The Respiratory System
The Respiratory System
The Respiratory System Overview
The primary function of the respiratory system is to bring in oxygen into the body and remove carbon dioxide from the body
Other functions include inhaling
and exhaling, and conditioning the air entering the body.
The respiratory system primarily consists of the lungs and the airways that connect them to the outside world
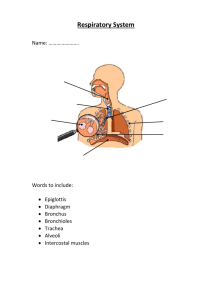
The Respiratory System Labelled
Pleural
Membrane
Diaphragm
Inhalation
The process of taking air into the lungs
Occurs when air pressure outside the body is greater than inside
Diaphragm contracts creating more space in lungs this creates low pressure
Rib cage muscles also contract so that the rib cage expands.
Exhalation
The process of taking air out of the lungs
Occurs when air pressure inside the body is greater than outside
Diaphragm relaxes creating less space in lungs this creates high pressure
Rib cage muscles relax causing the rib cage to shrink
Inhalation and Exhalation
Exhalation vs. Inhalation Video Clip
Inhalation: Air Flow
Following inhalation air is pulled into the body entering the nasal cavity or mouth
Nasal cavity filters, warms, and moistens incoming air.
The air passes over epithelial cells which are covered in mucous and also contain cilia
Cilia = hair like projections that trap dust and bacteria
Mucous = secretions of the nose also responsible for trapping bacteria and dust
Mouth Breathers
Lacks proper filtration system whereas the nose has the cilia and mucous
Air entering the mouth is not as warm when compared to the nose (nose blood vessels warm the blood)
Mouth breathing is thought to be connected to abnormal facial development, gingivitis, and crooked teeth.
Can cause lack of sleep and poor academic performance.
Break Time – Collect H/W Assignment
From Nasal Cavity to Larynx
Air in the nasal cavity will move towards the pharynx
Is the entrance of the throat
The epiglottis is a muscular flap that prevents food from entering the trachea.
From the Trachea to Bronchioles
The trachea carries air to the
bronchi (sing. Bronchus).
Each bronchus carries air to the lung
The bronchus then forms many branches called bronchioles which are spread throughout the lung
Bronchiole muscle tissue can contract or relax to control oxygen intake.
From Bronchioles to Alveoli
The alveoli are tiny sac structures at the ends of bronchioles where gas exchange occurs.
Capillaries tightly surround each of the alveoli.
The capillaries will be exchanging their carbon dioxide for the oxygen in the alveoli sacs using diffusion.
Alveoli and Capillary Gas Exchange
Diffusion
Diffusion
Diffusion only takes place with a concentration gradient
Gases will flow from a high concentration to a low concentration
A high oxygen concentration in the alveoli and low oxygen concentration the blood capillaries causes oxygen to move into the capillaries.
The opposite is true for carbon dioxide.
Diffusion
Oxygen Absorption
Oxygen is absorbed by the structure named haemoglobin on a red blood cell.
Specifically it is the iron on the haemoglobin that absorbs the oxygen.
How is breathing controlled?
Breathing is controlled by the
medulla oblongata.
Our body detects the level of acid which is produced by the carbon
dioxide within our body.
If there is a high level of carbon dioxide (low oxygen) in the blood, then the body sends signals to the diaphragm to breathe in.
If there is a low level of carbon dioxide
(high oxygen) in the blood, then the body will send signals to breathe out.
Pharynx
Trachea
Bronchus
Bronchiole
Alveoli
Air Flow Chart
Respiration Review Video
Lungs and Smoking
Statistics
By 2030, if current trends continue, smoking will kill one in six people.
Every eight seconds, someone dies from tobacco use.
About 15 billion cigarettes are sold daily - or 10 million every minute.
Among young teens (aged 13 to 15), about one in five smokes worldwide.
Between 80,000 and 100,000 children worldwide start smoking every day - roughly half of whom live in Asia.
Inside/Outside Activity: Cigarette
Chemicals and Related Diseases
Lungs and Smoking Summary
Smoking primarily damages cilia
Recall: Cilia helps filter out harmful bacteria and dust particles
Cigarette smoke has over 1000 times the level of carbon monoxide that is known to be harmful to human health.
Cigarette smoke contains 4000 chemicals
40 of which increase the incidence of cancer
Homework
Read pages 103-107
Answer questions # 5-7 (Pages 107)
Chapter 3 Review: # 9-18