Virtual Lab Instructions (Mrs. McLean added what is in red) Skull
advertisement

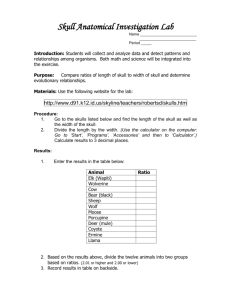
Virtual Lab Instructions (Mrs. McLean added what is in red) Skull Analysis Safety Notes: Skull casts are fragile, so always handle with care. (You are not really handling them) Materials: (This is all on the computer) Skull casts: 4 known species and 1 unknown Calipers Purpose: Observe and compare physical features of primate skulls. Examine possible relationships based on the observed features. Hypothesis: Predict the species of your skull based on first observation, giving an explanation for your prediction. (Write your prediction here): Procedure: Qualitative Observations: (Qualitative means it is does not involve numbers) 1. Line up each of the skulls on the lab table, facing to the left, with the Frankfurt planes parallel to the ground. 2. Observe each skull from the side, recording your observations about the following features: 1. Forehead: Is the angle of the forehead sloping or more vertical? Is the brow ridge above the eyes small, medium, or large? Does the forehead extend out above the eyes? 2. Face: Is the shape of the face sloped or flattened and vertical? 3. Teeth: Are the teeth long or short? Sharp or dull? 3. Observe each skull from the bottom view and locate the foramen magnum. This is the hole that connects the brain stem to the spinal cord. Record your observation of the location of each skull’s foramen magnum. Is it located toward the front or the rear of the skull? 4. Observe each skull from the top and record your observations of the shape of the brain cavity. Is it more round or oval? Are the edges more squared off or pointed? Make comparisons between the skulls. Quantitative Observations: Determine Supraorbital Height (Follow these directions to get the numbers you put on the chart) 1. Use the calipers to measure the distance AC (from point A to point C on the skull). (blinking green circle) 2. Use the calipers to measure the distance BC (from point B to point C on the skull). 3. These measurements will be used to calculate the skull’s supraorbital height according to the formula: (BC/AC) × 100 = Supraorbital Height (you can use a calculator) 4. Record the skull’s supraorbital height in the data table. 5. Take the same measurements for each of the skulls, recording the supraorbital heights in the data table. Data and Observations: Create a data table to record your observations and measurements for each skull: Everything is an observation except the last column for supraorbital height). Click the blinking green circle in the lab to get the measurements to calculate this Skull Forehead Face Teeth Foramen Magnum Brain Cavity Supraorbital Height (cm) Pan troglodytes (modern chimpanzee) Homo sapiens (modern human) Homo erectus (extinct hominid) Australopithecus afarensis (extinct hominid) Unidentified Fossil Skull Conclusion: Be sure to answer the following reflection questions in the conclusion of your lab report: Was your hypothesis correct? Which of the four species does the unidentified skull most resemble? Predict how you think it may relate to the other species in terms of evolution. Justify your answer with specific observations. How do the shapes of the face, forehead, and teeth differ between the various species? What do you think accounts for these differences? How might some of these differences be possible adaptations? In what way do you think the location of the foramen magnum relates to the movement of each species? What might the shape of the skull and the supraorbital height tell us about each species?