Notes: Upper Respiratory System
advertisement

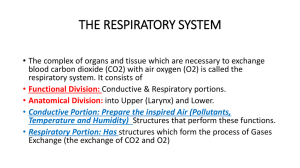
UPPER Functions of the Respiratory System 1. Gas exchanges between the blood and external environment – Occurs specifically in the alveoli of the lungs 2. Passageways to the lungs purify, humidify, and warm the incoming air 1. Organs of the Upper Respiratory System Nose nasal cavity paranasal sinuses 2. Pharynx nasopharynx oropharynx laryngopharynx 3. Larynx thyroid cartilage epiglottis vocal folds glottis 4. Trachea 1. The Nose • Only externally visible part of the respiratory system Basic Anatomy: • External nostrils (nares) • Interior of the nose nasal cavity nasal septum Paranasal sinuses Nasal Cavity • Top of nasal cavity is the Cribriform plate of the ethmoid bone contains openings for olfactory nerves • The nasal cavity is lined with respiratory mucosa that – Moisten air (humidify) – Trap incoming foreign particles (purify) • Lateral walls have projections called conchae (remember the nasal conchae) – Increase surface area – Increase air movement within the nasal cavity in order to increase collection of foreign particles Paranasal Sinuses • Cavities within bones that are surrounding the nasal cavity and share mucosa from the nasal cavity are called sinuses • Sinuses are located in the following bones – Frontal bone – Sphenoid bone – Ethmoid bone – Maxillary bone Paranasal Sinuses Function of the sinuses – Lighten the skull – Act as resonance chambers for speech – Warms and moistens air – Produce mucus that drains into the nasal cavity Sinuses are connected which is why a sinus infection can cause secretion from the eyes and ears http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ge5uUHmk2bE&NR=1 2. Pharynx (Throat) • Muscular passage from nasal cavity to larynx • Three regions of the pharynx 1. Nasopharynx—superior region behind nasal cavity also connects to middle ear 2. Oropharynx—middle region behind mouth, carries air and food 3. Laryngopharynx—inferior region attached to larynx, carries air and food https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yQR8OWfLnMU 3. Larynx (voice box) A. Thyroid cartilage – Largest of the hyaline cartilages – Protrudes anteriorly (Adam’s apple) B. Epiglottis – Routes food to the esophagus and air toward the trachea – When swallowing, the epiglottis rises and forms a lid over the opening of the larynx http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Ri8bBhw9msQ Structures of the Larynx (voice box) C. Vocal folds (true vocal cords) – Vibrate with expelled air to create sound (speech) D. Glottis —opening between vocal cords Video of Vocal Cords http://www.youtube.com/watch ?v=-XGds2GAvGQ 4. Trachea (Windpipe) • Four-inch-long tube that connects larynx with bronchi • Walls are reinforced with C-shaped hyaline cartilage (allows esophagus, which is behind the trachea, the ability to expand for swallowing) • Lined with ciliated mucosa – Beat continuously in the opposite direction of incoming air – Expel mucus loaded with dust and other debris away from lungs and into the esophagus