Global Desk
advertisement

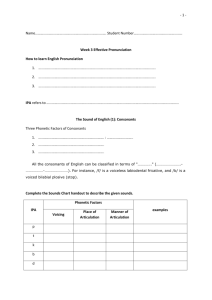
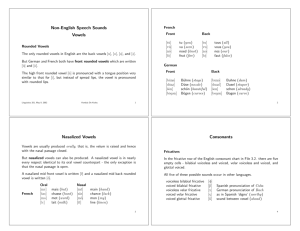
PHONETICS An Introduction to Linguistics Phonetics The study of speech sounds •How to ‘write down’ sounds A transcription system should be consistent and unambiguous. One sound One symbol •Is English a good transcription system? The same sound is spelled differently. • Sea, see, receive The same letter represents different • Sign, pleasure, resign sounds A single sound is spelled by more than one letter. A single letter represents more than one sound. • Shop, chair, special • Exit, use Letters might represents no sound at • Doubt, psychology all. •What do we use to transcribe the sounds? • IPA • International Phonetic Alphabet •An anatomy of articulation •CONSONANTS •How to describe consonants Voicing Place of articulation Manner of articulation •PLACE OF ARTICULATION •labials/bilabials [p], [b], [m] •dentals/interdentals [ð] [θ] •labiodentals [f], [v] •alveolars [t], [d], [s], [z], [n], [l], •palatals [ž]/[ʒ], [š]/[ʃ], [ʧ]/[č], [ʤ], •velars [k], [g], [ŋ] •glottals [h] •Summary: place of articulation category places examples bilabials Two lips [b], [p], [m] Labiodentals Lip & teeth [f], [v], Inter-dentals Between teeth [θ], [ð] alveolars Alveolar ridge palatals palate [t], [d], [n], [l] [s], [z] [ž]/[ʒ], [š]/[ʃ], [ʤ], [ʧ]/[č] velars Velum [k]. [g], [ŋ] glottals glottis [h] •MANNER OF ARTICULATION •Manner of articulation 1 stops • By forming the complete obstruction of the airstream in the oral cavity • [p, b, t, d, k, g] fricatives •By forming the nearly complete obstruction of the airstream in the vocal tract and therefore producing slight ‘friction’ or ‘turbulence’. •[s, z, ʃ, ʒ] affricates • By shortly obstructing the airstream completely and then releasing it [a stop + a fricative] • [ʤ, ʧ] •Manner of articulation 2 liquids • The constriction of the airstream is not narrow enough to block the vocal tract or cause turbulence. • [l], [r] glides • By forming a slight closure of the articulators. Little or no obstruction of the airstream with the tongue in gliding fashion • [j], [w] Nasals • By lowering the velum so that the airstream goes through the nasal cavity only. • [m], [n], [ŋ] •Manner of articulation (1) category distinction example Voiced vs. voiceless Vibration of vocal cord [p] vs. [b] Aspirated vs. unaspirated The ‘timing’ of vocal cord closure Top vs. stop Nasal vs. oral Air thru nose [m], [n], [ŋ] •Web Resources • Phonetic flash • http://www.phon.ucl.ac.uk/ho me/johnm/flash/flashin.htm •VOICING voicing The vibration of vocal cords voiced voiceless •How to describe a sound Voicing Place of articulation Manner of articulation Consonant description •Exercise 1 [p]=voiceless bilabial stop • [v]= • [g]= • [z]= • [ʤ]= • [ŋ]= • •Exercise 2 • Voiceless interdental fricative= [ ] • Voiced palatal affricate= [ ] • Voiceless alveolar stop= [ ] • Voiceless labiodental fricative = [ ] • Bilabial nasal=[ ] • Voiceless palatal fricative= [ ] • Voiced velar stop= [ ] •VOWELS •How to describe vowels: criteria • Height • High, mid, low • The • of tongue part of the tongue is involved Front, central, back • Position • of lips Rounded, non-rounded • Tense vs. lax •Vowel Chart FRONT BACK ROUND HIGH [i] (T) [I] [u] (T) [U] MID [e] (T) [ɛ] [o] (T) [ɔ] LOW [æ] [a] •How to describe a vowel • [vowel]= • Tense/lax + (Rounded) + High/mid/low + front/back • [æ]= low front vowel • [o]= tense rounded mid back vowel •SUPRASEGMENTAL FEATURES Segmental • Individual sounds suprasegmental • length • Intonation • Tone • Stress • Pitch •Length • The contrast of meaning due to length difference • Inherent differences High vowels are shorter than low vowels • [i] < [æ] • • Influenced • by the sounds around. Bead > beat •Intonation • The pattern of pitch movements across a stretch of speech • Two intonational patterns Pitch accents • Edge tones • Pitch accents: The word with particularly higher or lower pitch. JOHN loves Mary. John LOVES Mary. John loves MARY. John loves Mary Edge tones: Occurs at the end of the phrase John loves Mary! John loves Mary, Alice, and Doris. John loves Mary?. John loves Mary •Tone • The pitch variation that causes the contrast of meaning. • Level tones • A relatively fixed tone • Contour • tones A single syllable produced with tones that glide from one level to another. •Mandarin Chinese: a tone language segments [ma] [ma] [ma] [ma] Tone pattern High level High rising Low falling rising High falling Tone type Level Contour Contour Contour •Web Resources • Online Intonation • • http://www.phon.ucl.ac.uk/ho me/johnm/oi/oiin.htm Pitch • http://www.phon.ucl.ac.uk/cgi -bin/wtutor?tutorial=pitch •Summary • Describing consonants Place of articulation • Manner of articulation • Voicing • • Describing • vowels Height, front, roundness • Suprasegmental • features pitch, tone, intonation Questions?