Heirs to Rome I: The Byzantine Empire
advertisement

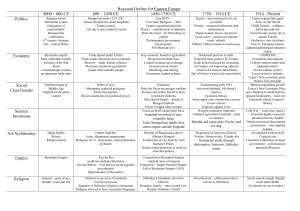
Heirs to Rome: The Byzantine Empire World History: Libertyville HS Where Was the ERE? • Capitol, Constantinople, located at narrowest point between Europe, Asia (Hellespont) Major trade routes to North / South • – – • North, to Rus / Vikings South, to Anatolia / ME Major trade routes West / East – – West, to Europe East, to India / China Bosphorus Straits, location of Constantinople (Istanbul) Why Constantinople? • • • • • Great location for a city (trade, easily defended) Control the Black Sea assured Legacy of the Greeks, Romans City first built as a fortress (walls, location) Riches of East allowed for tribute to pay off invaders Who Were They? • • To inhabitants, they were simply the Roman Empire Emperors continued in unbroken succession from Caesar to Diocletian and beyond Statue of Augustus When did Byzantine Empire Begin? • When Diocletian divided empire? • When Constantine moved capitol from Rome to Const? • When Theodosius made divisions of Empire permanent? • Or Fall of Western Empire in 476 AD? • Or when Heraclius (ca. 620) made Greek the official language of the East & its conflicts focused in that direction? Hmm . . . So when did it begin? Justinian I (527-565) • • Introduced Law Code, a revision of old Roman laws, in Greek Great general, Belisarius, helped recapture much of traditional Roman Empire (Italy, Africa, part of Spain) Expansion of Byzantine Empire from start of Justinian’s rule to his death Justinian I Construction of the Hagia Sophia, the greatest church built east of Rome, completed Justinian I • But with death of Justinian, territory gained in West was quickly lost Empire almost fell in late 500s • – – Persians reached Nile River & Bosphorus Slavs overran the Balkans in Europe and laid siege to Constantinople itself Byzantine Empire, 600-1025 • Savior of Empire = Heraklius (610-640) – • Emperor who considered abandoning Constantinople Reforms – – – – Gave soldiers land in frontier Soldiers paid no taxes Sons of soldiers = soldiers themselves Reorganized provinces into themes, under control of General Byzantine Themes, ca 620 AD (yellow) and 900 AD (in pink) Heraklius • Successes – Longest period of Byz. Empire success, creativity – Re-established Byz. Empire in Balkans – By 629 AD, recaptured most of ME (Jerusalem) • Rise of Islam put Byz, Empire on the defense – Lost Mesopotamia, Syria, Egypt, Africa by 700 AD Byzantine Empire, 600-1025 • Spread of Orthodox Christianity – Two monks, Cyril and Methodius, spread Orthodox faith into Balkans and Slavic lands (Poland, Russia, etc) – Cyrillic Alphabet, to Russians • Greek orthodox spread throughout Eastern Europe – Monks, scholars, artists followed, giving culture distinct Byzantine flavor Cyril and Methodius Decline of the Byzantine Empire • • Death of Basil II in 1025 led to conflict between military themes, civilian nobility in capital By 1081, Byzantine Empire had been reduced to Greece due to civil war, pressure from Turks Byzantine Empire, 1081 Decline of Byzantine Empire • 1100s were a “Renaissance” of the Empire – Economy flourished, revival in art, re-captured SE Europe – Helped by Western Crusaders, starting in 1097 Fall of the Byzantine Empire • • • • Weak ruler took throne in 1185 (emptied treasury for gifts, churches - not defense) 1204 – Fourth Crusade and the sack of Constantinople by Crusaders / Venetians Led to fragmentation of empire & successor states trying to control area Sack of Constantinople in 1453 by Ottomans: 85k v. 7k defenders Crusaders enter Constantinople Legacy of Byzantine Empire • • • • Most (only!) stable state during European Middle Ages Expert military, diplomacy saved Europe from Muslim invasion Trade center brought many peoples into contact with one another Transmission of classical knowledge from Islamic world to West, helping bring about European Renaissance