welfare reforms - Gazi Asha

Why did the
Liberals introduce welfare reforms?
Learn: To understand why the Liberals needed to introduce welfare reforms.
• Create a mind map of the reasons that the government introduce reforms today.
• Feedback.
• Prioritise Liberal reform motives.
• Feedback.
• Place the reforms in chronological order and summarise them.
• 4 fingers and a thumb!
E
Identify at least 3 key reforms.
D
Describe the different reform acts.
C
Identify at least 3 reasons for reforming.
B
Prioritise the reasons for reforming.
A
A*
Explain why the Liberals implemented welfare reforms and identify the most important reason .
Explain in detail why the Liberals implemented welfare reforms and support your judgement with evidence . No spelling, punctuation grammar errors.
Key Terms:
Liberals
Political party that is often progressive.
Reforms
Make changes in something in order to improve it.
Typically a social, political, or economic institution or practice.
Welfare
The health, happiness, and fortunes of a person or group. In this case it was Britain.
Why does the
British government introduce reforms today?
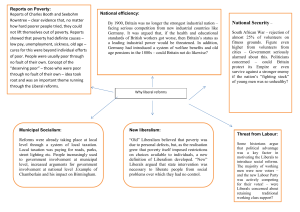
What motivated the Liberals to make reforms?
The social reformers
Booth, Rowntree and
Galt.
Increasing information about poverty from charities, civil servants and local authorities.
The scale of the problem
– life expectancy was 45.
The richest 10% owned
92% of the country’s wealth.
Key individuals like
David Lloyd George and Winston Churchill
Political rivalry
National efficiency:
The Boer War
40% of volunteers failed medical inspection
National efficiency: An effective workforce –
Britain’s position as the world’s leading industrial power was being challenged by
Germany and the USA.
Page: 395-397
Do: Prioritise the different reasons for the Liberal reforms.
Main reason
Least important reason
Extension: Explain your opinion. Why is it the most important reason for
Liberal reforms?
Do: Organise the Liberal reforms into chronological order.
Do: Summarise the reforms on your worksheet.
Do: Identify what influenced each reform out of...
• Political motives: the desire to be re-elected
• Moral motives: the desire to help and do good
• Nationalistic motives: the desire to make Britain a stronger country
Extension: Explain which motive was the most important drive behind Liberal reforms.
E
Identify at least 3 key reforms.
D
Describe the different reform acts.
C
Identify at least 3 reasons for reforming.
B
Prioritise the reasons for reforming.
A
A*
Explain why the Liberals implemented welfare reforms and identify the most important reason .
Explain in detail why the Liberals implemented welfare reforms and support your judgement with evidence . No spelling, punctuation grammar errors.
Who did the
Liberals reforms help?
Learn: To understand who benefitted from the Liberal welfare reforms.
• Identify who the reforms helped.
• Link the reforms to who they actually helped.
• Feedback.
• Complete table looking at the measures taken and limitations of the reforms.
• 5 awkward questions.
• Ball plenary!
E
Identify at least 3 key reforms.
D
Describe the different reform acts.
C
Identify who the reforms helped.
B
Explain why the Liberals helped certain groups.
A
Explain how the reforms had some limitations.
A*
Explain in detail how the reforms had some limitations and support with evidence . No spelling, punctuation grammar errors.
Key Terms:
New Liberalism
A term created by David Lloyd George. It described a new attitude that recognised that being poor was not always the fault of the poor and that it was the role of the government to support the poor when they needed it most.
Who did the reforms help?
Who did the reforms help?
School Clinics, 1912
National Insurance Act,
1912 Free School meals,
1906
National
Insurance Act,
1911
Tackling poverty & unemployment
School medical inspections, 1907
Labour Exchanges
Act, 1909
Children’s Charter,
1908
Pensions Act, 1908
Do: Draw and identify which reform helped who.
Do: Complete the following table.
Group
Children
How helped before
Liberal reforms...
Measures taken by Liberals to tackle problem...
No real system – some charities helped poor families but orphans cared for in workhouses.
Family, charities or the workhouse.
Limitations of the reforms...
The old
The sick
Family, charities or the workhouse.
The unemployed or underemployed
Voluntary labour exchanges.
Extension 1: Who was target number one for the Liberal reforms?
Extension 2: Who benefitted the most from Liberal reforms?
Do: 5 awkward questions.
• Imagine you are a reporter and you are going to a public meeting in 1914.
• You DON’T like the
Prime Minister.
• Come up with 5 different awkward questions relating to
Liberal reforms
1906-1914.
Asquith – Liberal Prime
Minister since 1908.
E
Identify at least 3 key reforms.
D
Describe the different reform acts.
C
Identify who the reforms helped.
B
Explain why the Liberals helped certain groups.
A
Explain how the reforms had some limitations.
A*
Explain in detail how the reforms had some limitations and support with evidence . No spelling, punctuation grammar errors.
Free School Meals (1906)
• Local councils were given powers to give free meals to children from poor families
• These meals were to be paid for from the local rates (local taxes on property)
• By 1914, over 150,000 children were having a daily free meal, every day.
• However, less than half the education authorities in England and Wales provided the free meals
• In 1914, the Government made it compulsory for authorities to provide these meals
School Medical Inspections
(1907)
• Doctors and nurses went into schools to provide free compulsory medical checks for children
• They could recommend any treatment that was necessary
• Any treatment required by the children had to be paid for by the parents (until 1912)
Education Act (1907)
• Introduced scholarships for children from poor families
• Secondary Schools that received money from local government were to reserve 25% for children from
Elementary Schools
• Children were chosen for scholarships through an examination
Children’s Act (1908)
• Children were now protected, by law, against cruelty from their parents
• Poor law authorities were responsible for visiting and supervising children who had suffered cruelty or neglect
• Children’s homes to be registered and inspected
• Children under 14 who committed crimes were now not to be sent to adult prisons
• Special juvenile courts to be set up to try children accused of crimes
• Criminal children were to be sent to borstals, specially built to cope with young offenders
• Children under 14 not to be allowed into pubs
• Cigarettes or alcohol not to be sold to children under 16
Old Age Pensions Act (1908)
• Weekly pensions were provided by the Government for the elderly
• 5s per week to single people over 70, 7s 6d to married couples
• Full amounts were only paid to those who earned less than £21 per year
• A sliding-scale of payments for those earning between £31 and £21 p.a.
• For British citizens who had lived there for + 20 yrs
• Not for anyone who had been in prison during the
10 years before claiming their pension
• The first pensions were paid in January 1909 and were very popular among the pensioners.
Labour Exchanges Act (1909)
• Set up a national string of state labour exchanges
• Meant that the unemployed could go to an exchange to look for a job
• Much more efficient for those seeking a job and those offering them
…
• By 1913 there were 430 exchanges in
Britain
National Insurance Act (1911)
Set up an insurance scheme to prevent poverty arising from illness …
1. All manual workers and people in low-paid jobs had to join
2. Workers paid 4d for insurance stamps which they stuck on a special card
3. Employers gave 3d per worker in the scheme
1. The Government gave 2d for each worker in the scheme
2. If a worker in the scheme fell ill, they got sick pay of 10s per week for 13 weeks, then 5s per week for a further 13 week in the year
3. Workers in the scheme could have free medical care
National Insurance Act (1912)
1. Scheme open to those in industries where there was seasonal employment (e.g. shipbuilding, engineering)
2. Workers, employers and
Government all paid 2d per week for insurance stamps
1. When unemployed, workers could be paid 7s 6d a week for up to 15 weeks in any one year.