Syllabus - Adnan Farah
advertisement

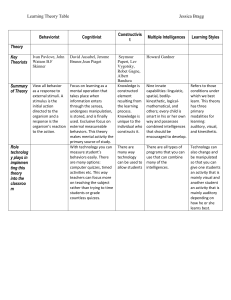
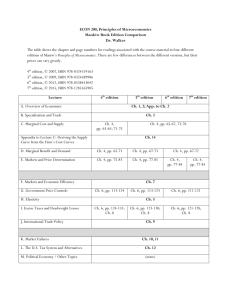
BAHRAIN TEACHERS COLLEGE UNIVERSITY OF BAHRAIN Course Outline Psychology of Learning (TCPB 113 - BED Program) COURSE DURATON: LECTURER: Room: Email: Website: 45 HOURS Professor Adnan Farah 126 dr_adnanfarah@hotmail.com www.adnanfarah.com COURSE DESCRIPTION This core unit involves the study of how students learn and the implications that follow for how they should be taught. The emphasis is on exploring the rich interconnections between theory and practice, and illustrating the power of effective theories in guiding complex practice. It has several themes which include but are not limited to: cognitive approaches to learning and knowledge construction; motivation; and multiple intelligences. It emphasizes a teacher’s role in the development of students as self-directed learners. Drawing on teacher candidates’ learning in related units and observations in the pre-coursework school placement, this course is prerequisite to Teaching Practice 1. COURSE OBJECTIVES This course seeks to equip student teachers to be professionals who are capable of engaging in theory driven and research-based practice. More specifically, upon completion of the course, student teachers should be able to: 1. Appreciate why and how students learn 2. Understand and analyse the different factors that have a bearing on student learning outcomes 3. Understand ways to enhance student learning and know how to apply this knowledge to their teaching practice 4. Implement a multiple intelligences approach to teaching and problem-based learning in their classrooms COURSE REQUIREMENTS 1. 2. 3. 4. Class Participation Formative Evaluation - 2 Quizzes Problem-Based Learning – Group Assignment Summative Evaluation – Final Examination 10% (2 x 5%) 40% 40% 1 Course Assessment Details Individual Components: 1. Class Participation (10%) Task Description The student teacher will demonstrate committed participation in course learning activities and demonstrate fundamental professional competencies. He or she will be expected to be: • • • • • • Punctual for all lessons and associated activities; Participate with good will in all lessons and associated activities; Complete all tasks in a timely fashion and submit assessment tasks on time; Act with personal dignity and afford dignity to all others; Comply with academic and ethical codes of the University; and Comply with scholarship conditions imposed by the Ministry of Education. 2. Formative Evaluation – 2 Quizzes 2 short quizzes to consolidate understanding • Week 5 – Quiz 1: Topic: Motivation (5%) • Week 12 – Quiz 2: Topics: MI and Assessment (5%) 3. Final Summative Examination 40% Group Component: 4. Problem-Based Learning – Group Assignment 40% • • • Portfolio Presentation Reflection REQUIRED TEXTS Eggen, P., & Kauchak, D. (2006). Educational psychology: Windows on classrooms (7thEd). NJ: Pearson.(ISBN: 978-0131724488). Campbell, L., Campbell, B., & Dickinson, D. (2004). Teaching and learning through multipleintelligences (3rd Ed). Boston: Pearson. (ISBN: 978-0205363902) Tan, O. S. (2003). Problem-based learning innovation: Using problems to power learning inthe 21st century. Singapore: Thomson Learning. (ISBN-9812437177) 2 Suggested Weekly Content Schedule Wk Content Focus References Introduction 1. The Psychology of Learning: An Introduction Cruickshank, D. R., Bainer, D. & Metcalf, K. (2001). The act Aspects of student learning Characteristics of the learner Major psychological approaches to learning of teaching (2nd Ed). OH: McGraw-Hill. Eggen, P., Educational & Kauchak, D. (2006). psychology: Windows on classrooms (7th Ed). (Chapters15). NJ: Pearson. Tan, O. S., Parsons, R. D., Hinson, S. L., & Sardo-Brown, D. (2003). research Educational psychology: A practitioner- approach (An Asian edition). (Chapters 1-5). Singapore: Thomson. Understanding Student Motivation 2. Perspectives of Motivation What is motivation? Perspectives on Motivation A closer look at selected motivation theories Eggen, P., & Kauchak, D. (2006). Educational psychology: Windows on classrooms (7th Ed). (Chapters 10&11). NJ: Pearson. Brophy, J. (1998). Motivating students to learn. New York: McGraw-Hill. Schunk, Pintrich, Meece (2008). Motivation in education: Theory, research and applications. NJ: Pearson-Merrill/Prentice Hall. Stipek, D.J. (2002). Motivation to learn: Integrating theory and practice (4th Edition). Boston: Allyn and Bacon. 