Chapter 11 PPT Notes
advertisement

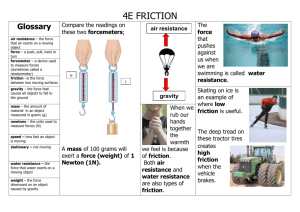
Chapter 11 Force – A push or pull that one body exerts on another Force is measured in a Newton (N) or (Kg m/s2) Can be measured with a spring scale What forces are being exerted on the Fkick football? ▪ Force of kick ▪ Force of gravity ▪ Maybe force of air resistance Fgravity There are two types of forces: Balanced Forces – no movement occurs ▪ Equal forces on both sides ▪ Ex) tug of war game with neither side moving Unbalanced Forces – movement occurs ▪ Unequal forces on both sides Normal (@ a right angle) Friction/Drag (slows it down) Contact (touching) Gravitational (a pull) Electric (movement of electrons) Magnetic Air Resistance (slows it down) Compression (pushing) Tension (pulling) Exists between two solid objects when their surfaces are pressed together due to other forces acting on one or both objects Ex) a solid sitting on or sliding across a table Ex) a magnet attached to a refrigerator Always directed at a right angle Force that opposes sliding between two surfaces The force on an object always points in a direction opposite to the relative motion of the object Friction causes thermal energy between objects Which direction is the friction? Motion Pushing Force Friction Friction is greater: Between rough surfaces When there’s a greater force between the surfaces (for example – more weight) The diagram below shows two people having a tug-of-war. Determine the unknown tension force. T = 900 N Tension is constant throughout the entire rope. Tension is always opposite and equal. When an object falls, it is pulled down by gravity Also pushed up by air resistance The force of air resistance is in the opposite direction to the force of motion Amount of air resistance depends on the speed, size, and shape of the object If no air resistance is present, then an apple and a feather fall at the same rate Example of Feather and Hammer Falling at the Same Rate because there is no air on the moon to slow it down from Apollo 15 Mission. They fell at the same rate because they have a similar shape, not because of their mass. Acceleration towards the center Requires an unbalanced force Ex) On a roller coaster, the coaster cars zoom around the loop, the track exerts a centripetal force toward the center of the loop Ex) Bucket of water spun around Water stays in bucket Gravitational Force is proportional to its mass Weight can be found by: Fg = m x g Fg = force of gravity m = mass g = 9.8 m/s2 on Earth A robot rover used by NASA has a mass of 90 kg. What is its mass on Earth? ▪ Fg = mass x gravity ▪ Fg = (90 kg) x (9.8 m/s2) ▪ Fg = 882 kg m/s2 On the Moon (gravity is 1/6 less than on Earth)? ▪ Fg = mass x gravity ▪ Fg = (90 kg) x (1.6 m/s2) ▪ Fg = 147 kg m/s2 If the same astronaut stands on the Earth and the Moon their weight is different. Why? ▪ The mass of an object stays the same wherever it is, but its weight can change. ▪ The Moon has less mass than the Earth, so its gravity is less than the Earth's gravity. This means that objects weigh less on the Moon than they do on the Earth.