Spinning earth and climate
advertisement

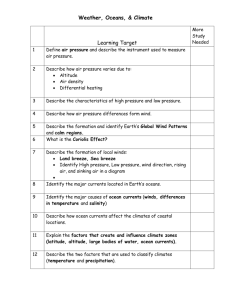
The effect the spinning earth has on water and wind currents. The earth is spinning all the time as it moves through space. The earth’s spinning makes the water in the oceans and the air we breathe move. The movements of the larger air and water currents can be mapped. At certain times of the year, winds can cause a great deal of rain. The winds that cause this rain are called monsoons. Earth spins. As the earth turns, the side pointed toward away from the sun has daylight. The side of the earth pointed away from the sun has nighttime. It takes 24 hours for the earth to spin around once, which is why there are 24 hours in a day. One complete spin of the earth is called a rotation. The earth is tilted as it faces the sun. The earth is warmer at the equator and cooler at the poles because of the angle at which the sun’s ray meet the earth’s surface. There is almost a direct hit at the equator. A large part of the earth is covered with water. As the waters of the oceans move, they strike land. This causes them to move around the land and along the shorelines of the continents. Moving through the ocean water are currents. Currents are like rivers in the ocean. Ocean currents can be mapped/ The spinning of the earth affects the waters of the ocean. Spinning jar. The earth’s spinning affects the oceans’ waters just as the water in the spinning jar was affected. Water in the Northern Hemisphere and Southern Hemisphere move in different directions due to the Coriolis force. Ocean currents have different temperatures. Water at the Poles are cold, and water at the equator is warm. Ocean currents from the Poles are cold, and at the equator are warm. The air that surrounds the earth is also affected by the spinning of the earth. The Coriolis force affects winds just as it does water. Wind belts that move one way in the Northern Hemisphere move the other way in the Southern Hemisphere. The winds are also affected by the season of the year. Some winds blow one way during the summer and the other way during the winter. These are called seasonal winds. Monsoon winds bring heavy rains. It brings water from the equator. Farmers count on these regular heavy rains to help their crops. In Bombay, India, there is no rain from November to March, but from June until September there is an average of 88 inches of rainfall. There are 5 factors. 1. Ocean Currents (what we just went over) 2. Nearness to water (NYC vs Omaha Nebraska) 3. Latitude ( Close to equator vs Far from the equator) 4. Altitude ( Height of the land; elevation; mountains vs plains) 5. Winds and Mountains (Winds source (warm waters vs cold waters, winds blowing from the land vs winds that carry moisture with them) winds over mountains)