotypes • Chromosomes are comprised of a single, uninterrupted DNA molecule and proteins (histones) • A karyotype is a visual display of the chromosomes of an individual. Karyotype A picture of a complete diploid set of chromosomes arranged in pairs of decreasing size Amniocentesis 16-22 Weeks Chronic Villus Sampling (CVS) 10-12 Weeks How Do We Look at the Chromosomes? Cells are treated with Colchicine - WHY? Prevents Spindle Fibers form forming Cells will be stuck in Metaphase Chromosomes will be condensed and VISIBLE Cells are placed in pure water (hypotonic) – WHY? Color or Black and White? Black & White – Most Common Each chromosome has a characteristic banding pattern that helps to identify them; both chromosomes in a pair will have the same banding pattern. Let’s Make It Pretty - Way to Go Photoshop Karyotypes are arranged with the short arm of the chromosome on top, and the long arm on the bottom, called p and q, respectively. • Sex Chromosomes• determine an individual’s sex »X and Y chromosome • Autosomes-the other 44 chromosomes Normal Female Karyotype Normal Male Karyotype Let’s Make It Pretty - Way to Go Photoshop So, whose Karyotype is this? What is wrong with this picture? Nondisjunction • Occurs when homologous chromosomes or sister chromatids fail to separate during meiosis • Results in gametes with an abnormal number of chromosomes (missing or extra) Meiosis I Meiosis II Results in Trisomy Results in Monosomy Nondisjunction Does this remind you of something? Hint: What happened when we played – Mutated Tumor suppressor gene? Nondisjunction Consequences • Nondisjunction produces abnormal gametes (sperm and egg) • Fertilization wit an abnormal gamete can result in Monosomy or Trisomy • Monosomy – missing 1 chromosome • Trisomy – having 1 extra • Most monosomies and trisomies do not survive to birth Down Syndrome Trisomy 21 • • • • 1 in 700 babies (6000 babies/year) 400,000 Americans Rate increases with maternal age 5% of cases traced to father Turner Syndrome (XO) • 1 in 2500 females • Monosomy of X chromosome • 10% of all miscarriages • Highly variable Turner Syndrome (X0) Kleinfelter’s Syndrome (XXY) • 1 in 700-1000 males • Many times they may not know






