Temporary Works
advertisement
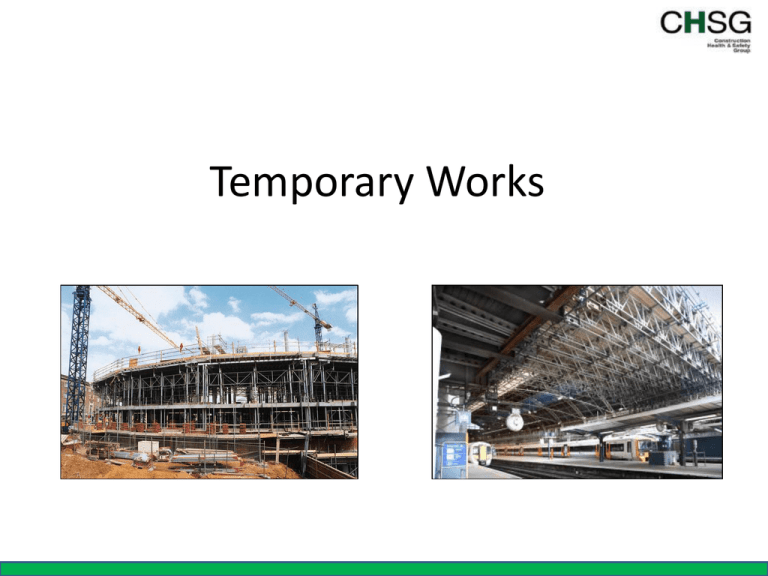
Temporary Works Temporary Works • • • • What do we mean by Temporary Works? Why is it important ? What can go Wrong? What do you need to know? Definition of Temporary Works An engineered solution used to : support or protect an existing structure or the permanent works during construction, or to support an item of plant or equipment, or the vertical sides or side-slopes of an excavation, or to provide access. Typical Forms of Temporary Works Hoardings Façade Retention Piling Propping Working Platforms Aluminium HD Shoring Ground works Column Forms Wall Forms Refurbishment Mast Climbing Platforms Scaffolding Edge Protection Size • There is no official determination of what size of project needs a formal Temporary Works Procedure • Risk is the main factor • The policy requirements of BS5975 may, however, be applied to small jobs in principle . Why Is TW important? • History is repeating itself with incidents • The supply chain is more fragmented into numerous subcontractors • Fewer main contractors now have their own temporary works department • Proprietory systems are now widely used, and the design skills and product knowledge sits largely with the specialists. • Sometimes conflict between finance and safety • BS5975 now gives clear guidance on procedures and responsibilities. Common Problems With Temporary Works • • • • • • • No procedure, TWC or responsible person. Lack of a competent contractor No temporary works equipment available! Inappropriate use of TW equipment Incorrect estimation of loads to be supported. Inadequate lateral bracing to resist lateral (wind) loads. Lack of knowledge and experience of persons involved in temporary works design and erection/maintenance. • Unauthorised changes to an approved temporary works design. Still Going Wrong? • “Three cranes dismantled whilst foundations checked and strengthened” • “Demolition contractors damaged gas main causing major leak” • “Reversing Tipper Truck struck Groundworker” • “Workman trapped as building collapsed during demolition” • “Member of public injured after fall into excavation” • “Inadequate support for floor decking caused collapse” • “HSE prosecute over fall risks discovered ” • “Ground worker escapes death in 4m deep excavation” • “Large fine follows failure to ensure contractor planning and control” • “Developer failed to inspect and maintain sign on major London project” Source: PP Construction Safety Still Going Wrong ? 11 Prevention Temporary Works Co-Ordinator “ The appointment of a temporary works co-ordinator ( TWC) should be the first operation in a chain of events culminating in the construction of a temporary works scheme” “ The TWC should be the first point of contact between the designer and the site team, in all instances” BS5975: 2008 Code of Practice for temporary work procedures and the permissable stress design of falsework. 14 Temporary Works Co-Ordinator Competencies Required of a TWC: • • • • • Engineering knowledge and understanding Management and leadership Independent judgement Health, safety and welfare Interpersonal skills and communication And • Experience appropriate to the complexity of the project temporary works procedures and issues associated with the type of temporary works Source: Temporary Works Forum Temporary Works Co-Ordinator Role includes: Co-ordinate all temporary works activities Ensure : • a temporary works register is established • • • • • a design brief is prepared a satisfactory temporary works design is carried out changes are managed checks are made a permit to load and unload is issued Supervisors • Assist and liaise with the Temporary Works Co-ordinator • Supervise and check the temporary works Supervise: The erection/installation Use Maintenance Dismantling • Liaise with TWC re any changes or modifications What do you need to know? • Legal requirements: CDM, WAH, HASWA,LOLER etc. • BS5975 Code of Practice for Temporary Works Procedures • HSE SIM: The management of temporary works in the construction industry • Relevant Codes of Practice and industry guidance for : Hoardings, Formwork & Falsework, Scaffolding, Excavations, Working Platforms, Edge Protection etc. What Should You Do? “Plan, manage and monitor the construction phase in a way which ensures that, so far as is reasonably practicable, it is carried out without risks to health and safety” CDM Regulations Considerations Double- check your procedures? for: • Design Briefs • Design changes during construction • The checking of the structure • TWC’s ability to spot scaffold hazards • Signing off the Permit to Load Be in a position to respond to these questions………. Steve Parncutt, HSE Specialist Inspector, ICE , Nov 2012 Temporary Works Definitions • • • • • • • • • Back Propping Stop End Dywidag Lacing Angle of Repose Characteristic strength Alsi percha Class ‘A’ System Node Point • • • • • • • • • AGR’s Bending Moment Top restraint Residual Risk A-Frame CFA Soft Spot Drag Box Designated Individual 27