Essentials Of Business Law
Chapter 19
Introduction To Commercial Paper
McGraw-Hill/Irwin
Copyright © 2007 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Characteristics Of
Commercial Paper
Legally binding documents used to transfer
money from one person to another
Notes, checks, and drafts
Negotiable instruments
Freely transferable
Unconditional written promise to pay a certain sum of
money on demand or at a definite time
Highly trusted
Form the bases of contracts
Presumption of consideration
Issued for value
Essentials of Business Law
Chapter 19-2
Types Of Commercial Paper
Promises to pay
A written note in which one person promises to pay a
certain amount of money to another at a definite time
Orders to pay
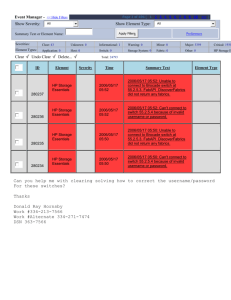
Check
• A written order that requests the bank to pay a sum of money
to the order of a specified person
Draft
• An unconditional written order to a person instructing him or
her to pay money to another, third person
Essentials of Business Law
Chapter 19-3
“Pay To The Order Of”
Give commercial paper negotiability
The ability to be transferred freely from one
person to another
Makes commercial paper an order
instrument
Checks, drafts, and notes
Essentials of Business Law
Chapter 19-4
Parties To Commercial
Paper
Promissory note
Maker is the person who makes the promise
Payee is the person to whom the promise is made
Check or draft
Drawer is the person who draws or creates the check
or draft
Payee is the person who receives the money
Drawee is the person who is ordered to pay the
money
Holder is whoever is in possession of commercial
paper
Essentials of Business Law
Chapter 19-5
Requirements Of
Commercial Paper
It must be in writing and signed by the maker or
drawer
It must contain an unconditional promise or
order to pay a definite sum in money
It must be payable on demand or at a definite
time
It must be payable to order, to bearer, or to cash
A draft or check must name or indicate the
drawee with reasonable certainty
Essentials of Business Law
Chapter 19-6
Nonessentials Of
Commercial Paper
The words “for value received” are not
needed
Specification of consideration given by the
maker or the drawer is not needed
Date may be written in by holder in due
course if omitted by drawer
May be antedated or postdated
Numbering is not required
Essentials of Business Law
Chapter 19-7
Checks
Provides a safe means of transferring money
Serves as a receipt
Payable on demand
Stale check
A check presented more than six months after its
issue date
Certified check
A check that the bank has promised to pay when it is
presented for payment
Essentials of Business Law
Chapter 19-8
Checks
Cashier’s check
A check issued by the cashier of a bank and drawn
against bank funds
Traveler’s check
A certified check issued by banks, travel agencies,
and financial services companies
Bad check
A check against a bank in which the drawer has
insufficient funds on deposit to cover the check
Essentials of Business Law
Chapter 19-9
Checks
Forged check
A check signed by a person other than the drawer
Raised check
A check on which the amount has been raised by the
payee or bearer
Postdated check
A check that is dated later than the date the check is
written
Stop-payment order
An instruction a depositor gives to his or her bank not
to pay a particular check
Essentials of Business Law
Chapter 19-10
Electronic Funds Transfer
Electronic applications for handling money
ATMs, point-of-sale systems, direct deposit
and withdrawal,
Facilitates international trade
Electronic funds transfer act
Limits consumer liability to $50
• Consumer must notify the card issuer within two
days that a card has been lost or stolen
Essentials of Business Law
Chapter 19-11