igneous rock
advertisement

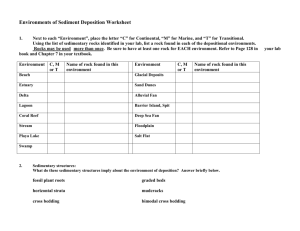
Learning Log What are the three types of rock, as defined by how they’re formed? Give an example of each type. Essential Question What are the different types of rocks? Earth Day Info Solutions for helping the Earth and ourselves Sedimentary Rocks Noticeable Characteristics of a Sedimentary Rock? • Often have layers or bands across them. • Often contain fossils which are fragments of animals or plants preserved within the rock. • Scrape and often crumble easily Sedimentary Rocks • Much of Earth’s surface is covered with sediments – pieces of solid material deposited on Earth’s surface by wind, water, ice, gravity, or chemical precipitation – Sediments formed through weathering (breakdown of rocks) – When sediments become cemented together, they form sedimentary rocks (form in layers) The formation of Sedimentary Rocks Weathering • Weathering –physical and chemical processes that break rock into smaller pieces. – Chemical weathering – minerals in a rock are dissolved or chemically changed (rock changes) – Physical weathering – minerals are not chemically changed, rock fragments simply break off the solid rock (rock does not change) Weathering Chemical Weathering caused by Physical Weathering caused by – Water: dissolves minerals – Temperature: water expands as it freezes, breaking rocks – Oxygen: oxygen reacts with open substances (oxidation) • Ex. Formation of pot holes – Carbon dioxide: forms carbonic in roads acid that dissolves minerals – Acid precipitation: changes pH – Pressure: removing rocks above decreases pressure and of water – Temperature: influences rate of allows layers to peel off • Ex. Rock removal can chemical reactions decrease pressure, causing large pieces of rock to explode off walls, burying miners. What is Erosion? Erosion is the removal and movement of surface material (sediments) from one location to another location. Four Main Agents: Water, Wind, Gravity, and Glaciers – – Eroded materials are always carried downhill Streams and rivers carry the small bits towards the sea (continually wearing down as they progress). What is Deposition? When sediments are laid down on the ground or sink to the bottoms of bodies of water. – – The sediments are dropped by size. The largest sediments will drop first and the smallest will drop last. Sediments deposited when transport stops What is Lithification? Lithification is the process where sediments are converted into solid rock (physical and chemical process). Lithification is a two part process: Compaction: where the particles are compressed together due to the weight of the overlying sediments. As more and more sediment is deposited, the bottom layers are subjected to increasing pressure and temperature Cementation: is where the particles are glued together. Lithification From pile of sand to solid rock What is bedding? • It is the horizontal layering of deposits and is the primary feature of sedimentary rock Importance of Sedimentary Rocks • Geologic “snapshot” of surface conditions in Earth’s past. – Fossils – Flow and direction of ancient rivers – Natural resources-oil, coal, and natural gas found in sedimentary rocks – Deposits of phosphate- used for fertilizer – Limestone- used to make cement; used for building Rock Identification Each of you have had the opportunity to observe at least one sample of a sedimentary rock. In the space below note all of the observations you made about it. IGNEOUS ROCK What are Igneous Rocks? • Crystallize from molten material: Magma – molten rock below the Earth's surface Lava – magma that erupts onto the Earth's surface through a volcano or crack (fissure) • Nickname- “fire form rock” Factors That Affect Magma Formation: Temperature • The deeper you go in the Earth’s crust the hotter it gets. Water Content • As the water content of the rock increases the melting temperature decreases. Pressure • The deeper you go pressure increases. • An increase in pressure increases melting temperature. Mineral Content • Different minerals melt at different temperatures. Compare and Contrast Igneous Rock Types of Igneous Rock • Extrusive – Fine-grained rock that cooled quickly on Earth’s surface when lava is EXTRUDED from the Earth • Intrusive – Course grained igneous rock that cooled slowly underground Intrusive or Extrusive Extrusive Rock Intrusive Rock Andesite Basalt Rhyolite Gabbro Granite Diorite Useful Characteristics of Igneous Rocks • Building Material – resistant to weathering – Strength • Ore deposits- minerals that contain a useful substance • Veins • Pegmatites • Kimberlites –diamonds Rock Identification Each of you have had the opportunity to observe at least one sample of an igneous rock. In the space below note all of the observations you made about it. Metamorphic Rock What is Metamorphism? Metamorphism is the alteration of existing rocks by either excessive heat and pressure, or through the chemical action of fluids. – During metamorphism, a rock changes form while remaining solid. Types of Metamorphism Regional Metamorphism • Occurs when rocks are buried deep beneath Earth’s surface and changed by increase in temperature and pressure. Covers a large area Contact Metamorphism • Occurs when rocks are heated by contact with magma or lava. Covers a small area Hydrothermal Metamorphism • Extremely hot water reacts with rock and alters its chemistry and mineralogy. • Common around igneous intrusions and active volcanoes Metamorphic Rock Textures: Foliated Texture: Mineral crystals arranged in parallel layers or bands (flatten under pressure) Slate (from clay or shale) Schist (from granite, basalt, or shale) Gneiss (from granite) Foliated Texture: Slate Foliated Texture: gneiss: Foliated or Nonfoliated Nonfoliated Foliated Rock Identification Each of you have had the opportunity to observe at least one sample of a metamorphic rock. In the space below note all of the observations you made about it. The Three Rock Types Re-Cap • Sedimentary, Igneous, and Metamorphic • Grouped according to how they form: – Sedimentary rocks form from cemented sediments – Igneous rocks crystallize from magma – Metamorphic rocks form by changes in temperature and pressure to existing rock