Newton*s Laws
advertisement

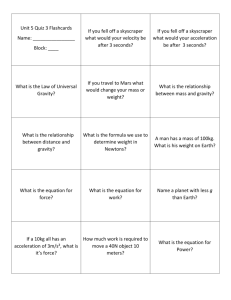
N EWTON’ S L AWS N EWTON ’ S 3 L AWS Inertia mass motion F=ma Equal and opposite forces “Newton” Push and Push Back relationship Action and Reaction I NERTIA An object will stay at rest or in constant motion until a force acts upon it. The more mass an object has, the more inertia it has. F ORCE IS EQUAL TO MASS TIMES ACCELERATION The force that an object experiences is equal to the mass times acceleration. F=ma F OR EVERY ACTION THERE IS AN EQUAL AND OPPOSITE REACTION Push and Push Back N EWTON ’ S 3 L AWS ??? N EWTON ’ S 3 L AWS ??? N EWTON ’ S 3 L AWS ??? N OTES Q UESTIONS : PG . 271, 272 What is free fall? What is Earth’s free fall acceleration? How do you calculate weight? Why do astronauts float in space? How is mass and weight different? How is mass and weight similar? How are animals bodies designed to respond to gravity in their environments? What causes terminal velocity? G RAVITY, W EIGHT, & M ASS Gravity is the natural pull that exists between two objects. Gravity depends on 2 variables: Mass Distance MORE MASS , MORE GRAVITY MASS GRAVITY MORE DISTANCE , LESS GRAVITY DISTANCE GRAVITY G RAVITY IS WHAT KEEPS THE PLANETS GOING AROUND THE SUN W EIGHT = MASS X GRAVITY Force = mass X acceleration F=ma Weight = mass (kg) X gravity (9.8 m/s2) w=mg Weight is measured in Newtons because it is a measurement of Force 1 lb = 4.4 Newtons Objects weigh more on planet Earth than on the moon, because the Earth is more massive. That is to say that it has more mass! E VERYTHING FALLS TO EARTH AT AN ACCELERATION OF 9.8 M / S 2 W HAT IS TERMINAL VELOCITY, AND WHAT CAUSES IT ? M EASURE THE MASS ( IN KILOGRAMS ) AND WEIGHT ( NEWTONS AND POUNDS ) OF THE FOLLOWING OBJECTS Mass (kg) Pencil Piece of paper Marble Ball Ruler Cell phone Weight (N) Weight (lbs) In my own words define work illustrate Physical Science Book Page 284 -287 Use in a sentence define In my own words power illustrate Use in a sentence W ORK Work is equal to the amount of force that is applied to an object times a certain distance. W=Fd Measured in Joules (J) This hammer applies a force to the nail for a certain distance. The hammer “does work” on the nail P OWER Power is the amount of work that is done over a certain amount of time. P=W/t Power is measured in Watts (W) This bicyclist has a certain amount of power. He does a certain amount of work over a certain amount of time. This 500 kg car travels from 45 m/s to 100 m/s in just 2.5 seconds. In that time, it travels 181 meters. What is the car’s: Acceleration? Force? Work? Power? W ORK AND P OWER L AB Complete the Inquiry Lab on page 287. Your weight in pounds X 4.4 gives you your weight in Newtons. If you don’t want to share your weight, that is fine. Just use the imaginary weight of 600 N. You have 20 minutes to complete this assignment. I will come around and check this in your notebook. DO NOT TURN IT IN!! H OW TO STUDY FOR YOUR TEST Make sure that you have all of your notes organized. Read your warm-ups, notes, and activities several times. Make note cards for the main ideas/key terms. H OW TO STUDY FOR YOUR TEST Note Cards Inertia Gravity, mass, weight Newton’s Laws Force (F=ma) Work (W=Fd) Power (P=W/t)