3. Goal Orientation Theory Eggen, P., & Kauchak, D. (2006). Educational Conceptual overview Mastery and performance goals psychology: Windows on classrooms (7th Ed) (Chapter Relations with motivational and cognitive outcomes Personal and contextual predictors of goals From Schunk, Pintrich, Meece (2008). Motivation in education: 10). NJ: Pearson. Theory, research and applications (pp. 183-206). NJ: Pearson-Merrill/Prentice Hall. 3 theory to practice Stipek, D.J. (2002) Motivation to learn: Integrating theory and practice (4th Edition)(Chapter 10). Boston: Allyn and Bacon. 4. Self-Determination Theory Conceptual overview Types of behavioral regulation in SDT Research on selfdetermination From theory to practice 5. (Quiz 1 on Motivation) Overview of Key Eggen, P., & Kauchak, D. (2006). Educational psychology: Windows on classrooms (7th Ed) (Chapter 10). NJ: Pearson. Liu, W. C., Tan, O. S., Wang, C. K. J., Koh, C., & Ee, J. (2007). Motivation in the context of project work: The self-determination perspective. In D. M. McInerney, S. Van Etten and M. Dowson (Eds.), Research on sociocultural influences on motivation and learning: Standards in education (Vol. 7, pp. 189-213). Greenwich, CT: Information Age Publishing. Schunk, Pintrich, Meece (2008). Motivation in education: Theory, research and applications. NJ: Pearson-Merrill/Prentice Hall.p. 248-253 Eggen, P., & Kauchak, D. (2006). Educational psychology: Windows on classrooms (7th Ed). (Chapters 2, 6, 7, 8). NJ: Pearson. Classical 5. Exploring Classical and Contemporary Perspectives on Learning through Problem-Based Learning (PBL) Theories of Learning: Bandura, Skinner, Vygotsky, Piaget, Information Processing Tan, O. S. (2003). Problem-based learning innovation: Using problems to power learning in the 21st century. Singapore: Thomson Learning. Overview of PBL: Philosophy, Objectives and Evaluation Process Introduction to the 3 PBL Case Scenarios 4 6. Classical and Contemporary Tan, O. S. (2003). Problem-based learning innovation: Using problems to power learning in the 21st century. Theories of Learning: PBL Singapore: Thomson Learning. Problem Encounter Problem Scenario and Analysis Formulation of Problem Statement 7. Classical and Contemporary Theories of Learning: PBL Problem Analysis and Learning Issues Formulation of learning objectives Tan, O. S. (2003). Problem-based learning innovation: Using Preparation for SelfDirected Learning and Peer Teaching Relevant chapters from Eggen, P., & Kauchak, D. problems to power learning in the 21st century. Singapore: Thomson Learning. (2006). Educational psychology: Windows on classrooms (7th Ed). NJ: Pearson. Other relevant references and resources 8. Classical and Contemporary Theories of Learning: PBL Discovery and Reporting Relevant chapters from Eggen, P., & Kauchak, D. (2006). Educational psychology: Windows on classrooms (7th Ed). NJ: Pearson. Other relevant references and resources Approaches to Maximizing Student Learning 9. Multiple Intelligences What is Intelligence? Chapman, C. (1993). If the shoe fits ...:How to develop multiple intelligences in the classroom. Glenview, IL: Pearson-Skylight. Gardner, H. (1999). Intelligence reframed: Multiple intelligences for the 21st century. New York: Basic Books. Kagan & Kagan (1988). Multiple Intelligences: The Intelligent? complete MI book. San Clemente, CA: Kagan Cooperative Gardner’s theory of Multiple Learning. How does one become Intelligences My MI Profile Recognizing and Responding 5 10. Teaching with Multiple Intelligences 8-in-1 lesson or unit plan Planning for a 8-in-1 Lesson Campbell, L., Campbell, B., & Dickinson, D. (2004). Teaching and learning through multiple intelligences (3rd Ed). New York: Pearson-Allyn and Bacon. Lazear, D. (2003). Eight ways of teaching: The artistry of teaching with multiple