Mast cell
advertisement
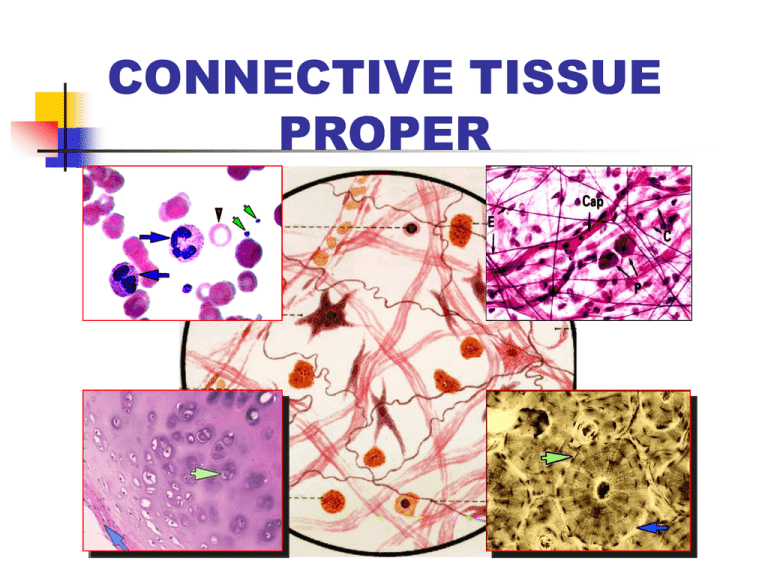
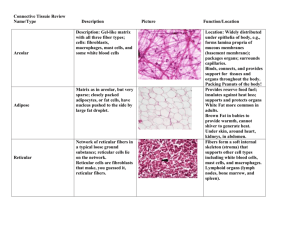
CONNECTIVE TISSUE PROPER Epithelium Connective tissue Pay attention to the differences b/w Epi & CT 一、CHARACTERISTICS: Small number of cell large amount of intercellular matrix Cell: separate and no polarity Intercellular matrix: fibers + ground substance + tissue fluid Filled with B.V., L.V., & N. Function: support, connect, nourish, defence, and repair etc. 二、CLASSIFICATION Connective tissue proper: Loose C.T. Dense C.T. Adipose tissue Reticular tissue Cartilage and bone Blood and Lymph 三、LOOSE CONNECTIVE TISSUE I. Characteristics: Small number of cell & large number of cell category small number of fibers & great amount of ground substance Sponge-like structure (areolar tissue) Distributed b/w cells, tissues and organs. II. Cells Fixed cells: fibroblasts fat cells undifferentiated mesenchymal cells Wandering cells: macrophages plasma cells mast cells leukocytes 1、Fibroblasts Structure: Nu: Cytoplasm: EM: rich in rER & r., developed G.l. F.b. * Fibrocytes: F.C. F.b. Function: Synthesize & secrete collagenous pro. & elastic pro. (to form collagenous f., elastic f. & reticular f. ); and ground substance (proteoglycan & glycoprotein). 3、Plasma cells Structure: Nu.:eccentrically, heterochromatin in wheel shape Cytoplasm: strong basophilic w/ lightly-stained area near Nu. P.C. EM:rich in rER & r., developed Gl. Source: B lmphocytes Function: synthesize immunoglobulin & cellular factors participate in humoral immunity 2、Macrophages(Histocytes) Structure: Nu.: Cytoplasm: Mac. F.b. Mac. EM:a large number of Ly., pinosome & phagosomes, bundles of MT & MF Function: Mobility chemotaxis chemotactic factor: complement C5a, bacterial products etc. Phagocytize specific:depend on identify factors: Ab, C, Fibronectin etc (the receptors of these factors are on surface of the macrophage). non-specific: independently Ag p.s . L.y 残余体 Capture! Ag participate in immune regulation p.s. L.y. capture process antigen present antigen presenting molecular:MHCII Ag-MHCII co. macrophage surface lymphocytes immune reaction secrete bioactive products chemotactic factor(for polymorphonuclear leukocytes) immunosuppressive factor leukotriene interleukin(IL) interferon(INF) tumorous necrosis factor(TNF) etc. Source: the monocytes in blood 4、Mast cells Location & Structure: Nu.: Cytoplasm: basophilic granules, metachromatism M.C. B.V. Toluiding blue staining EM: a great number of granules w/ crystals, containing: heparin, histamine, leukotriene, slow-reacting substance, eosinophil chemotactic factors (ECF-A) plasma cell Ab(Ig E) Function: allergic reactions Ag1 Ag1 plasma cell mast cell Ab(Ig E) R-Ab Ag2 degranulation anticoagulation attract eosinophil Ag2 degranulation mast cell R Ab-R degranulation Ag1 R-Ab . . .. .. . .. . . ... . .. . . . .. . . .. . .. . . . .. . .. . Mast cell . . . .. . . .. . . . . . . . .. . . . . . . . . . . . .. .. . . . .. . . . ... Ab Plasma cell Ag2 5、Fat cells (Adipose cells) Shape: Nu.: Cytoplasm: Function: synthesize & store lipid Osmic acid staining HE staining B.V. b N 6、Undifferentiated cells Structure: similar to fibroblasts, smaller Function: differentiate