CELL-ebration minimum expectations per group
advertisement

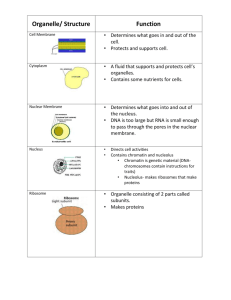
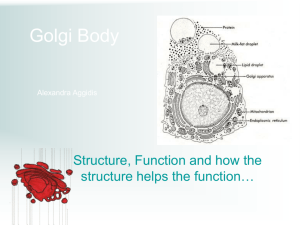
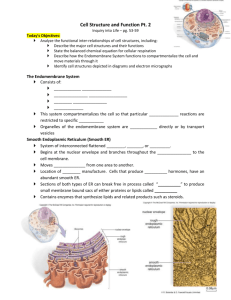
Minimum Expectations for CELL-ebration Groups Finding Information You may find the information for these points in a combination of locations: 1. Your text book or any other Biology based textbook 2. Online: a. Google your specific question i. Note: Wikipedia is an acceptable place to gain information for this biology topic b. Use Khan Academy: https://www.khanacademy.org/science/biology/structureof-a-cell c. Use links off of Class Website: https://fcsbiology.wordpress.com/cell-structureand-function/ MINIMUM CELL-EBRATION EXPECTIONS PER GROUP: NUCLEUS, RNA, DNA (minimal CELL-ebration requirements) Structure & function of nuclear envelope (double phospholipid bi-layer) DNA mRNA Proteins (Central Dogma) Role of the nucleolus Role of the nuclear pores Significance of DNA Significance of RNA Role in the endomembrane system MINIMUM CELL-EBRATION EXPECTIONS PER GROUP: RIBOSOMES, RER, SER (minimal CELL-ebration requirements) Structure & function of ribosomes What does endoplasmic reticulum literally mean? How are the proteins built by ribosomes into the RER? Structure & function of RER What is a polyribosome? How do vesicles form from the RER? Role in the endomembrane system Difference between bound and free ribosomes MINIMUM CELL-EBRATION EXPECTIONS PER GROUP: PROTEINS, AMINO ACIDS, CELL MEMBRANE (minimal CELL-ebration requirements) Structure of an amino acid Each level of protein structure and function, including the bonds How does the protein structure change as it is moved through the endomembrane system? What types of proteins are synthesized by different types of cells? What is the structure of the cell membrane and ALL membrane bound organelles? Why can all components of the endomembrane system interact for protein synthesis? MINIMUM CELL-EBRATION EXPECTIONS PER GROUP: GOLGI BODY & VESICLES (minimal CELL-ebration requirements) Structure & function (what does the Golgi do to the proteins) Cis and trans faces of the Golgi How is the Golgi like the UPS or FedEx store? How do vesicles enter & leave the Golgi? What types of vesicles enter the Golgi? Leave the Golgi? Where do vesicles go? Cisternae Role in the endomembrane system MINIMUM CELL-EBRATION EXPECTIONS PER GROUP: MITOCHONDRIA & ATP (minimal CELL-ebration requirements) Specific structure of the mitochondria double membrane Endosymbiosis? Cristae, matrix, own circular DNA, own ribosomes, own proteins Specific structure of ATP How does ATP store energy What kinds of cells have lots of mitochondria? Name of the process that generates ATP What is phosphorylation? MINIMUM CELL-EBRATION EXPECTIONS PER GROUP: CYTOSKELETON & PLASMA MEMBRANE (minimal CELL-ebration requirements) Structure of the Plasma membrane Function of the Plasma membrane Specific structures of each: microtubules, microfilaments, intermediate filaments Specific functions of each: microtubules, microfilaments, intermediate filaments What parts of the CELL-ebration represent each cytoskeletal component? How does the cytoskeleton aid in protein synthesis? Vesicles move along cytoskeleton using ATP and motor proteins