America: A Narrative History (Ninth Edition)
advertisement

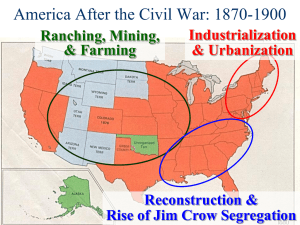
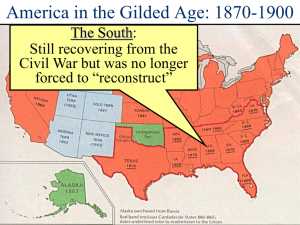
America: A Narrative History (Ninth Edition) Tindall/Shi Chapter 19 - The South and West Transformed I. Prophets and goals of the New South o A. Henry Grady of the Atlanta Constitution 1. Advocated popular ideas to create a “New South“ a. Industrial development b. Agricultural variety other than cotton c. Economic diversity leads to real democracy II. Economic growth in the New South o A. Textile mills o B. Tobacco 1. The Dukes and the American Tobacco Company o C. Coal and iron ore o D. Lumber III. Agriculture in the New South o A. Problems in southern agriculture 1. Land ownership rare a. Sharecropping b. Tenant farming 2. Small landholders use the crop-lien system a. Fosters perennial debt among small landowners b. Pushes farmers to grow cash crops, primarily cotton or tobacco 3. Efforts to increase yield of cash crops cause immense environmental damage a. Tenants lack incentive to protect the soil b. Fertilizers and over-cultivation exhaust fertility of land c. Abandoned lands lead to further problems with erosion o B. Impact of rural stagnation 1. High poverty and low education levels throughout South a. Both whites and blacks affected b. Former slaves affected most IV. The political leaders of the New South o A. The “Redeemers“ 1. Wealthy southern leaders who supposedly saved South from “Yankee dominations“ a. Rising class of lawyers, merchants, and entrepreneurs b. Eager to promote more diversified industrial economy 2. Called “Bourbons“ by opponents who sought to paint them as reactionaries a. Name refers to French royal family that supposedly learned nothing from the French Revolution b. “Redeemers“ supposedly learned nothing from theCivil War o B. Bourbon policies 1. Greatly reduced spending on education 2. Convict leasing a. Primarily black convicts leased to work for white farmers b. Saved prison expenses and generated revenue c. Justified on basis of black inferiority and benefits to blacks who would experience the discipline of working for others 3. Flexibility in Bourbon race relations a. Believed in white supremacy b. Allowed enough black voting and political involvement to disarm contemporary critics 4. Led South into new economic era without sacrificing mythic reverence for the “Old South“ V. Development of the New West o A. Emigrants to the West 1. Mexicans, Canadians, Germans, Scandinavians, Irish, and others 2. Exodusters, or African Americans from the South a. Benjamin Singleton b. The Exoduster experience 3. Buffalo soldiers o B. Mining the West 1. Valuable mineral deposits foster development of mining communities 2. Great gold and silver strikes of latter half of nineteenth century a. Concentrated in California, Colorado, and Nevada 3. Western states admitted to the Union America: A Narrative History (Ninth Edition) Tindall/Shi 4. Mining and the environment a. Individual “placer“ mining gives way to industrial corporate mining b. Hydraulic, draft, and shaft mining transform landscapes and pollute streams c. First major environmental lawsuit, Woodruff v. North Bloomfield Gravel Mining Company VI. Native Americans in the West o A. Emigrant and Indian conflict 1. Fort Laramie meeting, 1851 2. The Sand Creek Massacre, 1864 3. “Report on the Condition of the Indian Tribes,“ 1867 a. Decision to place Indians on reservations 4. George Custer and the Battle of Little Bighorn, 1876 5. Continued Native American resistance a. Modocs, 1871–1872 b. Nez Pearce and Chief Joseph, 1877 c. Geronimo and the Apache, 1886 d. The Ghost Dance and Wounded Knee, 1890 o B. Demise of the buffalo 1. Negative impact on Indians 2. Environmental factors diminishing buffalo separate from settlement o C. Reform of Indian policy 1. Impact of Helen Hunt Jackson’s A Century of Dishonor 2. The Dawes Severalty Act a. Goal of Dawes Act: well intentioned effort to “Americanize“ Indians b. Effect of Dawes Act: more opportunities for white plundering of Indian lands, further undermining of traditional Indian cultures VII. Cowboys and cattle in the West o A. Joseph McCoy and Abilene o B. Impact of railroads on expansion of the cattle industry o C. Growing cattle industry spurs rapid growth of the region o D. The role of railroad refrigeration o E. Decline of long drives and end of the open range 1. Joseph Glidden and barbed wire 2. Expanding number of homesteads 3. Rise of sheepherding 4. Impacts of severe winters and long droughts 5. Range wars over conflicting land and water rights VIII. Farmers in the West o A. Homestead Act of 1862 encourages settlement o B. The problem of aridity 1. Homestead Act of 1862 designed for smaller, wetter farms 2. Rangers controlled water resources 3. The Newlands Reclamation Act of 1902 a. Belated effort to develop irrigable land o C. Technological advances affected farmers 1. Railroads 2. Iron “sodbuster“ plow o D. Pioneer women 1. Numerical minority in the West 2. Faced legal obstacles and social prejudice 3. Fight for survival made them more independent than eastern counterparts XIII. The end of the frontier o A. Census of 1890 claimed frontier no longer existed o B. Frederick Jackson Turner and “The Significance of the Frontier in American History,“ 1893 America: A Narrative History (Ninth Edition) Tindall/Shi