Homeostasis_Unit_Map..
advertisement
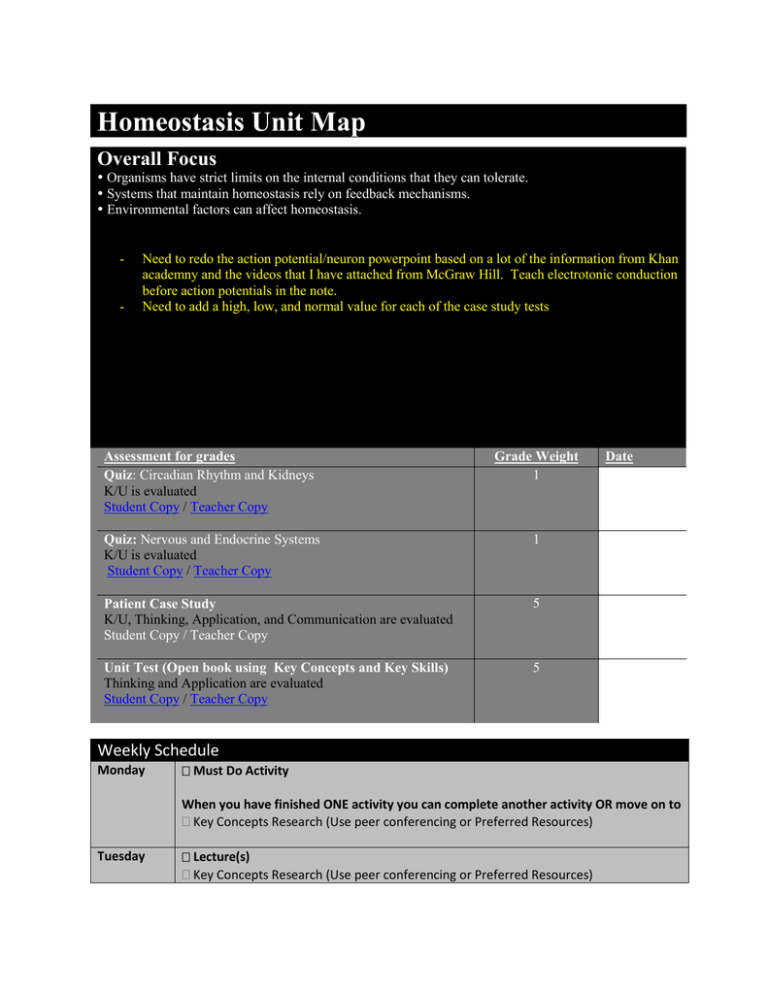
Homeostasis Unit Map Overall Focus Organisms have strict limits on the internal conditions that they can tolerate. Systems that maintain homeostasis rely on feedback mechanisms. Environmental factors can affect homeostasis. - - Need to redo the action potential/neuron powerpoint based on a lot of the information from Khan academny and the videos that I have attached from McGraw Hill. Teach electrotonic conduction before action potentials in the note. Need to add a high, low, and normal value for each of the case study tests Assessment for grades Quiz: Circadian Rhythm and Kidneys K/U is evaluated Student Copy / Teacher Copy Grade Weight 1 Quiz: Nervous and Endocrine Systems K/U is evaluated Student Copy / Teacher Copy 1 Patient Case Study K/U, Thinking, Application, and Communication are evaluated Student Copy / Teacher Copy 5 Unit Test (Open book using Key Concepts and Key Skills) Thinking and Application are evaluated Student Copy / Teacher Copy 5 Date Weekly Schedule Monday Must Do Activity When you have finished ONE activity you can complete another activity OR move on to Key Concepts Research (Use peer conferencing or Preferred Resources) Tuesday Lecture(s) Key Concepts Research (Use peer conferencing or Preferred Resources) Wednesday Must Do Activity When you have finished ONE activity you can complete another activity OR move on to Key Concepts Research (Use peer conferencing or Preferred Resources) Thursday Case Study Research Friday Lecture if required Tutorial questions Unit Organization Tutorial questions will be placed at desks in each corner of the room. Students must sit at the desks that have the questions at them to solve the problem. They will rotate to various desks to solve each of the problems. They are allowed to use wireless internet devices to help them, but are encouraged to discuss amongst the group at the desks. They will record the questions and answers and will include them in their unit map booklets. A large roll of paper will be placed at the front of the classroom. If a student feels very confident explaining a particular area of focus, they will write their name under that topic so that other students will know that they are offering their support in that area. There will also be another column that allows students to write down websites or other resources that they have found useful in learning about a particular topic. The paper will also have a column that lists all of the resources that they use throughout the unit that they felt were very useful. If a second student agrees, they will put a checkmark next to it. By the end of the unit, this paper will act as a large source of student feedback about which material was the easiest and hardest to master which will allow me to develop new resources for the harder material, a continued source of professional development as new websites and resources are listed each year, and an assessment of effective an ineffective resources that I am using. Key Concepts (K/U) ☐e1.1 assess, on the basis of findings from a case study, the effects on the human body of taking chemical substances to enhance performance or improve health (e.g., the risks and benefits of taking large quantities of vitamins or amino acids; the effects on the human body of substances that people use to cope with stress) What have you learned about this topic? ☐e1.2 evaluate, on the basis of research, some of the human health issues that arise from the impact of human activities on the environment (e.g., the effects of synthetic estrogen compounds released into our water systems; the effects of leaching of compounds from plastic products into soil and water) What have you learned about this topic? ☐e2.1 use appropriate terminology related to homeostasis, including, but not limited to: insulin, testosterone, estrogen, nephron, dialysis, pituitary, synapse, and acetylcholine What have you learned about this topic? ☐e3.1 describe the anatomy and physiology of the endocrine, excretory, and nervous systems, and explain how these systems interact