Weather Review
advertisement

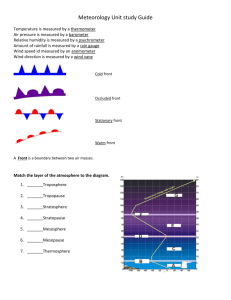
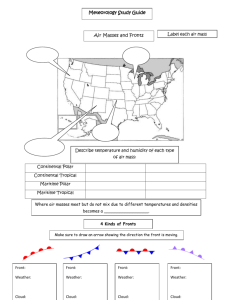
Weather Review Atmosphere in Motion Winds blow from _____ pressure to _______ pressure. Winds blow from High pressure to Low pressure. They also blow from COLD to WARM air How would you describe the winds in the NE section of the US? How would you describe the winds in the NE section of the US? HIGH WHY? How would you describe the winds in the NE section of the US? HIGH WHY? Isobars are very close together indicating large change in pressure A B Remembering that winds are named by the direction from which they come, which one of these is a land breeze? Remembering that winds are named by the direction from which they come, which one of these is a land breeze? A B B is a land breeze. Explain why. Remembering that winds are named by the direction from which they come, which one of these is a land breeze? A B B is a land breeze. Because the land cools off very quickly at night, while the ocean temperature stays basically the same. Since Winds blow from cool to warm, the breeze at night comes from the land. Remembering that winds are named by the direction from which they come, which one of these is a land breeze? A B A is a sea breeze. During the day, the land heats up much more quickly than the water, and therefore, since wind blows from cool to warm, the breeze comes from the water. Air movement •Put: conduction, convection and radiation in order of how air masses are formed. (Describe a convection current) •Put: conduction, convection and radiation in order of how air masses are formed. (Describe a convection current) Radiation – heats up the land Conduction – heats up the air Convection – moves the warm air around Draw a cold front and describe the associated weather Draw a cold front and describe the associated weather Cold dry air collides with warm moist air Cooler temps, rain, storms Draw a warm front Draw a warm front Warm air rises up and over the cooler more dense air List the four terms associated with describing air masses List the four terms associated with describing air masses Maritime – moist Continental – dry Polar – cool/cold Tropical – warm/hot Name the air mass that would form over the Gulf of Mexico Name the air mass that would form over the Gulf of Mexico Maritime Tropical = warm and moist Explain why coastal climates are cooler in the summer and warmer in the winter Water does not heat up or cool down as fast as land, so the sea breezes near the coastal areas keep those temperatures more moderate (average) What causes hurricanes to form? Hurricanes start as tropical storms near the tip of Africa. They travel across the Atlantic Ocean picking up LOTS of warm moist air – which causes EXTREMELY LOW PRESSURE on the surface. EQUIPMENT USED FOR FORECASTING barometer thermometer Psychrometer (humidity) Anemometer (wind speed) Describe the formation and results of Low pressure Describe the formation and results of Low pressure • Low pressure is formed as warm air rises, leaving less air molecules at the surface. • As the warm air rises, it cools, condenses and forms clouds. • Resulting weather is usually warmer and cloudy Describe the formation and results of High pressure Describe the formation and results of High pressure Cool, dense air aloft sinks, pushing air molecules toward The surface. With the added pressure, clouds are unable to form, so clear skies prevail. CONTINENTAL POLAR CLEAR WINDY COLD FRONT RAINY MARITIME TROPICAL
![wind [Repaired]](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/009822995_1-d740f770c04b871f35a8b5ad3684a975-300x300.png)