THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
advertisement

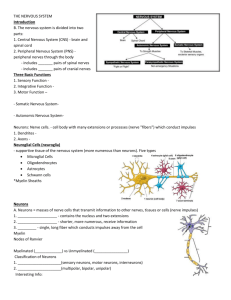
Name:_________________________ THE NERVOUS SYSTEM 9.1 Introduction A. Neurons = masses of nerve cells that transmit information to other nerves, tissues or cells (nerve impulses) 1. Cell Body - contains the nucleus and two extensions 2. Dendrites - shorter, more numerous, receive information 3. Axons - single, long fiver which conducts impulses away from the cell body B. The nervous system is divided into two parts: 1. Central Nervous System (CNS) - brain and spinal cord 2. Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) - peripheral nerves through the body - includes 31 pairs of spinal nerves - includes 12 pairs of cranial nerves 9.2 Three Basic Functions 1. Sensory Function - gathers info about changes occurring within and around the body - Sensory receptors, at ends of peripheral nerves send signals (nerve impulses) to the CNS. Sensory Neuron 2. Integrative Function - information is "brought together," interpreted, to create sensations, create thoughts, add to memory, make decisions, etc. Association neuron or interneuron 3. Motor Function - responses to signals (impulses). Signals sent from the CNS to effectors (muscles or glands). The goal is usually to maintain stable conditions (especially internal) - Homeostasis. Motor neurons. - Somatic Nervous System (skeletal muscles) - Autonomic Nervous System (smooth muscles, glands) C. Neurons: Nerve cells. Unique structure - cell body with many extensions or processes (nerve "fibers") which conduct impulses. There are two types of processes: 1. Dendrites - shorter, more numerous. These, along with the cell body, form the receptive surfaces of neurons. 2. Axons - single, long "fiber" which conducts impulse away from the cell body. Sometimes it is "branched" (collaterals). End has many fine branches. Name:_________________________ 9.3 Neuroglial Cells (neuroglia) - supportive tissue of the nervous system (more numerous than neurons). Five types 1. Microglial Cells 2. Oligodendrocytes 3. Astrocytes 4. Ependymal Cells 5. Schwann cells *Myelin Sheaths 9.4 Neurons Axon Dendrite Neurofibril Chromatophilic substance Myelin Nodes of Ranvier Myelinated (white matter) vs Unmyelinated (grey matter) Name:_________________________ Classification of Neurons 1. Functional (sensory neurons, motor neurons, interneurons) 2. Structural (multipolar, bipolar, unipolar) 9.5 Cell Membrane Potential Resting Potential / Threshold Potential / Action Potential 1. Neuron membrane maintains resting potential 2. Threshold stimulus is received 3. Sodium channels open 4. Sodium ions diffuse inward, depolarizing the membrane 5. Potassium channels open 6. Potassium ions diffuse outward, repolarizing the membrane 7. The resulting action potential causes a local bioelectric current that stimulates adjacent portions of the membrane. 8. Wave of action potentials travel the length of the axon as a nerve impulse 9.6 Nerve Impulse *Propagation of action potentials along a nerve axon Impulse Conduction – speed of an impulse proportionate to diameter of axon (greater diameter = faster impulse) Myelinated axons conduct faster than unmyelinated axons Example: Motor neuron associated with skeletal muscle 120 m/2 Sensory neuron on skin (unmyelinated) travels at .5 m/s A: Neuron (Presynaptic) B: Neuron (Postsynaptic) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Mitochondria Synaptic vesicle full of neurotransmitter Autoreceptor Synaptic cleft Neurotransmitter receptor Calcium Channel Fused vesicle releasing neurotransmitter Neurotransmitter re-uptake pump Name:_________________________ 9.7 The Synapse Synapse – junction between two communicating neurons Nerve pathway – nerve impulse travels from neuron to neuron Synaptic Transmission Dendrite cell body along axon synapse (gap) To complete the signal, a NEUROTRANSMITTER is released at the gap to signal the next neuron Excitatory – increase membrane permeability, increases chance for threshold to be achieved Inhibitory – decrease membrane permeability, decrease chance for threshold to be achieved Types of Neurotransmitters Acetylcholine – stimulates muscle contraction Monoamines – Norepinephrine & Dopamine (sense of feeling good, low levels = depression) Serotonin (sleepiness) Endorphins (reduce pain, inhibit receptors) Synapses are highly susceptible to drugs and fatigue Curare (poison used by S. American Indians) and atropine stops Acetylcholine from depolarising the post-synaptic membrane, i.e. become paralysed. Strychnine and some