to maintain homeostasis What have you learned about this topic? ☐e3.2 explain how reproductive hormones act in human feedback mechanisms to maintain homeostasis (e.g., the actions of male and female reproductive hormones on their respective body systems) What have you learned about this topic? ☐e3.3 describe the homeostatic processes involved in maintaining water, ionic, thermal, and acid–base equilibrium, and explain how these processes help body systems respond to both a change in environment and the effects of medical treatments (e.g., the role of feedback mechanisms in water balance or thermoregulation; how the buffering system of blood maintains the body’s pH balance; the effect of medical treatments on the endocrine system; the effects of chemotherapy on homeostasis) What have you learned about this topic? Key Skills (Thinking) Assessment that is not for grades I will discuss with you your performance of the skills required during various activities and lab investigations in order to judge how well you are able to demonstrate these skills. Date Ongoing throughout the unit ☐e2.2 plan and construct a model to illustrate the essential components of the homeostatic process (e.g., create a flow chart that illustrates representative feedback mechanisms in living things) How can you demonstrate your skills in this area? ☐e2.3 plan and conduct an investigation to study a feedback system (e.g., stimulus response loop) How can you demonstrate your skills in this area? ☐e2.4 plan and conduct an investigation to study the response mechanism of an invertebrate to external stimuli (e.g., the instinctive behaviour of an invertebrate in response to a stimulus such as light), using appropriate laboratory equipment and techniques How can you demonstrate your skills in this area? Key Skills (Application) All of these skills can be demonstrated by conducting and reporting on an inquiry lab investigation using the sections in the lab grading checklist below. Assessment that is not for grades I will view your lab books and problem research methods during various lab investigations in order to these skills. Date Ongoing throughout the unit Lab Grading Checklist Section Title (COMM) Criteria o Indicates EXACTLY what was studied or what test was conducted (eg. Disk Diffusion test for antibiotics) o Provides the names of all organisms or materials that are the focus of the investigation (eg. Micrococcus luteus bacteria, Pepsin enzyme) Purpose/ Question (THINKING) Materials (APPLICATION) o Clearly identified/stated and accurately describes the goals of the study (eg. The purpose of this study is to Procedure/ Methods (APPLICATION) Observations and Results (APPLICATION) o Clearly describes how and what was done and allows for EXACT replication of experiment determine if temperature has an effect on amylase enzyme activity.”) o All materials are listed o All quantities are included (eg. 50 ml of ethanol) o All key observations are present o Graphs/charts/images are provided where appropriate o All graphs/charts/images contain descriptive titles (eg. Graph #1: Using iodine and Benedict’s solution to measure the effect of temperature on the ability of amylase enzyme to digest starch) Discussion (THINKING) o What have you learned from the results of your investigation? (eg. Images #1 and #2 indicate that lemon juice and black pepper are effective as antibiotics when used on Micrococcus luteus. This is confirmed by the clear zone of inhibition in both images.) o Trends or patterns are stated and thoroughly explained (eg. From the results presented in Graph #1, it is evident that as pH increases, trypsin activity decreases.) o Appropriate comparisons to control samples have been made (eg. The control test tube did not experience any change in enzyme activity in comparison to test tube #1, which was heated to 70oC, and to test tube #2 which was cooled to -10oC.) o Attempt to explain results that don’t make sense by explaining sources of error AND possible problems with the procedure o Explain what other published research information says in comparison to your results. (eg. The