File

The American Revolution
Patriots
• American colonists who were determined to fight the British until American independence was won
Loyalists (Tories)
• Colonists who chose to side with the British
• Did not think unfair taxes were a good reason for rebellion
• Strongest loyalist support was in the Carolinas and Georgia
• Weakest loyalist support was in New England
• Many fled the colonies for England
Neutral
• Taking no side in a conflict
British Advantages
• Most powerful Navy in the world
• Huge population advantage
• More experienced military
• Plenty of financial support
American Advantages
• Fighting on land they knew very well
• Were eager to defend their land
• British had to ship soldiers and supplies thousands of miles across the Atlantic Ocean
• British depended heavily on mercenaries
• Hired soldiers
Mercenaries
Hessians
• What the Americans called the British mercenaries.
• Name comes from the region in Germany most of them were from
• Main goal for winning the war was money
• Enlist
Recruit
Margaret Corbin
• Followed husband when he joined the
Continental Army.
• Took his place on the battlefield when he was killed
Mary Ludwig Hays McCauley
“Molly Pitcher”
• Followed husband when he joined the
Continental Army
• Became known as “Molly Pitcher” for carrying water pitchers around the battlefield for soldiers
Deborah Sampson
• Disguised herself as a man and joined the army to fight
Thomas Paine
• Wrote Common Sense prior to the war
– The issue was freedom not taxes
• Wrote The American Crisis early in the war
– “These are the times that try men’s souls”
– “The harder the conflict, the more glorious the triumph”
Nathan Hale
• Teacher from Connecticut
• Hero at the battle of Long Island despite the
American defeat
• Spied on the British as a Dutch schoolteacher
• Discovered by British and hung
• Last words were “I only regret that I have one life to lose for my country”
African Americans in the War
• Many fought with the British after being offered freedom to fight against the Patriots
• General George Washington asked to have free
African Americans enlisted
• Southern states feared a revolt from armed
African Americans because of their large slave population
• Rhode Island was the first state to have an all
African American regiment
• Every state eventually state enlisted African
Americans except South Carolina
Christmas Night 1776
• British soldiers were taking a break from fighting because of the harsh winter.
• Washington led his men across an icy
Delaware River and attacked a group of
Hessian soldiers.
• Americans used momentum from this victory to defeat the British again at Princeton
Benedict Arnold
• Led the Americans to victory in Albany
Saratoga
• Americans, led by General Horatio Gates, defeated the British, led by General John
Burgoyne, forcing them to surrender
• Showed European powers that the Americans might win and led to support from other nations who hated Britain
France
• Originally only gave money secretly to the
Americans.
• After the Battle of Saratoga they officially supported the Americans.
• Began to send money as well as equipment to assist the Americans.
Spain
• Did not officially recognize America as a nation until after the Revolutionary War.
• Sent troops to fight the British
• Forced the British to pay attention to two enemies.
• Defeated the British in the Mississippi Valley and along the Gulf of Mexico
Netherlands
• Declared war with Britain
• Loaned money to the Americans
Valley Forge
• Winter camp for George Washington and the
Continental Army in the winter of 1778
• Army suffered because of a lack of food, clothing, blankets, shelter and shoes
• Washington’s wife Martha helped by making clothes for the troops and caring for the sick
• Greatest challenge was keeping the army together
• Many men deserted the army
Deserted
• To leave without permission
Marquis de Lafayette
• French nobleman who joined the Continental
Army after reading the Declaration of
Independence
• Spent the winter at Valley Forge with the
Continental Army
• Became a trusted advisor to General
Washington
Friedrich von Steuben
• Former German officer who helped turn the
Continental Army into an effective fighting unit.
• Drilled the Continental Army in proper military technique during the winter at Valley Forge
Causes of French-American Alliance
• Longstanding hostility between Britain and
France
• Conflict between Britain and France during the French and Indian War
• Victory at Saratoga boosts French confidence in Patriots
Effects of French-American Alliance
• France signed a treaty of alliance with the
United States in 1778
• France lends money to the Continental
Congress
• France sends soldiers and ships to help
American forces
• Americans win indepedence
Inflation
• A continuous rise in the price of goods and services
• Caused Congress to stop issuing paper money
Francis Marion
• The British called him the Swamp Fox
• Led a small group of expert fighters from
South Carolina
• They lived off the land and continually surprised attack the British
• Him and his men hid in the swamps between attacks
Guerrilla Warfare
• Hit and run technique of fighting
Native Americans
• Mostly fought against the Americans
• Felt the British were less of a threat to their land
Blockade
• to cut off an area by means of troops or warships to stop supplies or people from coming in or going out
• British blockade prevented supplies and reinforcements from reaching the Continental
Army
Privateers
• Privately owned warships
• Captured several British ships to assist the weak American Navy
John Paul Jones
• Successful American privateer commander
• Famously said “I have not yet begun to fight.”
• Captured the British ship Serapis despite his ship the Bonhomme Richard’s severe damage
• The Bonhomme Richard sank shortly after the battle
Charleston, South Carolina
• Location of the worst defeat for Americans during the American Revolution
• British captured thousands of prisoners
General Charles Cornwallis
• Commanded the British forces in the south
• Won the Battle of Camden
• Surrendered at the Battle of Yorktown after being defeated by American and French forces
General Horatio Gates
• Commanded American forces in the south
• Lost the battle of Camden due to several bad decisions
Guerilla Warfare
• a hit and run technique used in fighting a war, using small bands of warriors using tactics such as sudden ambushes
Comte De Rochambeau
• Led a unit of French soldiers, who were originally trapped by the British in Newport,
Rhode Island, to Yorktown to assist General
Washington and his men.
Francois Joseph De Grasse
• French admiral who prevented the British from escaping at the battle of Yorktown
Battle of Yorktown
• Battle that finally showed the British that the war was to costly.
Treaty of Paris
• Officially ended the American Revolutionary
War on September 3, 1783
• American representatives at the meetings were Benjamin Franklin, John Adams, and
John Jay
• Britain promised to withdraw all troops from
American territory
• Great Britain officially recognized the United
States as a nation
Pension
• A fixed amount of money paid at regular intervals for past services.
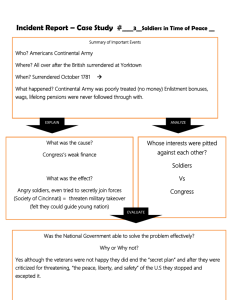
Newburgh Conspiracy
• Potential revolt by the soldiers of the
Continental Army over Congress’ original refusal to pay their pension.
George Washington
• Resigned his command of the Continental
Army on December 4, 1783
• Returned to his home in Mount Vernon in time for Christmas