Science – Cells and Systems PowerPoint
advertisement

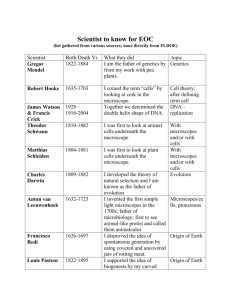
Cells and Systems By: Abhishek, Chan, Jim, Matthew Driving Question We can make sense of the vast diversity of living things because as we get closer to the middle of the equator the diversity of living things grow and as we get away from the equator the diversity of living things lessen. We can tell because Antarctica has many extinct animals and it is possibly the furthest away from the equator. Although there are over 20 million different species around the world life in several forms exists everywhere around the world. What living things have in common is that all living organisms need energy for the reason that they all let go of energy every day and to replenish that all living things need food, proteins and a water source. The organisms use energy to build a life and maintain it. For humans, we get energy from eating and for plants they get energy by taking in direct sunlight. Another way animals get energy is by breathing in oxygen and breathing out carbon dioxide, and plants breathe in carbon dioxide and breathe out air for us to breathe in. Another thing is that all living organisms respond and adapt to their environment and adapt to the conditions their living in, in order to survive. For example, if the temperature increases many animals may have to respond to it if they want to live; such as many animals may hibernate which is adapting to it, and others might just move to a different place to live, which is responding to it. This also refers to humans because if it’s cold or really hot, some people may just stay inside in order to respond to that. The third thing was that living organisms reproduce in order to continue the type of specie that is reproducing. In other words, it is like having a baby. Humans have babies and that’s how the populations are increasing. If babies were not being born then there would be a limit to the amount of people in the world and sooner or later there will be no one left in this world. Same thing goes with plants and animals because plants have seeds and animals have the different types of animals such as cubs. Next it is that living organisms grow in order to well develop and mature their reproductive system therefore, they can reproduce. Lastly living organisms produce wastes because if it wasn’t let go, it can be poisonous and we can die. We produce waste so we can let go of the stuff we don’t need in our body but we don’t let go of nutrients and minerals essential for us to grow a living. All in all, all living organisms have mostly everything in common. Driving Question - Part 2 Variation we could find is that many organisms may not get the energy they need to live and if the animals can’t get energy they won’t be able to do anything since everything requires energy. Such as growth and reproduction because you need energy to grow and reproduce. Characteristics of Living Things Responsiveness All living things are able to respond to changes in the environment. For example, living things respond to changes in light, heat, sound, etc. To detect changes, organisms have means for receiving information, such as eyes, ears, and taste buds. The organism responds to the changes by means of a number of effectors, such as muscles and glands. Energy is generally used in the process. Organisms change their behavior in response to changes in the surrounding environment. The behavior is active, not inactive; an animal responding to a change is different from say a stone rolling down a hill. Metabolism Living things display a fast turnover of chemical materials, which is referred to as a metabolism. Metabolism generally involves the release or use of chemical energy. Characteristics of Living Things Growth Growth needs an organism to take in material from the environment and organize and disturb the material into its own body structures. To accomplish growth, an organism uses some of the energy it obtains during metabolism. Each organism has a different pattern for accomplishing the building of their growth structures. Evolution/Progression Populations of living organisms have the ability to adapt to their environment through the process of evolution/progression. During evolution, changes occur in populations, and the organisms in the population become better able to metabolize, respond, and reproduce to their environment. They develop abilities to cope with their environment that their previous generation did not have. Characteristics of Living Things Complex Organization Existing things have a high level of complexity and organization not found in other lifeless objects. All living thing are composed of one or more cells otherwise the organism would not be able to survive. These cells are generally too small to be seen with the naked eye. These cells are then organized into tissues. A tissue is a series of cells that accomplish a shared function. Tissues then form what is called organs. Reproduction A living thing has the ability to produce copies of itself by the process known as reproduction. Asexual reproduction involves only one parent, and the resulting cells are usually identical to the parent cell. More complex organisms engage in a type of reproduction called sexual reproduction, in which two parents contribute to the formation of a new individual. During this process, a new combination of traits can be produced. What is the Basic Unit of all Living Things? Cells are the basic unit of living things. Cells - Cells are the foundation of the living world. Living things as diverse as bacteria, algae, fungi, animals, and plants all consist of one or more cells. They have more than one cell because living organisms wouldn’t survive with a single cell. Cells are made up of components that help living things to eat, respire, expel wastes, and perform all of the necessary functions of life. What is Cell Theory? Basic - All living organisms are composed of cells. - They may be unicellular or multicellular. - The cell is the basic unit of life. - Cells arise from pre-existing cells - Energy flow occurs within cells - Heredity information (DNA) is passed on from cell to cell. - All cells have the same basic chemical composition What is Cell Theory? In-depth The cell theory states that all living organisms have a basic unit of structure and function, which is the cell. This was a very important biological statement because it suggested that all living things have something in common and it was cells. This took nearly 200 hundred years of research by many different scientists led to this same conclusion. The early discovery of cells was done by Robert Hooke, an English scientist, in 1665. Hooke designed one of the first microscopes and used it to look at plant material/life. He also examined a thinly sliced specimen of cork. By looking at the cork through the microscope, he discovered that it was made up of many small units. Hooke named these units cells and, without realizing it, he had discovered the basis of all living substances. What is Cell Theory? Continued In-depth Hooke and other scientists observed other samples of plant material and discovered that they were also made up of cells. As more and more material was examined, scientists began to distinguish a pattern. It wasn’t until 1838 that a German scientist stated that all plant material was made up of cells. The following year, another scientist came to the same conclusion about animals. Their findings are what have become known as the cell theory. Robert Hooke > Microscopes Compound Microscope One of the most common kinds of microscopes are compound microscopes, which can be found often in science labs and schools labs. These mechanical microscopes have lights in them to view the specimen and offer changeable levels of magnification. They can magnify specimens although the resolution of the specimen isn't the best, it functional. Using this kind of microscope you can look at a variety of specimens both living and dead. Microscopes Fluorescence Microscope Fluorescence microscopes are similar to the basic ones that use light to display the specimen, but they use a unique wavelength of light. This light engages with the specimen, making it emit light to showcase its parts. This microscope identifies the smaller parts of a specimen that you would otherwise not notice with a basic lighted microscope that simply shines light onto the specimen. Microscopes Digital Microscope A digital microscope is similar to a compound in its viewing abilities. In a digital microscope, a camera is attached inside that transfers images to an outside monitor for improved viewing. Hence, instead of a traditional eyehole which many microscopes have, the eyehole is a large screen that the can be viewed by multiple people at once. Microscopes Pocket Microscope Pocket microscopes are used in a number of fields including science. They are used in banks for inspecting money for fakes and for jewelers the gems and stones. These small portable handheld microscopes use a much lower level of magnification than laboratory microscopes, but still yield a good enough amount to see details the naked eye cannot. In this microscope you have to sacrifice magnification for portability. Microscopes Dissecting Microscope A dissecting microscope uses light to take the specimen in a three-dimensional view. These microscopes are unique in that they can aid in the dissection of a specimen. With two separate eyeholes to give two views, they can help see all angles of the specimen, but have a lower magnification quality than other microscopes and don't allow you to see specimen on a cellular level. In this microscope your sacrificing magnification for an allaround view of the specimen. Microscopes Electron Microscope Electron microscopes are a very powerful kind of microscope that has one of the highest magnification abilities of any microscope without sacrificing any resolution. These microscopes use small electrons, which reflect off of gold coating placed on the specimen. Pictures have a three-dimensional quality that allows for viewing small precise details of specimens. These microscopes are quite expensive and usually used in professional research labs and hospitals only. Who Invented the First Microscopes? Anton Van Leuwenhoek Invention of the first microscope was invented by a person named Zaccharias Janssen a Dutchman in the 1590ies. From 1632-1723 Anton Van Leuwenhoek was getting better results with a more powerful single lens, which he made himself. Anton kept his method of lens making a secret. After his death microscopic investigation slowed down because nobody knew how to make lenses as well as he did, 19th century lenses were perfected by the other scientists and they were able to look through clear microscopes again. Zaccharias Janssen Two Categories of Living Things With Examples Prokaryote(Single-Celled) - The prokaryotes are a group of organisms whose cells lack a cell nucleus, or any other membrane-bound. The organisms whose cells have a nucleus are called eukaryotes. Example include … Salmonella Bacteria, E. coli Bacteria, and Bacillus Bacteria Eukaryote(Multi-Celled) - A eukaryote is an organism whose cells contain complex structures enclosed within membranes. The organisms whose cells don’t have a nucleus are called Prokaryote. Examples include … Animalia, Plantae, Fungi, and Protista What are the Structures in Cells Called in General? Plants Plant cells are cells that are in plants. Plant cells are like animal cells, but they have a cell wall and chloroplasts. What are the Structures in Cells Called in General? Definitions … Cell Membrane: A thin layer that surrounds the cell. Cell Wall: A rigid layer that surrounds the cell membrane of a plant cell. Chloroplast: (KLOR-o-plast) A cell structure in which photosynthesis takes place, and it contains the chlorophyll. Chlorophyll: (KLOR-a-fil) A green substance in plant cells that helps to make food. Cytoplasm: (SIGH-ta-plaz-em) The jellylike liquid in cells where activities take place. Nucleus: (NEW-kle-us) The dark structure inside the cell that controls the cell's activities and contains material such as