Unit VII: States of Consciousness: Psychoactive drugs
advertisement

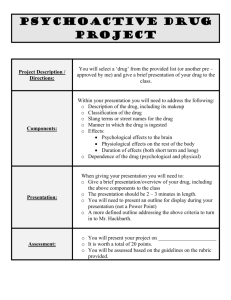
Unit VII: States of Consciousness: Psychoactive drugs Background Psychoactive drugs categorized: • Medically • Specifically, how they effect the CNS Unit VII: States of Consciousness: Psychoactive drugs Background Five Major categories 1. Depressants 2. Stimulants 3. Opioids / Opiates 4. Hallucinogens/psychedelic drugs 5. Marijuana Unit VII: States of Consciousness: Psychoactive drugs Psychoactive drugs My suggestion, make yourself a chart of the five categories of drugs to help you keep the information in order, like what’s on page 301 For example: • Category • What they do • Effects • Examples Unit VII: States of Consciousness: Psychoactive drugs 1) Depressants What they do • Slows (depresses) neural activity • Mostly effects: –Frontal lobe –Hindbrain Unit VII: States of Consciousness: Psychoactive drugs 1) Depressants Effects on the nervous system & body Afferent & efferent neurons, motor cortex all affected (slowed) • Slows reaction time Unit VII: States of Consciousness: Psychoactive drugs 1) Depressants Effects on the nervous system & body Association areas in frontal lobe depressed • Impairs judgment • Impairs long-term planning • Lessens inhibitions • Reduces self-awareness Unit VII: States of Consciousness: Psychoactive drugs 1) Depressants Effects on the nervous system & body Broca’s area affected • Slurring of speech Unit VII: States of Consciousness: Psychoactive drugs 1) Depressants Effects on the nervous system & body Effects cerebellum • Overconsumption -> balance, coordination problems Unit VII: States of Consciousness: Psychoactive drugs 1) Depressants Effects on the nervous system & body Effects brainstem (Medulla oblongata) • Depresses automatic functions, could stop if too much consumed • Heartbeat, breathing, ability to vomit Unit VII: States of Consciousness: Psychoactive drugs 1) Depressants Effects on memory • No effect on short-term recall or existing long-term memories • However, difficult to create long-term memories Unit VII: States of Consciousness: Psychoactive drugs 1) Depressants Effects on memory • Also, state dependant memory • Memories made while intoxicated are hard to remember when sober. • Able to remember next time in that state (drunk) Unit VII: States of Consciousness: Psychoactive drugs 1) Depressants Major depressants • Alcohol • Barbiturates –Anesthesia –Sleeping pills –Also known as “Downers” Unit VII: States of Consciousness: Psychoactive drugs 1) Depressants Major depressants, continued • Tranquilizers –AKA: Sedatives –Treat anxiety –Examples: Valium & Xanax Unit VII: States of Consciousness: Psychoactive drugs 2) Stimulants What they do • Increase activity of the CNS Unit VII: States of Consciousness: Psychoactive drugs 2) Stimulants Effects on the nervous system & body • Heighten alertness • Increase energy • Speed up bodily functions Unit VII: States of Consciousness: Psychoactive drugs 2) Stimulants Effects on the nervous system & body • Speeds up CNS/automatic functions (respiratory, cardiac) • Can overtax/permanently damage these parts of the body Unit VII: States of Consciousness: Psychoactive drugs 2) Stimulants Effects on the nervous system & body • Many mimic effects of neurotransmitters • Highly physically addictive • Tolerance built up quickly • Makes withdrawal difficult Unit VII: States of Consciousness: Psychoactive drugs 2) Stimulants Major stimulants • Amphetamines –Synthetic stimulant –“Speed” Unit VII: States of Consciousness: Psychoactive drugs 2) Stimulants Major stimulants • Cocaine –Derived from leaves of coca plant –Crack: concentrated form Unit VII: States of Consciousness: Psychoactive drugs 2) Stimulants Major stimulants • Ecstasy –Methyenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA) • Anything in large enough amounts is a hallucinogen (i.e., stimulant) Unit VII: States of Consciousness: Psychoactive drugs 2) Stimulants Major stimulants • Caffeine –Most popular drug in the world –Found in coffee, tea, chocolate, soda, etc. Unit VII: States of Consciousness: Psychoactive drugs 2) Stimulants Major stimulants • Nicotine –Highly addictive –Found in tobacco Unit VII: States of Consciousness: Psychoactive drugs 2) Stimulants Major stimulants • Nicotine, continued –Mimics neurotransmitters: • Acetylcholine • Dopamine • Vasopressin: causes high blood pressure Unit VII: States of Consciousness: Psychoactive drugs 2) Stimulants How cocaine works: 1/3 • Agonist – blocks reuptake of: –Dopamine –Serotonin –Norepinephrine • More of them bind to neuroreceptor site than usually do • Excess of neurotransmitters causes euphoric rush Unit VII: States of Consciousness: Psychoactive drugs 2) Stimulants How cocaine works: 2/3 • Stop use of cocaine • Natural neurotransmitters used up quicker than usually • Body producing at same rate Unit VII: States of Consciousness: Psychoactive drugs 2) Stimulants How cocaine