Household Production Theory
advertisement

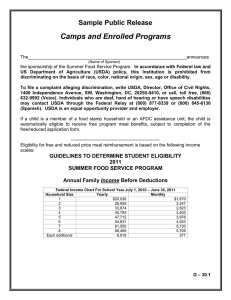
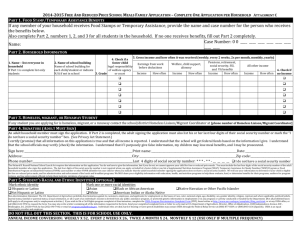
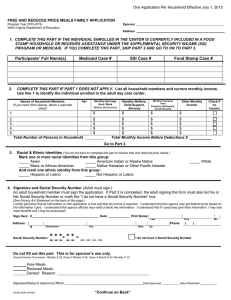
Household Production Theory Treat Household as a Firm Output is Utility G=goods T= Time U = F(G, T) Household Production Theory Goods Isoquant; Slope = -(MUt /MUG) G0 Budget constraint; Slope = -(W/P) U t0 Home Time Wages and Goods Intensive vs Time Intensive Home Production How do we cook? Huffman, 2006. “The Story Behind the Post-War Decline in Women’s Housework: Prices, Income, Family Size and Technology Effects in a Demand System Huffman, 2006. “The Story Behind the Post-War Decline in Women’s Housework: Prices, Income, Family Size and Technology Effects in a Demand System Daily time allocation to meal preparation, by gender and income Lisa Mancino and Constance Newman Who Has Time To Cook? How Family Resources Influence Food Preparation May 2007. USDA ERRN 40. http://www.ers.usda.gov/publications/ERR40/err40.pdf Daily time allocation to meal preparation for women, by income and market work intensity Lisa Mancino and Constance Newman Who Has Time To Cook? How Family Resources Influence Food Preparation May 2007. USDA ERRN 40. http://www.ers.usda.gov/publications/ERR40/err40.pdf Births per 1000 women aged 15-44, 1920-1998 140 120 100 Rate 80 60 Depression 40 20 0 1920 1930 1940 1950 1960 Year 1970 1980 1990 2000 Quantity Quality Tradeoff in Fertility Behavior How do wages affect household size? Mammen, Kristen and Christina Paxson. “Women’s Work and Economic Development.” Journal of Economic Perspectives 14 (Fall 2000): 141-162. Mammen, Kristen and Christina Paxson. “Women’s Work and Economic Development.” Journal of Economic Perspectives 14 (Fall 2000): 141-162. How should spouses divide market and home time? How do relative wages affect time allocation? Weekly Hours Spent in Work and Leisure by Men and Women, Age 25-64, in the United States, 1965–1981 Average time in home production per week for married men and women Men 17.7 Women 29.8 Men spend 9 more hours per week in the labor market Hersch and Stratton, Journal of Human Resources, Winter 2002. Bureau of Labor Statistics. “Variations in Time Use at Stages of the Life Cycle.” Monthly Labor Review 128 (September 2005): 38-45. Father Bureau of Labor Statistics. “Variations in Time Use at Stages of the Life Cycle.” Monthly Labor Review 128 (September 2005): 38-45. Minutes per day spent in total market and nonmarket work for men and women, 21 countries Equal minutes per day Fitted line, nonMeditaranean countries Fitted line, Meditaranean countries U.S. difference is 4 minutes Michael Burda, Daniel Hamermesh, and Philippe Weil. 2006. "TOTAL WORK, GENDER AND SOCIAL NORMS,"