1 - Bowie Aquatic Science
advertisement

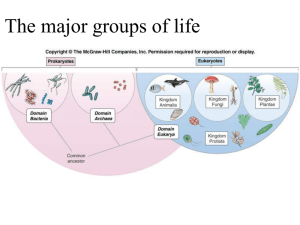
Name _______________________________________ Date _____________ Per _______ Spring 2014 Aquatic Science Final Review Plankton,Bacteria and Protista 1. Where do we find most plankton in the ocean and why? 2. What adaptations do plankton have to avoid sinking? 3. Define the following types of plankton a. phytoplankton b. zooplankton c. holoplankton d. meroplankton 4. Why are plankton important organisms in aquatic ecosystems? 5. What is the difference between prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells? 6. What is a protozoan? 7. What is algae? 8. Why are cyanobacteria important? 9. What is another name for cyanobacteria? 10. Why do phytoplankton have pigments such as phycoerythrin, xanthophyll and chlorophyll? 11. What is the difference between an osmoregulator and an osmoconformer? 12. Why can’t saltwater fish live in a freshwater environment? And freshwater can’t live in a saltwater environment? 1 Macroalgae and Plants 13. What kingdom are algae in? ______________________ 14. What are the three ways mangroves tolerate their salty environment? A: B: C: 15. List four ecological benefits that mangrove forests can provide. List the phylum to match the word origin. 16. Phylum: _______________________________: pore bearing 17. Phylum: _______________________________: jointed feet 18. Phylum: _______________________________: soft-bodied 19. Phylum: _______________________________: spiny skin 20. Phylum: _______________________________: sponges 21. Phylum: _______________________________: stinging cells Chordata List Classes of the following organisms. 22. Class: _______________________________: alligators, crocodiles 23. Class: _______________________________: Skates, rays, sharks 24. Class: _______________________________: catfish, perch, bass, trout 25. Class: _______________________________: lamprey, hagfish 26. Class: _______________________________: sea lions, whales, dolphins 27. The structure found in bony fish that is responsible for controlling buoyancy is called: 2 28. The largest internal organ in the dogfish shark is the liver, what is the function of the liver in sharks? 29. What is the purpose of the Ampullae of Lorenzini in the cartilaginous fish such as sharks, skates and rays? 30. What is the purpose of the lateral line in fish? 31. Define the following types of egg/embryo development: a. Oviparous b. Ovoviviparous c. Viviparous 32. Briefly describe the following species of sea turtles include: diet, size, weight, and distinguishing characteristics. a. Green b. Loggerhead c. Hawksbill d. Leatherback 33. What characteristics do all mammals have in common? 34. What type of organisms are in the Order Cetacea and are known as Cetaceans? 35. What is the purpose of the melon in the toothed whales? 3 36. Fill in the following chart on the two types of Cetaceans. Type of whale Common name for suborder Teeth or baleen Number of blowholes Type of food General size of whale Special adaptations Migration habits Odontocetes Mysticetis 37. For the following types of marine mammal groups list their distinguishing features, temperature regulation, feeding and reproduction (from comparison chart on the back of the vertebrate animal story project) Sea snakes: Marine iguana: Pinnipeds: Sea Otter: Sirenians: Arthropods and Echinoderms 38. The symmetry of arthropods is referred to as: 39. The symmetry of echinoderms is referred to as: 40. Which characteristics do all crustaceans have? Define the following terms. 41. cephalothorax 4 42. carapace 43. hemocyanin 44. chelipeds 45. swimmerets Mollusks Name the class of the following of the mollusks. 46. Class: _______________________________: snails, nudibranchs, abalone 47. Class: _______________________________: cuttlefish, squid, octopus and nautilus 48. Class: _______________________________: clam, oyster, mussels Define the following terms. 49. excurrent siphon 50. incurrent siphon 51. proboscis 52. radula 53. operculum 54. chromatophores Porifera and Cnidaria 55. Define the following terms. Nematocysts Cnidoblast Identify the correct class or phylum based on the description. 56. Phylum: ___________________________: invertebrates with nematocysts and radial symmetry 57. Phylum: ___________________________: invertebrates with asymmetry and bear pores 5 58. Class: ___________________________: invertebrates with the medusa as the dominant form 59. Class: ___________________________: cnidarian with the polyp as the dominant life form 60. Class: __________________________: cnidarian usually found in colonies each with special “jobs” Define the following symbiotic relationships: 61. Mutualism: 62. Commensalism: 63. Parasitism: 64. List all the characteristics that all cnidarians have in common: 65. Corals and jellyfish are both classified as cnidarians because they both have stinging cells called: List the function of the following cells/structures in a sponge and label them on sponge diagram 66. Choanocytes: ____________________________ 67. Ameobocytes: ___________________________ 68. Porocytes: ______________________________ 69. Epithelial cells: __________________________ 70. Spicule: ________________________________ 71. Osculum: _______________________________ Identifying structures Jellyfish 6 7 8