nerve gases inhibit or destroy acetylcholinesterase formation. Prolongs and enhances any stimulus, i.e. leads to convulsions, contraction of muscles upon the slightest stimulus. Cocaine, morphine, alcohol, ether and chloroform anaesthetise nerve fibers. (inhibitory) Mescaline and LSD produce their hallucinatory effect by interfering with nor-adrenaline & serotonin 9.8 Impulse Processing Neuronal pool – groups of neurons that make hundreds of synaptic connections and work together to perform a common function Name:_________________________ 9.9 Types of Nerves Sensory Nerves – conduct impulses into the brain or spinal cord Motor Nerves – carry impulses to muscles of glands Mixed Nerves - contain both sensory and motor nerve 9.10 Nerve Pathways Reflex arc – simple pathway, includes only a few neurons (reflexes) Reflex Behavior – automatic, subconscious responses to stimulu Knee-jerk reflex (patellar tendon reflex stimulus knee sensory nerve spinal cord motor nerve Withdrawal reflex – occurs when you touch something painful Name:_________________________ Neuron Label Name:_________________________ Nerve Cells Coloring Oligodendrocytes (purple) Astrocyte (green) Ependymal Cells (orange) Body of Neuron (blue) For each of the cells above, color the nucleus a darker shade of purple, green, blue, orange Myelin sheaths (pink) Capillary (red) Microglial cells (yellow) Nodes or Ranvier and the Axon (brown) What is the function of: 1) Oligodendrocytes ______________________________________________________________ 2) Astrocytes ____________________________________________________________________ 3) Microglial cells ________________________________________________________________ 4) Myelin sheaths _______________________________________________________________ 5) Trace the path of a nerve impulse in a neuron: _________________________________________ Name:_________________________ Nervous System Review 1. The skeletal muscles are controlled by the ___________________________nervous system. 2. The smooth muscles and glands are controlled by the _______________________ nervous system. 3. Neurons are composed of a network of fine threads called ____________________ 4. The nervous system consists of two parts, the brain and spinal cord make up the ______________ nervous system, and the nerves throughout the body make up the ___________ nervous system. 5. ______________________________are cells found between neurons and blood vessels. 6. Neurons consist of a cell body, axons, and _________________________, which receive information. 7. Neurons that have a single process extending from the cell body are classified as _________, if they have two processes, they are classified as _____________ 8. White matter is composed of axons that are sheathed in ______________________ 9. Two ions necessary to create an electric current in a nerve fiber are potassium and ______________. 10. The ______________________ function of the nervous system refers to information being interpreted so that the brain can make decisions. 11. The junction between two communicating neurons is called the ________________ 12. Acetylcholine, serotonin and endorphins are all forms of ___________________ 13. The _________________________arc refers to a simple nerve pathway that would be involved with involuntary actions (like knee-jerk, or withdrawal) 14. Groups of neurons that perform a common function, such as the storing of procedural memory (tying your shoe) are called neuronal __________. 15. __________________________________cells help destroy bacterial cells and cellular debris. 16. There are 31 pairs of ____________________________ nerves. 17. These types of neurotransmitters increase membrane permeability, thus increasing the chance that threshold will be achieved. 18. When a threshold is achieved, an event called the __________________ potential occurs. 19. Gaps in the myelin sheath are called Nodes of _________________________________ 20. These support cells are responsible for secreting the myelin sheaths: _________________________ 21. A nerve impulse is received by the dendrites and then travels down the ___________________ 22. There are twelve pairs of ________ nerves. 23. This neurotransmitter stimulates the muscles to contract. __________________ 24. These cells form a membrane that covers specialized brain parts: ___________ 25. These cells have the same function as oligodendrocytes, but are packed within the myelin: _________________ Locate words from the Review on the Word Search: Name:_________________________ Nervous System Review Word Search