Chapter 16
advertisement

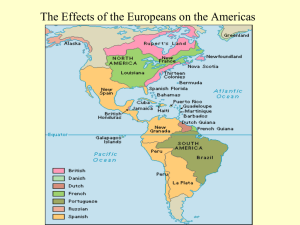
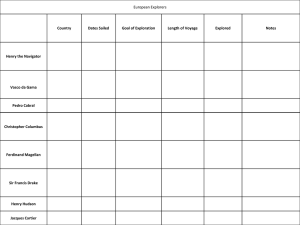
Chapter 16 The World Economy The West’s First Outreach Rising awareness of the world around them (Crusades) combines with several key disadvantages Ignorance of wider world Early explorations (Vikings) unsuccessful Belief that the world was flat (seriously) New Technology Explain the importance of each in your notes space: Round-hulled sailing vessels Compass Cartography (mapmaking) Explosives Portugal and Spain lead the Pack 1434—Portuguese explore the African coast Henry the Navigator Vasco da Gama reaches India (1498) 1514—Indonesia 1542—Japan Spanish fleets move west Columbus Amerigo Vespucci Ferdinand Magellan circumnavigates the globe Question Slide Characterize early European exploration—motives, methods and interactions with native peoples. Northern European Expeditions France, England and Holland (Protestants) join the hunt against Spain & Port. (Catholics) Used lighter, faster ships Britain permanently weaken Spanish Armada in 1588 (signals end of Spanish domination) Charter trading companies Dutch East India Co. British East India Co. READ the In Depth section on “Causation and the West’s Expansion” Toward a World Economy THREE major changes Columbian Exchange New Import-Export Patterns Emergence of new overseas empires Columbian Exchange Refers to the exchange of plants, animals and disease between the Old World and New World Question Slide Compare the effects of the Columbian Exchange on the Old & New Worlds. West’s Commercial Outreach West dominates ocean trade routes, but key players from post-classical period retain power Muslims active in M.E. and Swahili Coast Indian Ocean trade still has many players China and Japan remain independent Profit allows Europeans to : Defeat Ottomans (only potential, Muslim threat) Gain more harbors in Africa Influence formation/colonization of international trade cities (Constantinople, Moscow, St. Petersburg and Nagasaki) Imbalances in World Trade Intense competition between European nations Core Nations—profit from world eco., control banking & shipping, import raw materials in exchange for manufactured goods (mercantilism) Dependent Nations—produce low-cost goods (cash crops) or human labor in return for manufactured goods Question Slide Who are the core nations and dependent nations? International Inequality Core-dependent system still in place today Asia and parts of Africa still outside of the c-d system, as were some in Latin America Rise of coercive labor systems Racial intermixing in Americas creates new groups (mestizos and mulattoes) How Much World in World Economy? China—benefits w/out fully participating (rebuffs European efforts at contact) Japan and Korea—initial interest followed by selfimposed isolation India (Mughal Empire) encourages European port cities in Indian Ocean trade Middle East (Ottomans and Safavids) focus on building land-based empires Russia—still isolated until the 18th century (d@%* Mongolians!) Expansionist Trend 17th c.—Western traders advancing into India Trade companies extending influence 18th c.—Europeans starting to view powerful trade networks (India) as sources for materials and markets as opposed to trade partners Eastern Europe brought into the fold Colonial Expansion Establishment of colonies in Americas, parts of Africa and Asia Balance of power shifting in South Asia The Americas Advantages—guns, germs, steel (this sounds vaguely familiar…) Spain colonizes West Indies, C. and S. America Vasco de Balboa Francisco Pizarro Initial control is loosely organized (just here for the booty) but becomes more organized as plantation economies form (we came, we conquered, we farmed) British & French North America Holy crap this is a long section! To sum it up: North American colonies are very different form Latin American colonies English, French and Dutch settlers dominate (variety of motivations to settle N. America) Value of N. American products small by comparison to L. America (fur vs. silver/gold) Colonies will eventually become more valuable Colonies become models of Western styles (more so than L. America), and Western political ideology will shape its future revolutions Native American groups decimated by disease; slavery shapes southern colonies North America and Western Civ. Key Western habits transplanted to New World Family patterns (Americans marries slightly earlier) Emphasis on children, familial affection (awww…) Political and economic ideas reflect Western ideals Africa & Asia: Coastal Trading Stations Africa still largely unexplored—harsh climates, rough rivers, disease Exceptions—Cape Colony (Boers) SE Asia—Dutch East India Co. controlled parts of Indonesia and Thailand S. Asia—Mughals weaken while British and French vie for control Calcutta Seven Years War Impact on Western Europe Competition creates hostility Creates first “world war”—Seven Years War Ordinary Europeans benefit from new plants, animals and foods, especially corn, potatoes and sugar (yum, yum and yum) Impact of the New World Order Coercive labor systems impact New World, west Africa & Eastern Europe Individuals in many areas profit from trade Many profit from new goods Silver improves the economies of many— China, India etc. The World Economy & the World Its complex (now there’s a shock) Who wins and who loses? Who was winning but no longer is? Who do you think will win in this next unit? Who cares? (wait, don’t answer that one)