lecture 14
Announcements 10/1/10
Prayer
Tutorial Lab only open 12-2 pm tomorrow
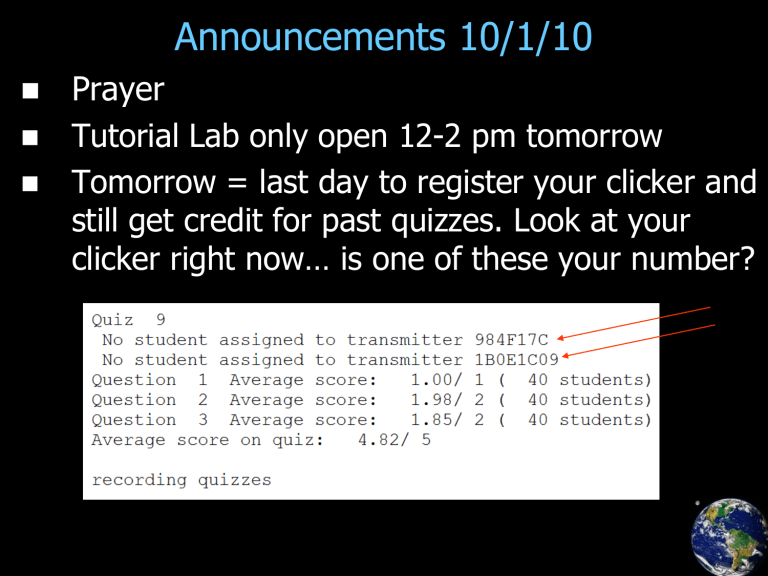
Tomorrow = last day to register your clicker and still get credit for past quizzes. Look at your clicker right now… is one of these your number?
The Exam
“What’s on the exam” handout
Exam starts tomorrow in Testing Center (HGB).
Anyone not know about the T.C.? See http://testing.byu.edu
.
a. T.C. opens tomorrow at 8 am.
Exam ends next Saturday a. Correction to syllabus: on Saturdays, the Testing
Center gives out last exam at 3 pm, closes at 4 pm.
Can bring handwritten 3x5 card (both sides)
I will give you all constants/conversion factors you need
Can use your own calculator (storing stuff in calc memory violates spirit if not letter of the law)
Time goal: 2 hours avg (took me 35 mins)
Foxtrot
Demo
“Adiabatic Cotton Burner”
Waves
Skipping: Oscillations, Ch. 15
Today: Basic wave info
Next week: Detour to “Physics Phor Phynatics”, Dr.
Durfee’s book a. For Monday, S&J 16.3-16.6; PpP 2.1, 2.2. b. 2.4.1 & 2.4.2 also recommended (but not 2.3 or
2.4.3)
Wed = complex numbers. Quick survey via clickers: a. Do you know complex numbers fairly well?
A = “know fairly well”; B = “not” b. Have you seen: e ix = cosx + isinx ?
A = “have seen”; B = “not”
Reading quiz
Which of the following phenomena can NOT exhibit a combination of transverse and longitudinal waves?
a. sound waves in air b. surface water waves c. waves in the earth generated by an earthquake
Wave intro: some math
What do these functions look like?
a. f(x) = x 2 b. f(x) = (x – 1) 2
Quick writing: What would be an equation for a parabola that moves 1 m to the right every second?
What will this function look like at 0 s? at 1 s? at 2 s?
a. f(x) = (x – 5t) 2 b. What is its “velocity”?
Sinusoidal waves
Nothing special about parabolas…
What does f(x) = cos(x – vt) look like at t = 0? at t = a little later?
Add in “amplitude”
Add in “phase”
What if you want wave to move right-to-left?
“Wave function”
Wave properties
Definition: oscillating disturbance that transfers energy (but not mass).
Direction
Medium
Transverse vs Longitudinal
Examples… a. Water b. Earthquake (P & S) c. Sound d. Light e. Rubber tubing (demo) f. Slinky (demo)
Wikipedia: “S-wave”
Did you say “Slinky”?
The handing out of the slinkies a. We only have 34 b. There are 46 students in the class
Web demo
http://paws.kettering.edu/~drussell/Demos/waves/wavemotion.html
Wave properties, cont.
Web demo: Stokes’ “Traveling Sine Wave” http://stokes.byu.edu/sinewave_script_flash.html
Wavelength l a. m/wave
Period T
v = f l a. s/wave
Frequency ( f = 1/T ) a. waves/s
Speed v a. m/s
Worked Problem
AM1320 KFAN broadcasts the Utah Jazz games at a frequency of 1320 kHz. (Check out www.jazzfanz.com
.) Radio waves travel at the speed of light, 3 10 8 m/s. (a) What is the wavelength of the AM1320 radio waves? (b)
What is the period?
Wavefunction
Let’s call it “s(x)” (because “f” is used for frequency)
What does s(x) represent?
a. For transverse waves… b. For longitudinal waves…
What does s (x) represent?
The (Linear 1D) Wave Equation
2 s
t
2
C
2 s
x
2
C
v
2
Why is it called the wave equation?
a. Because traveling waves are solutions of the equation!
s
A cos(
) Any function that has
“x-vt” will work! …or “x+vt”
s
x
A sin( x
vt )
2 s
x
2
A cos( x
vt )
s t
A sin( x
vt )
Av sin( x
vt )
2 s
t
2
Av cos( x
vt )
Av
2 cos( x
vt )
k and
w
What’s the difference between these: s
cos( x
5 ) s
cos(2( x
5 ))
General form of cosine wave: s
A cos( (
)
)
…sometimes written as: s
A cos( kx
w
)
k = “wavevector”; w = “angular frequency” w = …