works: 3/3 • Body crashes because lacks these neurotransmitters • Leads to agitation (lack of dopamine) depression (lack of serotonin & norepinephrine) Unit VII: States of Consciousness: Psychoactive drugs 2) Stimulants How ecstasy works: • Dopamine & Serotonin Agonist –Vesicle release excess of both –Blocks reuptake of both • More of them bind to neuroreceptor site than usually do • Causes good feeling (Serotonin), want to keep taking it (Dopamine) Unit VII: States of Consciousness: Psychoactive drugs 3) Opiods/Opiates What they are • Derived from alkaloids of resin of opium plant • Can be natural, synthetic, partially synthetic Unit VII: States of Consciousness: Psychoactive drugs 3) Opiods/Opiates What they are • Used as pain relief • Decreases perception & reaction to pain Unit VII: States of Consciousness: Psychoactive drugs 3) Opiods/Opiates What they are • Agonist • Mimics endorphins (body’s natural pain block) Unit VII: States of Consciousness: Psychoactive drugs 3) Opiods/Opiates What they are/effects • Sometimes (incorrectly) put into the depressant category • Can depress bodily functions (respiratory functions, etc) • Different method than depressants Unit VII: States of Consciousness: Psychoactive drugs 3) Opiods/Opiates What they are/effects • Depressants slow hindbrain • Opioids depress respiratory function itself • Causes drowsiness Unit VII: States of Consciousness: Psychoactive drugs 3) Opiods/Opiates Effects on the nervous system & body Intense feeling of euphoria Highly physically addictive Tolerance builds up very quickly More and more needed to prevent withdrawal • No longer produces euphoria, just maintaining level to function • • • • Unit VII: States of Consciousness: Psychoactive drugs 3) Opiods/Opiates Major opiods • Opium (natural) • Morphine (natural) • Codeine (natural) • Diacetylmorphine (heroin) (semi-synthetic) • Methadone (fully synthetic) Unit VII: States of Consciousness: Psychoactive drugs 4) Hallucinogens/psychedelic drugs What they are • Distort perceptions • Cause heightened sensory alertness (colors seem brighter, sounds clearer, etc.) • Cause hallucinations Unit VII: States of Consciousness: Psychoactive drugs 4) Hallucinogens/psychedelic drugs Addiction • Not physically addicting • Strongly psychologically Types • Natural substances • Synthetic Unit VII: States of Consciousness: Psychoactive drugs 4) Hallucinogens/psychedelic drugs Natural • Mesculine: peyote cactus • Psilocybin: certain types of mushrooms Unit VII: States of Consciousness: Psychoactive drugs 4) Hallucinogens/psychedelic drugs Natural • Mesculine: peyote cactus • Psilocybin: certain types of mushrooms Synthetic Unit VII: States of Consciousness: Psychoactive drugs 4) Hallucinogens/psychedelic drugs Natural • Mesculine: peyote cactus • Psilocybin: certain types of mushrooms Synthetic • Phencyclidine: PCP or angel dust • Lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD): acid Unit VII: States of Consciousness: Psychoactive drugs 4) Hallucinogens/psychedelic drugs Effects • How alter perceptions still unclear • Serotonin receptors? • Effects people differently in different situations (why is unclear) Unit VII: States of Consciousness: Psychoactive drugs 5) Marijuana Background • Sometimes put into one of the other categories • Or, considered its its own category Unit VII: States of Consciousness: Psychoactive drugs 5) Marijuana Background Depressants • Depresses the neural system • Depresses inhibitions, judgment, etc Unit VII: States of Consciousness: Psychoactive drugs 5) Marijuana Background Hallucinogenic • Causes (usually mild) hallucinations Unit VII: States of Consciousness: Psychoactive drugs 5) Marijuana Background Opioids • Feeling of euphoria • Drowsiness • However, not derived from opium poppy Unit VII: States of Consciousness: Psychoactive drugs 5) Marijuana Background Stimulant • Can stimulate mood • Intensifies mood of user Unit VII: States of Consciousness: Psychoactive drugs 5) Marijuana What it is • Delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) • Active ingredient of marijuana • Found in leaves, flowering top of hemp plant Cannabis • Hashish: cooked down, mashed into a paste Unit VII: States of Consciousness: Psychoactive drugs 5) Marijuana Effects on the nervous system & body • How THC effects brain largely unknown • THC neuroreceptors found in: –Frontal lobe –Limbic system –Motor cortex Unit VII: States of Consciousness: Psychoactive drugs 5) Marijuana Effects on the nervous system & body • Because THC neuroreceptor found, neurotransmitter in the body apparently • Haven’t found it & don’t know what it does • Have found similar neurotransmitters, just not for THC Unit VII: States of Consciousness: Psychoactive drugs 5) Marijuana Effects on the nervous system & body • Low physically addictive • High psychologically addictive • THC lingers in body for a month or so • Body does not build up a tolerance • Small dose needed to produce desired effect