Study Guide, Contract Law Part VI
advertisement

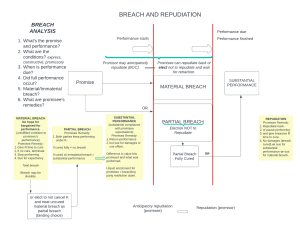
Law 3800 Dr. Edmonds Contract Law Study Guide, Part VI, Chapter 17 Chapter 17 Performance and Discharge I. What does it mean when we say a party to a contract is “discharged”? II. What is a condition and how does one differ from a simple term in a contract? III. What is a condition precedent and what happens if it doesn’t occur? Give an example. IV. What is a condition subsequent and what happens if it fails to occur? Who has the burden of proving that the condition subsequent did not occur? V. How do concurrent conditions work? Give an example. VI. What does performance mean in contract law language? VII. Explain strict performance. Do courts favor strict performance clauses? Give an example of when one might be appropriate. VIII. Explain substantial performance. Why would a party in breach of a contract want to prove substantial performance on their part? IX. List the four issues a court may consider in determining if a breaching party has substantially performed his/her obligation. X. If a breaching party cannot prove substantial performance, what if anything may they recover for their defective performance? XI. Explain how a personal satisfaction contract works. XII. Explain the duty of good faith and fair dealing; how did the court decide the Brunswick Hills case on page 390 and 391 and why? Contract Law Study Guide Part VI, page 2 XIII. Explain a “time is of the essence” clause. Is it not really a condition precedent? XIV. Differentiate between a breach and a material breach by describing the consequences of each. XV. Explain anticipatory breach (called anticipatory repudiation in class) and what options the non-breaching party has upon anticipatory repudiation. XVI. Explain the purpose and operation of a statute of limitations (also known as a limitation of actions). XVII. List the three situations which will perhaps support a claim of impossibility. XVIII. Explain the limitations on the doctrines of commercial impracticability and frustration of purpose. Explain the purpose of a force majeure clause from class discussion.