Seven Categories of Otherness
advertisement

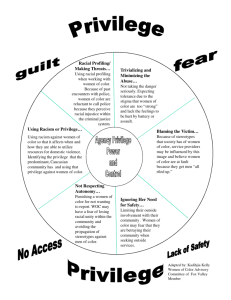
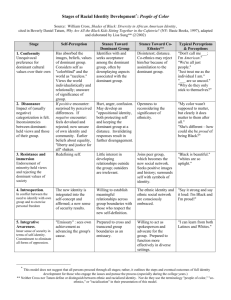
Sacramentality: Seven Categories of Otherness (KEY) (Adapted from: Beverly Daniel Tatum – Why Are All the Black Kids Sitting Together in the Cafeteria? and Peggy McIntosh – “White Privilege: Unpacking the Invisible Knapsack”) The Diversity Wheel 1. Primary Identifiers - “Internal” Categories/Fixed or Static Dimensions. Primary Identifiers of diversity are those human differences that are inborn and/or that exert an important impact on our early socialization, and that have an ongoing impact throughout our lives. 2. Secondary Identifiers - “External” Categories/Fluid or Dynamic Dimensions. Secondary Identifiers of diversity are those that can be changed, or are at least not inborn. Seven Categories of Otherness Though others certainly exist, distinctions made according to the following “Seven Categories of Otherness” arguably account for or have served to justify the vast majority of discrimination, prejudice, oppression, and violence in human history. According to each category, societies identify a Dominant group (perceived as the Norm), with the result that all those who fall outside become, to differing extents, Subordinates (perceived as the Exception(s)). The members of the Dominant (Norm) groups do not necessarily outnumber the members of the Subordinate (Exception) groups, but are those who have historically enjoyed greater social power, privilege, and influence in their respective societies. How does this operate in the United States of America? Associated Form of Discrimination Dominant (Norm) Subordinate (Exception) 1. Age (Primary Identifier) Ageism “Young” “Old” 2. Gender/Sex (Primary Identifier) Sexism “Male” “Female” 3. Physical/Mental Ability (Primary Identifier) Ableism “Able-Bodied” “Intelligent” “Disabled” “Unintelligent” 4. Race/Ethnicity (Primary Identifier) Racism/Colorism “White/Caucasian” “American” “Black/People of Color” “Foreigner” 5. Sexual Orientation (Primary Identifier) Heterosexism “Straight” “Heterosexual” “Gay” “Homosexual/Bisexual” Classism “Rich” “Poor” Religious Oppression/ Discrimination “Christian” “Non-Christian” Category 6. Economic Status/Class/Income (Secondary Identifier) 7. Religious/Spiritual Beliefs (Secondary Identifier) The perspective of the Dominant (Norm) Group(s) is generally characterized by: 1. The Assumption of Rightness 2. The Luxury of Ignorance 3. The Legacy of Privilege Racial Prejudice VS. Racism A. Prejudice – A preconceived judgment or opinion, usually based on limited information and usually adopted as the result of stereotypes, omissions, and/or distortions. B. Racial Prejudice – A preconceived judgment or opinion related to perceptions associated with skin color. C. Racism – A system of advantage based on race. 1. Racism = (Racial) Prejudice + (Social) Power 2. So defined, Racism is not only a personal ideology based on Racial Prejudice, but a system involving cultural messages and institutional policies and practices, as well as the beliefs and actions of individuals. 3. Most of us are taught to think of Racism only in terms of identifiable, malicious acts by members of one group toward members of another group, based on perceptions associated with skin color, and not in terms of invisible systems and structures conferring unsought and unearned social power, privilege, and influence on members of the Dominant (Norm) group. 4. According to this broadened definition of Racism, in our American society, a Person of Color can be “Racially Prejudiced,” but not “Racist,” because, as members of the Subordinate (Exception) category, owing merely to their skin color, they do not enjoy the social power, privilege, and influence that flow to members of the Dominant (Norm) group, owing merely to their skin color. 5. Racism includes BOTH Active Forms and Embedded Forms: a. Active Forms – Identifiable, malicious acts by members of one group toward members of another group, based on perceptions associated with skin color (e.g., Hate Crimes). b. Embedded Forms – Invisible systems and structures conferring unsought and unearned social power, privilege, and influence on members of the Dominant (Norm) group (e.g., White Privilege). White Privilege A. White Privilege – The systematic advantages of social power, privilege, and influence associated with being White in American society. An invisible constellation of unearned benefits/assets which flow to Whites, based solely on their skin color, owing to systematic and structural factors present in America. 1. Unearned Advantage 2. Conferred Dominance B. Some of the systematic advantages that can appropriately be grouped under the heading of “White Privilege” are merely what one would want for everyone in a just society. However, others make allowances for White members of American society to be ignorant, oblivious, arrogant, and destructive.