into various cell-types in C.T. during injury repairing e.g.: 7、Leukocytes Including: neutrophils, eosinophils, lymphocytes & monocytes Function: defence involve in allergic reaction (see blood chapter) L N III. Fibers: Collagenous fibers (white f.) Elastic fibers (yellow f.) Reticular fibers (argyrophilic f.) 1、Collagenous fibers Structure: LM: EM: fibrils:have periodic crossbandings at intervals of 64nm fibrils Collagen fibers Collagen fibrils Chemicals: collagen type I collagen type III type I type III Immunohistochemistry staining ① Fibroblast Synthesize: In rER / GL: → Polypeptide αchains ① → hydroxylated αchains ② → Procollagen ③ In Extracellular space: → Tropocollagen ④ → fibrils ⑤ → collagenous f. ⑥ ② ③ ④ 280x1.4nm ⑤ ⑥ 2、Elastic fibers Structure: LM: EM: elastin + microfibrils (no bandings) F.B. 3、Reticular fibers Sructure: LM: argyrophilia, PAS(+) EM: fibrils w/ periodic cross-bandings at intervals of 64nm, typeIII collagen covered carbohydrate Reticular fibers in liver Reticular fibers in lymph node IV. Ground substance Jelly-like & amorphous substance; Proteoglycan: in molecular sieve hyaluronic acid GAG(glycosaminoglycan) chondroitin sulfate keratin sulfate etc. protein: core protein & link protein glycoprotein: fibronectin (FN) laminin (LN) chondronectin (ChN); Side chain subnit hyaluronic acid Collagenous fiber Ground substance Intercellular material hyaluronic acid molecular sieve: hyaluronic acid -- link pr.-- side chain subunit subunit: core protein + chondroitin sulfate & keratin sulfate tissue fluid: flowing through the sieve pores side chain subunit Core pr. link pr. chondroitin sulfate Link pr. keratin sulfate core pr. glycoprotein: fibronectin (FN): produced by epithelial cells and fibroblasts play a role in events of identification, adhesion, migration and proliferation laminin (LN) : located in B.M., produced by epi. cells, function: adhesion the epi.cells and B.M. chondronectin (ChN): in cartilage tissue, fuction: a component of ground substances; adhesion chondrocyteS and colagen typeII leminin Function: Tissue fluid nourishes the cells & tissues; Molecular sieve acts as a barrier: to prevent the spread of bacteria & other microorganisms *haemolytic streptococci produce hyaluronidase & promote the invasion Glycoproteins (FN/LN/ChN): identification /adherence/migration/proliferation etc. 四、 DENSE CONNECTIVE TISSUE Characteristics: Small amount of cells & ground substance, large number of fibers Fibers: wide, arranged densely Function: connect & support tendons Category: dermis Dense regular C.T. (tendons, cornea, ligment): parallel c.f. & tendon cells Dense irregular C.T. Lig. nuchae (dermis, sclera): collagenous fibers network & fibroblasts Elastic tissue (Lig. Nuchae, Lig. flavum & Large artery ): elastic fibers mainly Large artery 五、ADIPOSE TISSUE Structure: Loose C.T.+ fat cells (in large aggregations) HE: / Osmic acid: Function: energy storage, shock absorber, insulating layer 六、RETICULAR TISSUE cells Structure: Reticular cells + reticular f. + G.S. Reticular cell: stellate, pale nucleus, obvious nucleoli, processes (rich in rER) Function: architectural framework of lymphatic & hematopoietic tissues Lymph node fibers BYE BYE