Patterns of Inheritance Gregor Mendel Pea plants Complete
advertisement

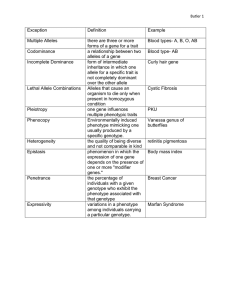
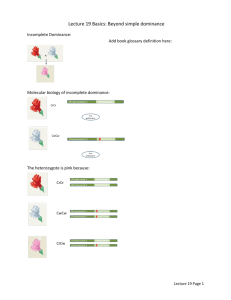
Patterns of Inheritance Gregor Mendel Pea plants Complete dominance Law of Segregation Law of Independent Assortment Law of Independent Assortment Practice Two organisms, with genotypes BbDD and BBDd are crossed. Assuming independent assortment occurs for both genes, what genotype ratios do you expect? Practice Y = yellow seeds and y = green seeds / T = tall plant and t = short plant An F1 generation yields 12 yellow, tall plants and 4 yellow, short plants. What are the genotypes of the P generation plants? Law of Multiplicatiom Used to determine whether two or more independent events will occur together in some specific combination. e.g. What is the probability that an Rr x Rr cross will yield the rr genotype? 1/2 x 1/2 = 1/4 Law of Additon Used to determine the probability that any one of two or more mutually exclusive events will occur. e.g. In the Rr x Rr cross, the Rr genotype can result from two mutually exclusive events. The sperm can donate the R and the egg r or vice versa. So, 1/4 + 1/4 = 1/2 chance at Rr. Practice What is the probability that YyRr will result from a YyRr x YyRr cross? What is the probability that ppYyrr will result from a PpYyRr x Ppyyrr cross? Mendelian Inheritiance Aka. complete dominance Each character is determined by a single gene, for which there are two alleles, one completely dominant and the other recessive. A note on dominance... Dominance does not mean the allele is most common in a population. It means that in a complete dominance situation, the heterozygote expresses only the dominant trait. Pedigrees Practice Draw the following pedigree. Identify the genotypes and whether the trait is dominant or recessive. Types of Characters Discrete (e.g. Tongue rolling, ear-lobe attachment) Quantitative (e.g. Height, skin color) Multifactorial (e.g. Height, build, skin, intelligence) Non-Mendelian Patterns Incomplete Dominance Neither gene is completely dominant. e.g. flower color in some plants, Codominance Each allele affects the phenotype in separate, distinguishable ways. e.g. Human mn blood group, flower color in some plants Multiple Alleles More than two alleles for a character exist in a population of organisms. e.g. ABO blood groups Practice Cross an individual heterozygous for type A blood with one who is heterozygous for type B blood. What are the expected genotype and phenotype ratios? Polygenic Inheritance When two or more genes have an additive affect on a single phenotypic character. e.g. Skin pigmentation Plieotropy One gene has multiple phenotypic effects. e.g. cystic fibrosis, sickle-cell disease Epistasis The phenomenon when the phenotypic expression of one gene alters the phenotypic expression of another gene. e.g. Fur color in mice and dogs Practice B = black fur, b = brown fur and E = pigment deposition, e = no pigment deposition These genes have an epistatic relationship. What are the expected fur color phenotype ratios (black : brown : yellow) when two dogs heterozygous for both traits are crossed? X-linked When a gene is located on the X chromosome. e.g. Color blindness, hemophilia Practice Neither Tim nor Rhoda have Duchenne muscular dystrophy, but their first born son has it. What is the probability that a second child of this couple will have the disease? Practice A man with hemophilia (a recessive, x-linked condition) has a daughter of normal phenotype. She marries a man normal for the trait. What is the probability that a daughter of this mating will be a hemophiliac? Patterns of Inheritance Overview Complete dominance Incomplete dominance Codominance Multiple Alleles Polygenic Inheritance Plieotropy Epistasis Sex-linked, X-linked The relationship between dominance and phenotype For any character, the observed dominant/recessive relationship of alleles depends on the level (organism all, molecular, biochemical) at which we examine the phenotype. e.g. See Tay-Sachs description on p. 272 Remember an allele is a nucleotide sequence.