Blood Pressure Lab
advertisement

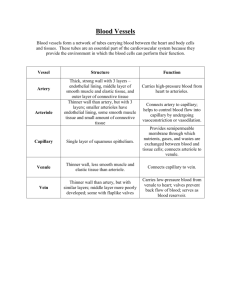
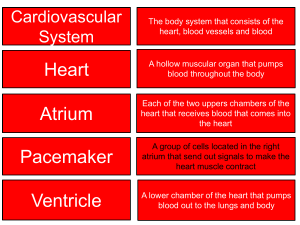
Take out background Dispatch 1) What is the difference between the sizes of an artery, capillary, and vein? 2) What do you think the relationship between temperature and heart beat is? 3) Blood pressure is…the force exerted against blood vessel walls. Responsible for the flow of blood The result of: ______________,______________, and ______________ – Pumping action of the heart – Resistance of the blood vessels – Volume of blood Announcements • Tomorrow 3-6pm -Muhammed -Nhi -Fernando -Chelsea -Valerie V -Antonio • Next week review Tues after school or Tues—nut/lun on PLANTS • Get AP 2008 scores on Thursday • 11:15 am Benchmark on Ecology and Evolution • Clear your name TODAY if you are on my board Draw and explain Explain • How does the structure of an artery relate to its function? The structure of ______ The function is________ The structure relates to function because_________ RBC from heart artery arteriole capillary RBC O2 Gas Exchange RBC back to heart vein venule capillary Follow a blood cell from the heart… • Start at the Aorta – largest artery in body – Contains OXYGEN • Cell leaves aorta = ARTERY • Continues to travel to a small artery = ARTERIOLE RBC from heart artery arteriole capillary Artery RBC O2 Arteriole CAPILLARIES “Gas Exchange” O2 CO2 out • An arteriole becomes and even smaller CAPILLARY • This is where OXYGEN leaves the red blood cell • This is where CARBON DIOXIDE enters the red blood cell Oxygen leaves RBC and enters tissue; Carbon dioxide leaves tissue and enters RBC TISSUE CO2 RBC bicarbonate O2 Follow a blood cell back to the heart… • Red blood cell with CARBON DIOXIDE • Cell travels in blood through a capillary and enters a VENULE (small vein) • Continues to travel to a VEIN • Returns to HEART RBC bica rbo nate Venule VEIN RBC back to heart vein venule capillary • Blood moving through the blood vessels exerts pressure against the vessel walls. This blood pressure is highest in the aorta. It decreases as the blood moves through the arterioles, capillaries, venules, and veins. Understanding Blood Pressure • When we measure blood pressure, we are actually measuring the systolic pressure and the diastolic pressure separately. • This is why you always see blood pressure reported as two numbers, one "over" the other. For example: • In a blood pressure reading of 110/80,110 = systolic pressure80 = diastolic pressure. • The numbers refer to the number of millimeters the pressure will raise a column of mercury. • The blood pressure of teenagers is frequently in the range of 120/70. Hypothesis • Will blood pressure be higher or lower if lying vs standing? • Will cold temp increase or decrease Daphnia heart beat? Daphnia • Humans are homeothermic (warm blooded) in that the body generates heat internally to maintain a certain temperature level. Lower animals do not generate heat internally and thus relay on external sources for their warmth. • This is known as poikilothermic (cold blooded). Daphnia is such an animal. This small, about 1 mm, aquatic crustacean draws its heat from the surrounding water in which it lives. As the temperature of the water increases, so does its body temperature. An increase in temperatures means an increase in activity, both physically and metabolically. This increase can be seen as an increase in heart rate. The object of this lab is to record the temperature vs heart rate for Daphnia. Data for Daphnia Copy and graph. Interpret graph Temperature (celsius) Heart Rate (beats/min) 5 108 10 152 15 211 20 290 Discussion Questions 1) Why does temperature affect heart rate in ectothermic organisms? 2) Discuss what results you might obtain if you repeated this experiment using an endothermic organism 3) Why does smoking cause a rise in blood pressure? 4) Explain why blood pressure and heart rate differ when measured in reclining position and in a standing position. • Blood pressure is a measure of how hard your blood is pushing against the walls of your veins while it is pumped. Blood pressure is lower when standing due to gravity. • http://www.medicalvideos.us/play.php?vid= 615 • http://www.bing.com/videos/search?q=Blo od+Pressure+arterial+flow+video&view=d etail&mid=B7DE91E4E45BF379F077B7D E91E4E45BF379F077&first=0 Why do some people feel faint when they go quickly from lying down to standing? The force of gravity causes the blood pressure in vessels going to the brain to drop. This causes temporary faintness until homeostatic mechanisms elevate blood pressure in these vessels. How and why does heart rate change with body position? The heart rate generally increases from lying to sitting to standing as more energy is required to maintain each of these postures. Virtual Lab • http://www.mhhe.com/biosci/genbio/virtual _labs/BL_08/BL_08.html Lab Quiz 1 • http://www.phschool.com/science/biology_ place/labbench/lab10/quiz1.html