Macromolecules - Carbohydrates & Lipids
advertisement
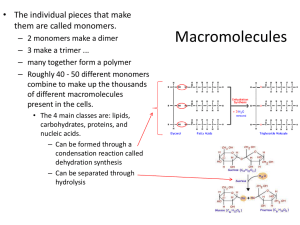
Macromolecules • Macromolecules are large, functional, carbon based structures that serve specific functions in living organisms. – 4 basic types • • • • Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids Carbohydrates & Lipids • The individual pieces that make them are called monomers. – 2 monomers make a dimer – 3 make a trimer ... – many together form a polymer – Roughly 40 - 50 different monomers combine to make up the thousands of different macromolecules present in the cells. Carbohydrates • Carbohydrates are sugars. – Used as the main source of energy in living things • Sugars can be single units which are monosaccharides (simple sugars), as disaccharides, or as long chains which are polysaccharides. • Monosaccharides (monos - single, sacchar - sugar) – empirical formula of (CH2O)n – Common forms… glucose, galactose, fructose • Molecular formula C6H12O6 • Are isomers of each other… same formula but different arrangement Synthesis of Carbohydrates • Can be formed through a condensation reaction – Each monosaccharide is added through the process of dehydration synthesis forming a glycosidic linkage • Removal of a water molecule when forming a bond • Can be separated through hydrolysis – Addition of water to break the bond Common Sugars • Common Disaccharides – Maltose… glucose + glucose – Sucrose… glucose + fructose – Lactose… glucose + galactose • Common Polysaccharides – Starch … plant storage for food – Cellulose… rigid structural material in plants • Not digestible in animals – Glycogen… animal storage for food • Lipids are macromolecules connected by ester linkage (via dehydration synthesis) between a glycerol molecule and 3 fatty acid chains (triglyceride or triacylglycerol). • Glycerol – 3 carbon alcohol molecule • each carbon is attached to a hydroxyl (-OH) functional group • Fatty acid – chain of about 16 - 28 carbon atoms – has a carboxyl g roup on the side that attaches to the glycerol – very hydrophobic (water hater!) – a fatty acid with no double bonds is said to be saturated • • • • most animal fats (lard, butter,...) solid at room temp chains can tightly pack (linear in shape) a diet rich in saturated fats leads to atherosclerosis …hardening of the arteries – a fatty acid with at least one double bonds is said to be unsaturated Lipids Lipids • Are used for… – Storage of energy… • Storage of fat in humans is called adipose – Cell membranes • Phospholipid bilayer – Chemical messengers… steroids – Insulation and shock absorption