Types of Mixtures PPT
advertisement

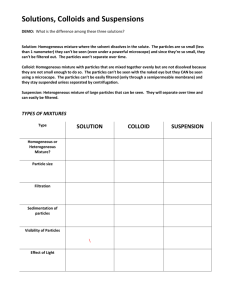
Types of Mixtures YEAR 1 SCIENCE Note-Taking Expectations notes must be written neatly letters should not be too BIG! write on each line, unless instructed to skip a line for another section have a puke page on standby: if you run out of room on the first page, then continue writing on the puke page (glue after the presentation!) Top of the Page Your notes should contain the following at the top of the page: The essential question (EQ: What are the different types of mixtures?) The date (7 November 2014) and page # The title (Types of Mixtures) REVIEW With your group, write down the answer to the previous EQ (What is the difference between a substance and mixture?) across from the previous notes. Substance: form of matter that cannot be separated by physical means (element and compound) Mixture: form of matter than can be separated by physical means (homogeneous and heterogeneous) Solution: a homogenous mixture; Solution: a homogenous mixture; one substance (solute) dissolves inside another (solvent) and never settles to the bottom; Solution: a homogenous mixture; one substance (solute) dissolves inside another (solvent) and never settles to the bottom; examples salt water, soda, vinegar, gasoline Sugar + Water = Sugar Water SKIP 1 LINE Suspension: a heterogeneous mixture containing liquid and solid particles; Suspension: a heterogeneous mixture containing liquid and solid particles; particles float (suspend) in liquid before they settle to bottom Suspension: a heterogeneous mixture containing liquid and solid particles; particles float (suspend) in liquid before they settle to bottom examples Italian dressing, muddy pond water, chocolate milk SKIP 1 LINE Colloid: similar to heterogeneous AND homogenous mixtures; Colloid: similar to heterogeneous AND homogenous mixtures; contain particles bigger than those in solutions, but are too light to settle to the bottom- particles stay suspended! Colloid: similar to heterogeneous AND homogenous mixtures; contain particles bigger than those in solutions, but are too light to settle to the bottom- particles stay suspended! examples milk (water + fat), fog (water + air), cool whip, butter SKIP 1 LINE Colloid Shining a beam of light through a colloid will make the light scatter- this is called the Tyndall Effect. Note Review highlight in yellow solution, solute, solvent, suspension, colloid, Tyndall Effect underline in red the definition of solute, solvent, Tyndall Effect circle in blue the examples of solution, suspension, colloid Ticket Out the Door (TOTD) Determine whether the following is a element (E), compound (C), homogeneous mixture (HO), or heterogeneous mixture (HE) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Chocolate chip cookie Water (H20) Milk Pile of leaves Oxygen (O2)