Cell Membranes - Rights4Bacteria
advertisement

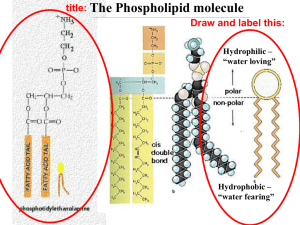
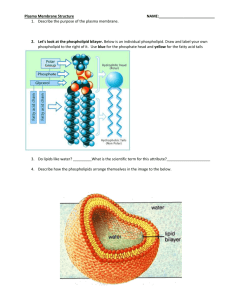
Cell Membranes What is the cell membranes structure and functions ? Starter: In biological terms, what do the following words mean? Semi permeable Cell surface Envelope Signalling Phospholipid Bilayer hydrophobic hydrophillic Cell membranes – success criteria. • Outline the roles of the membranes within cells and at the surface of cells. • State that plasma membranes are partially permeable. • describe the fluid mosaic model of the membrane. Membrane Vs envelope Membrane Vs envelope A cellular membrane is made up of a phospholipid bilayer. A cellular envelope is made up of 2 membranes which form the envelope. These are found around the chloroplast, mitochondria and nucleus. Roles of Membranes Read the information and make a bullet point list of the roles. Explain in your own words what this means. The major roles of the cell membrane 1) membranes are partially permeable. 2) Membranes separate components from each other and the outside. 3) cell signalling 4) Membranes provide attachment sites for enzymes and other molecules involved in metabolism. 5) Regulate the transport of materials into and out of cells. The phospholipid bilayer Phosphate head – hydrophillic Fatty acid tails Hydrophobic The phospholipid bilayer Phosphate head – hydrophillic. These are polar or charged, in this case negatively. This enables them to interact with water molecules which are also polar but slightly +ve. Fatty acid tails – Hydrophobic These have no charge and so do not interact with water. -ve -ve -ve -ve -ve -ve What would happen if this was mixed with water? The polar hydrophilic heads are water soluble and the hydrophobic heads are water insoluble Hydrophobic (water-hating) tail air aqueous solution Hydrophilic (water-loving) head Phospholipids form micelles when submerged in water In 1925 Gorter and Grendel proposed that the unit membrane is formed from a phospholipid bilayer Extracellular space (aqueous) Phosphate heads face aqueous solution phospholipid bilayer Cytosoplasm (aqueous) Hydrophobic tails face inwards Question: why does a phospholipid bilayer form?(3). • The phospholipid molecules have a hydrophobic tail and hydrophilic head. • The inside and outside of a cell are both aqueous. • This means the phospholipids align as a bilayer so that Click to reveal the answers the tails are not touching water. • Click here to hide answers The Bilayer • When completely surrounded by water, a bilayer can form where the tails are held away from the water. • The molecules are not bonded together in anyway so they are free to move about like a fluid. • The membranes are said to be fluid mosaic. That’s not all folks … But that is next lesson . • Complete the questions on the phospholipid bilayer. • The phospholipid bilayer has to have other components in order to do its job as a barrier etc. e.g. Presence of receptors on growing shoots to allow regulation of growth. Muscle cell membranes have extra channels for glucose uptake – why? Internal chloroplast membranes contain chlorophyll. White blood cell membranes contain proteins to recognise other cells. Task • Read the information and complete the questions.