Functional analysis
advertisement

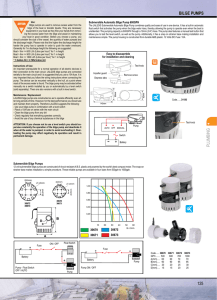
Business Ideas and Customer Value Oslo University 2007-08-28 Martin Edlund, Ph.D. martin@kebbison.com Challenges • Find the right users (customers) • Overcome different perceptions • Penetrate different types of needs • Provide the right competence where needed • Resources/willingness to invest in ”customer knowledge” • Put the new knowledge into the design process Innovation Each step involves customer need discovery and verification creation incubation demonstration promotion sustention An idea that potentially create Feedback from users Funcitionality test value for customers in a new (actual sales, warranty, of value creation way (business idea surveys) e.g. (test installation) formulation, problem description) Analysis the The first real test: Who value that can be created buys for how much? (the business plan, VoC, market (launch and initial sales) size estimation) We want to create customer value Customer Value = Perceived benefits Σ (Customer Costs) A Chain of Customers with Different and Conflicting Needs Linking Technology and Market - Functional analysis - Needs basic, spoken and latent Functions and performance Satisfy Solutions and features Provide Customer Needs Three types that are revealed in different ways Customer Needs - Example: Bilge Pump/Rule Industries • • • • • • • • • Reliable pump function Easy to install in bilge Easy to replace Less residual water in bilge Maintenance free Long service life High pump capacity Non-clogging Reasonable price • • • • • • Durable Appealing design Trusted brand Manual functionality test Mounting flexibility Good information to understand the system • Low impact on boat battery • Health status of system available remotely Functionality of a system Definition of functions: A=>B (Noun) - Verb - Noun - The car signals image. - The bottle contains water - The watch tells time. Hammer HITS Nail Functional performance characteristics Ex. the function to “show time” can be measured as: - Accuracy (how many minutes +/- in a year?) - Exactness (hours, minutes, seconds…) - How many time zones (three in parallel) Analysing a multilevel open system What system-levels and functions are relevant? supersystem Environment system subsystems subsystems subsystems customer/user Linking customer value and functions Main Functions Customer Value Additional Function = Unwanted Functions Perceived Benefits Total Customer Costs Purchasing Costs Operating Costs Decommissioning Costs A structured process to capture needs - VoC 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Undertand your invention/product (functional analysis) and prepare customer interviews Set up meetings (hard work!) Conduct and follow-up interviews/visits Analyze and compile results Quantify via surveys (if necessary) Voice of the customer (VOC) - Two vital steps for generation of new knowledge Exploration Verification (Testing of our hypothesis) Customer needs are created in different areas Need or Solution to a Problem A business idea Market B C Business Model The Dominant Managerial Logic • Overuse of existing knowledge • Which are the basic potential customer needs? • Who is the customer? • The difficult process of unlearning • The limit of a core competence approach to innovation and business extension The IBE Phenomenon - An Example Business diversity time Generic strategies to increase customer value - What is the long-term survival strategy? Creation of Customer Value Needs Perception Functionality Costs • Increase functionality • Influence the customers perception of value • Sell to the right customer • Lower the price User-driven innovation ? • Value for users is a driver through the innovation process • User-decisions is a driver for growth • End-users drive the commercial chain in the longrun • But, entrepreneurs/venture teams drive innovation The Creativity Aspect [Viktor Fey, TRIZ-group] Market and Industry Analysis 2007-09-04 Oslo University Martin Edlund Market Size Estimation A ten-step bottom-up approach to market estimation 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. See the product in the users hands (”Viceralization”) – who will use it? Discuss value and customer needs – how many are interested? Understand the customer chain – who win/who loose/who pay? Price in relationship to competition and substitution - how much will be paid and what will you get paid? How large is the population of potential buyers at that price (maximum size of market)? Adoption rate – how fast will customers buy? Life cycle of products – how long will sales last? Influence of competition – how will the buying pattern change? Product range extension and product differentiation – how can the market be develop further? Risk analysis: identify threats, consequences and how to mediate – what is the best, most likely and worst case? Example: Market Estimation • Use the step-wise process to guide your discussion • Estimate the market size of a wave-driven bailer for small boats in Norway 1. See the product in the users hands (”Viceralization”) – who will use it? • Links to the VoC work • A choice • Example: Automatic Welding Helmets – For everyone? – Indoor/outdoor – Type of welding (MIG, TIG...) – Large/small companies – Safety culture in different countries 2. Discuss value and customer needs – how many are interested? • The customer value equation: how does it apply for the different users? • What is the customer value in economic and other terms? • Use the functional analysis to penetrate this question • Example: The RV Maserator – Very unwanted funtions eliminated – Vacation and RV is expensive, Maserator cheap... 3. Understand the customer chain – who win/who loose/who pay? • It is your sales figures that are of interest! • Use the Five forces model • Who provides what in the customer chain from a customer value perspective? • Example: A new fuel-level sensor to the automobile industry – Car dealer, manufacturer, supplier, sub-supplier... – Low bargaining power? 4. Price - how much will be paid and what will you get paid? • Cost-based or Value-based • Competition • Substitites • Currency-rates/local buing power • Total costs for customer • Example: RV Maserator, oil detection tool, and composite wave guide 5. How large is the population of potential buyers at that price? • Stick to the right level of analysis when using macro data • Creativity is needed in most cases to extrapolate from known sources of statistics • Focus on the first target market that can prove your case • Example: Ultrasound diagnostics Logiq 700/500/400 – Known statistics on health-care operations – Known standard of living/buying power – A model of the market was created to make estimatins on size 6-7. Adoption rate and Life cycle– how fast will customers buy and for how long? • The adoption curve • Installed-base • Substitution curve • Crossing the chasm 8. Influence of competition • Price pressure • Economies of scale and scope • Substitutes 9. Product range extensions • Next version • Range • Price-differentiation • Modular offer “I was seldom able to see an opportunity until it had ceased to be one” Mark Twain