effectiveness of lemon juice as an antibiotic agent in our investigation is consistent with the results obtained by Robert Smith (2005) who investigated the effectiveness of citrus fruit as an antibiotic agent against various species of bacteria.) o Based on the results that you have obtained, suggest how your investigation might be useful and what the next step should be for researchers that are concerned with the topic of your investigation. (eg. Based on the results of this investigation it does not appear that flowering plants are effective antibiotic agents against Micrococcus luteus bacteria. Elijah Royles (2001) found that various types of cooking spices tend to be effective antibiotic agents against a wide range of bacteria. This might be an area worth investigating in further studies of antibiotics for Micrococcus luteus.) Conclusion (THINKING) o Directly answers the hypothesis or addresses the purpose of the investigation o Refers to specific data or results (eg. The results shown in Table #1 indicate that temperature ranges of 0oC to 59oC cause an increase in enzyme activity. However, temperatures that are greater than 59oC cause a sharp decline in enzyme activity and likely cause a denaturation of the protein structure.) ☐ (Purpose/Prediction) A1.1 formulate relevant scientific questions about observed relationships, ideas, problems, or issues, make informed predictions, and/or formulate educated hypotheses to focus inquiries or research ☐A1.2 select appropriate instruments (e.g., dialysis tubing, glassware, sphygmomanometer) and materials (e.g., DNA models, plants, plant cuttings, molecular models), and identify appropriate methods, techniques, and procedures, for each inquiry ☐ (Discussion) A1.3 identify and locate a variety of print and electronic sources that enable them to address research topics fully and appropriately ☐ (Materials and Method) A1.4 apply knowledge and understanding of safe laboratory practices and procedures when planning investigations by correctly interpreting Workplace Hazardous Materials Information System (WHMIS) symbols; by using appropriate techniques for handling and storing laboratory equipment and materials and disposing of laboratory and biological materials (e.g., plants and invertebrates); and by using appropriate personal protection ☐ (Materials and Method) A1.5 conduct inquiries, controlling relevant variables, adapting or extending procedures as required, and using appropriate materials and equipment safely, accurately, and effectively, to collect observations and data ☐ (Observations/Results) A1.6 compile accurate data from laboratory and other sources, and organize and record the data, using appropriate formats, including tables, flow charts, graphs, and/or diagrams ☐ (Discussion) A1.7 select, organize, and record relevant information on research topics from a variety of appropriate sources, including electronic, print, and/or human sources, using suitable formats and an accepted form of academic documentation ☐ (Discussion) A1.8 synthesize, analyse, interpret, and evaluate qualitative and/or quantitative data to determine whether the evidence supports or refutes the initial prediction or hypothesis and whether it is consistent with scientific theory; identify sources of bias and/or error; and suggest improvements to the inquiry to reduce the likelihood of error ☐ (Discussion) A1.9 analyse the information gathered from research sources for logic, accuracy, reliability, adequacy, and bias ☐ (Conclusion) A1.10 draw conclusions based on inquiry results and research findings, and justify their conclusions with reference to scientific knowledge ☐A1.11 communicate ideas, plans, procedures, results, and conclusions orally, in writing, and/or in electronic presentations, using appropriate language and a variety of formats (e.g., data tables, laboratory reports, presentations, debates, simulations, models) Tutorial Problems Provide the questions and answers to the weekly tutorial questions here. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Is urine salty? Why or why not? Why does taking a hot bath and then getting out of the tub make you sleepy? How would a constant lack of sleep affect your body? What might cause a person not to feel pain? Why do people faint? Hypothetically, IF they existed, how would zombies benefit from eating brains? How do sleeping pills work? How does the body control increases in blood pH (ie.blood becoming more alkaline/basic)? Explain all of the possible effects on the human body of having cancer in three different organs or glands. 10. Why does the body not release epinephrine all day long if it is so useful? 11. What might cause ongoing, daily stress and how does the body respond to it? Resources www.khanacademy.com www.dbausch.com Google Scholar (a good source of published scientific reports) MUST DO Inquiry (Lab Investigations and other activities) You will choose AT LEAST one of these activities or inquiry investigations to complete each Monday and Friday until the end of this unit. If you are choosing to do a lab, you should be investigating background information on the subject of the investigation BEFORE the day that you are conducting it. ☐ Activity: Mammalian Diving Response: pg. 340 Nelson Bio 12 Textbook ☐ Activity: Detecting Temperature Changes www.dbausch.com / RLDHS / Course Outlines / SBI4U / Homeostasis / Activities ☐ Take home investigation: Circadian Cycles Take Home Study www.dbausch.com / RLDHS / Course Outlines / SBI4U / Homeostasis / Lab Investigations ☐ Activity: Use modeling clay to build the structure of a kidney. Assign one group to construct the whole kidney and the others to construct a functioning nephron. Groups will then pair up with other groups and will explain their structures to each other. They may fix any mistakes at this point. ☐ Activity: Each student will now use clay to construct the different ions, water molecules, and other substances (ie. antibiotics) that are involved in the process of urine formation. They will pair up with other groups and use their nephron models to discuss the process of urine formation. (Nelson 12 Biology textbook pg. 350 diagram will help) After completing this model, students should record what they have learned (eg. diagram, notes about the model) ☐ Lab investigation: Kidney Disorders Student Copy / Teacher Copy www.dbausch.com / RLDHS / Course Outlines / SBI4U / Homeostasis / Lab Investigations ☐ Activity: Act the process of pH regulation by the kidneys by creating a diagram of the structures involved and cut-outs of the various molecules that are moving. Develop your own diagram of the process of pH regulation. ☐ Lab investigation: The Quest for Artificial Blood www.dbausch.com / RLDHS / Course Outlines / SBI4U / Homeostasis / Lab Investigations ☐ Activity: Each student gets into pairs. One student from each pair will then challenge another student from another group to an arm wrestling match. Before the challenge they will measure their heart rate. After the arm wrestling match they will then count their heart rate again. Discuss the role of the hormone adrenaline in the results of this investigation. ☐ Lab Investigation: Blood Glucose Two Day Lab Study www.dbausch.com / RLDHS / Course Outlines / SBI4U / Homeostasis / Lab Investigations Past Results May 2008: Effects of Different Breakfasts on Mr. Bausch’s Blood Sugar ☐ Activity: Homeostatic Disorders: Part One www.dbausch.com / RLDHS / Course Outlines / SBI4U / Homeostasis / Activities ☐ Activity: Complete the lab activity on page 452 of the Nelson Biology 12 text ☐ Activity: Each student will draw and cut out a LARGE NEURON, draw sodium and potassium channels on the axon body, cut out five square sodium ions and five circular potassium ions, and ten negatively charged proteins and/nucleic acids. It is VERY important that the neuron is large and the ions are small. Use the models to demonstrate how a resting potential is created and maintained. Each student will then act out how an action potential is transmitted within the neuron using their model. Keep the models for later use in explaining synaptic transmission. ☐ Activity: Homeostatic Disorders: Part Two www.dbausch.com / RLDHS / Course Outlines / SBI4U / Homeostasis / Activities ☐ Lab: Mink Dissection Student must correctly identify SEVEN organs involved in homeostasis and explain what their functions are (eg. Brain, kidneys, pancreas, testicles, ovaries, adrenal glands, thyroid ) ☐ Activity: Students will use their knowledge of reproductive hormones to design a birth control pill for females. They will be given a set amount of time in class to create their pill and will present their medication to the class, explaining how the pill works on a hormonal level. The class will vote for the best medication that is created. COULD DO Resources provided by Mr. Bausch o Note: Homeostatic Acid/Base Buffer o o o Video - Mammalian Diving Response http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JkhGeHLzHJ8 o Note - Homeostasis www.dbausch.com / RLDHS / Course Outlines / SBI4U / Homeostasis / Notes o Note - Circadian Rhythms www.dbausch.com / RLDHS / Course Outlines / SBI4U / Homeostasis / Notes o Video - Circadian Genes http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=17L5S7Kk7Cc o Video - Human Suprachiasmatic Nucleus http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1jd-Dl2OjRE o Note: Kidneys www.dbausch.com / RLDHS / Course Outlines / SBI4U / Homeostasis / Notes o Video - Adrenal glands http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=06jbq3bxKE0 o Note: Kidneys and Water Regulation www.dbausch.com / RLDHS / Course Outlines / SBI4U / Homeostasis / Notes o Note: Kidneys and pH regulation www.dbausch.com / RLDHS / Course Outlines / SBI4U / Homeostasis / Notes o Note: Endocrine System www.dbausch.com / RLDHS / Course Outlines / SBI4U / Homeostasis / Notes o Video- Endocrine System: Pituitary Gland http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Vae5CcaPN_8 Video - The Pancreas and Insulin (End viewing at 3:00) http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qzjjW--I-2Q o Video - Action of Epinephrine on Liver Cells http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/olc/dl/120109/bio48.swf o Video - Mechanism of Thyroxine Action http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/olc/dl/120109/bio47.swf o Note: Nervous System www.dbausch.com / RLDHS / Course Outlines / SBI4U / Homeostasis / Notes o Video - Reflex arc http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Y5nj3ZfeYDQ o Video - Resting Potential Tutorial http://bcs.whfreeman.com/thelifewire/content/chp44/4402001.html o Video - Voltage Gated Channels and Action Potentials http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/olc/dl/120107/anim0013.swf o Video - Action Potential K+ and Na+ Channels http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/olc/dl/120107/bio_d.swf o o o Video - Chemical Synapse http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/olc/dl/120107/anim0015.swf o Video - Action Potential and Neuromuscular Junction http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/olc/dl/120107/bio_c.swf o o Video - Sodium Potassium Pump http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/olc/dl/120107/bio_c.swf o Video - How normal brain cells communicate http://www.thirteen.org/closetohome/animation/neuron-main.html o Video - Effect of Cocaine on brain communication http://www.thirteen.org/closetohome/animation/coca-anim-main.html o Video - Effects of Alcohol on brain communication http://www.thirteen.org/closetohome/animation/gaba-anim-main.html o Video - Effects of a Stroke http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=b2GHf6TS490 o Note: Male Reproductive Hormones www.dbausch.com / RLDHS / Course Outlines / SBI4U / Homeostasis / Notes o Video: Spermatogenesis http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/olc/dl/120112/anim0043.swf o Note: Female Reproductive Hormones www.dbausch.com / RLDHS / Course Outlines / SBI4U / Homeostasis / Notes o Video: Female Menstrual Cycle Hormones http://msnbcmedia.msn.com/i/msnbc/Components/Interactives/Health/WomensHealth/zFlashA ssets/menstrual_cycle_dw2%5B1%5D.swf o Video: The Ovaries and Testes (Begin viewing at 3:00) http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FEsTIOIufiQ