DNA. Photosynthesis: (foto-SIN-thi-sis) The process when plants use lights energy to make food. Main Differences Between Plants and Animal Cells •Plants cells have a cell wall over the cell membrane, whereas, animals cells lack cell wall. Cell walls restrict movements, whereas cell membrane that animals have allow movement because most animals are active. •In plant cells, there is a single large vacuole present in the middle, whereas, in animal’s cell, there are many small vacuoles. Plant cells have a large vacuole due to the amount of water the cell must hold to maintain its shape. The water in the vacuole creates something called trigger pressure. When the vacuole has lots of water, the pressure is high and pushes against the cell wall so the cell is rigid. When the vacuole has little water, the pressure is low so the cell is soft. Animal cells don't have to worry so much since the cells are already in an moistened environment and get water in lots of other ways. Main Differences Between Plants and Animal Cells •Plant have chloroplasts, but, animal cells don't. Animals have legs, letting them to search high and low for food, thus they do not need chloroplasts. Plants are still. They can only move with the direction of sunlight. Thus, they need chloroplast to absorb the sunlight and convert it into chemical energy to make food for their survival. •Plant cells have chlorophyll for Photosynthesis (make their own food), and animal cells don't. Animals don’t need to use photosynthesis yet alone have it because we can catch our own food whereas plants are always stationary and rely on the sun and chlorophyll for photosynthesis. Do Cells Grow When an Organism Grows …Explain? Cells in a multi-cellular organism are usually not dramatically effected by that organism's growth. The cells will continue to grow until they are large enough. This is when the cell will divide and multiply. In humans, when we have growth-spurts as children and young adults, are bodies release chemicals that tell our cells to reproduce faster. So basically our cell will not get bigger when we grow they will simply just multiply. Explain Fluids and Nutrients Moving In and Out of a Cell Fluid and nutrients move in and out of a cell by the process called osmosis. The semipermeable membrane only allows certain materials to past through it. In these cells, the fluid and nutrients always move from areas of high concentration to area of low concentration until equilibrium is reached. This is done by the process of diffusion. Wastes then move from an area of higher concentration inside the cell to an area of lower concentration outside the cell. This again is done by diffusion. Diffusion is when a substance moves from an area of higher concentration to an area of low concentration. Diffusion is like osmosis but with diffusion there is no need for a semipermeable membrane. Describe Specialized Cells that are Found in Humans Neurons Neurons are specialized cells that carry messages within the human brain. These cells come in a variety of shapes and sizes. While these cells do share some similarities with other cells, they also have specialized features that enable them to complete the necessary communicative functions. These cells have extensions called dendrites and axons that bring information into and, release information from, the cell itself. This is what allows us to make basic thoughts and for our body to function efficiently. Describe Specialized Cells that are Found in Humans Muscle Cells Muscle cells make movement possible. These cylindrical cells are made up of lined fibers that allow for shrinkage. Through the functioning of these specialized cells the human body can complete an range of movement-based tasks. These cells, like many in the human body, join together to create larger body structures. Describe Specialized Cells that are Found in Humans Sperm Cells Specialized sperm cells are necessary for human reproduction. These cells are made up mainly of a nucleus. Unlike some stationary cells, these cells are highly mobile as they must move to locate an egg for fertilization to occur. Sperm cells have the energy that they need to move at such high rates of speed. Describe Specialized Cells that are Found in Humans Red Blood Cells Red blood cells carry oxygen around the body, delivering it to organs that require this life-giving gas. These cells lack an assortment of pieces commonly associated with cells, including a nucleus. The absence of the nucleus allows the cell to carry more oxygen around the body. Cells of this type are mostly composed of hemoglobin, a chemical that allows for the uptake and carrying of oxygen. Describe Specialized Cells that are Found in Humans Leukocyte Leukocyte cells work to keep the human body free of infection. These cells find and destroy microbes within the human body, reacting to and treating infection. Because these cells must move to the site of infection, they are very mobile and even capable of pushing through tube walls when necessary to reach sites of infection. Leukocytes are highly flexible, capable of shifting shape as necessary as they move throughout the body. Leukocyte will do almost anything to reach the sight of the infection. Cells and Systems Video Bibliography http://www.cliffsnotes.com/study_guide/Characteristics-of-LivingThings.topicArticleId-8741,articleId-8578.html http://kids.britannica.com/comptons/article-203973/living-things http://www.wisegeek.com/what-is-the-cell-theory.htm http://www.ehow.com/list_7594528_six-types-microscopes.html http://wiki.answers.com/Q/What_is_the_name_of_the_person_w ho_discovered_the_first_microscope http://library.thinkquest.org/C004535/prokaryotic_cells.html http://library.thinkquest.org/C004535/eukaryote_examples.html http://library.thinkquest.org/5420/cellsplt.html http://wiki.answers.com/Q/What_is_the_main_difference_betwee n_plant_and_animal_cells http://wiki.answers.com/Q/What_happens_to_the_cell_when_a_ organism_grows_larger http://www.ehow.com/list_7245490_specialized-cells-body.html Credits Abhishek Castelino Chan Patel Jim McCormick Matthew Morgan