intelligences (4th Ed). Glenview, IL: Skylight. Liu, W. C. (2006). Learning through multiple intelligences. In A. C. Ong & G. D. Borich (Eds.), Teaching strategies that promote thinking: Models and curriculum approaches (pp. 199 – 218). Singapore: McGraw-Hill. 11. Assessment and Student Learning Key issues and concepts related to learning: What, Why and How? Impact of assessment Black, P., Harrison, C., Lee, C., Marshall, B., Wiliam, D. (2003) Assessment for learning: Putting it into practice. NY: OUP Eggen, P., & Kauchak, D. (2006). Educational psychology: Windows on classrooms (7th Ed) (Chapters 15 & Rethinking Assessment: Assessment of learning and for learning Assessment in 16). NJ: Pearson. my classroom 12. (Quiz 2 on MI and Assessment) Independent Study Week: Preparation for PBL Group Presentation and PBL Portfolio Preparation for Summative Evaluation and Revision Lesson on Week 15 13. Classical and Contemporary Theories of Learning: PBL Solution Presentation 6 14. Classical and Contemporary Theories of Learning: PBL Solution Presentation Reflection on (i) Learning Theories; (ii) PBL as a Learning and Teaching Approach Eggen, P., & Kauchak, D. (2006). Educational psychology: Windows on classrooms (7th Ed). NJ: Pearson. Tan, O. S. (2003). Problem-based learning innovation: Using problems to power learning in the 21st century. Singapore: Thomson Learning. 15. Preparation for Summative Evaluation COURSE REFERENCES AND SUPPLEMENTARY READING Black, P., Harrison, C., Lee, C., Marshall, B., Wiliam, D. (2003). Assessment for learning: Putting it into practice. NY: OUP (ISBN: 978-0335212972) Brophy, J. (2004). Motivating students to learn. New York: McGraw-Hill. (ISBN: 978-0-8058-4772-7 (paperback)) Chapman, C. (1993). If the shoe fits ...: How to develop multiple intelligences in the classroom. lenview, IL: Pearson-Skylight. (ISBN: 9780932935649) Cruickshank, D. R., Bainer, D. & Metcalf, K. (2005). The act of teaching (3rd Ed). OH: McGraw-Hill. (ISBN: 0073126500) Elliot, S. N., Kratochwill, T. R., Littlefield, J. F. (2000). Educational psychology: Effective teaching,effective learning (3rd Ed). Madison: Brown & Benchmark. (ISBN: 9780697375407) Gardner, H. (1999). Intelligence reframed: Multiple intelligences for the 21st century. New York: Basic Books. (ISBN: 978-0465026111) Kagan & Kagan (1988). Multiple intelligences: The complete MI book. San Clemente, CA: Kagan Cooperative Learning. (ISBN: 978-1879097452) Lazear, D. (2003). Eight ways of teaching: The artistry of teaching with multiple intelligences (4th Ed).IL: Skylight Professional Development. (ISBN: 978-1575171197) Liu, W. C. (2006). Learning through multiple intelligences. In A. C. Ong & G. D. Borich (Eds.), Teaching strategies that promote thinking: Models and curriculum approaches (pp. 199 – 218).Singapore: McGraw-Hill. (ISBN: 0071256253) Liu, W. C., Tan, O. S., Wang, C. K. J., Koh, C., & Ee, J. (2007). Motivation in the context of project work: The self-determination perspective. In D. M. McInerney, S. Van Etten and M. Dowson (Eds.),Research on sociocultural influences on motivation and learning: Standards in education (Vol. 7,pp. 189-213). Greenwich, CT: Information Age Publishing. (ISBN: 978-1-59311-779-5) Ormrod, J. E. (2008). Educational psychology: Developing learners (6th Ed). NJ: Merrill. (ISBN:9780136127024). Santrock, J. W. (2006). Educational psychology (2nd Ed). Boston: McGraw-Hill. (ISBN: 9780073525822) Schunk, D. H., Pintrich, P. R., & Meece, J. L. (2008). Motivation in education: Theory, research, and applications. NJ: Pearson. (ISBN: 9780132281553) 7 Slavin, R. E. (2006). Educational psychology: Theory and practice (8th Ed). Singapore: Allyn &Bacon. (ISBN: 9780205566747) Stipek, D. (2002). Motivation to learn: Integrating theory and practice. MA: Allyn & Bacon. (ISBN-13: 9780205342853) Tan, O. S., Parsons, R. D., Hinson, S. L., & Sardo-Brown, D. (2003). Educational psychology: Apractitioner-research approach (An Asian edition). Singapore: Thomson. (ISBN: 9812430431) Tan, O. S., & Watson, G. (2004). Enhancing thinking through problem-based learning approaches:International perspectives. Singapore: Thomson. (ISBN: 9812437185) 8