Week of Sept. 30th
advertisement

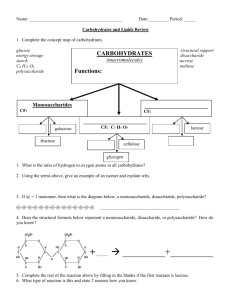
Week of Sept. th 30 - Oct. th 4 Mrs. Tate D110 Biology/Pre-AP International Scholars Academy Monday 9-30-13 Objective: demonstrate an understanding of the properties of water. Agenda: 1. Pre-Lab ( objective, background information) 2. Lab ( I will grade journals as you work at each station) Write up lab report on page 23R-24L. Paste/Tape web quest on page 24R 1. Closure/Clean up Homework : cut out carbohydrate figures ( due tomorrow) Properties of Water Lab: What Makes Water Special? Objective: demonstrate an understanding of the properties of water. Background: Water has some peculiar properties, but because it is the most common liquid on Earth, we typically do not recognize how truly peculiar water really is. Water is everywhere. It's in the air we breathe. It's in our sink faucets, and it's in every cell of our body. Water is an unusual substance with special properties. Just think about the wonder of water: How does water rise from the roots of a redwood tree to the very top? How do insects walk on water? Why does ice float rather than sink? Why do people become seriously ill, or die, if they go without liquid for a week or so? How would life in a lake be affected if ice sank and lakes froze from the bottom up? When it is your turn to run your station: read aloud the information and instructions to your group. Perform any necessary activity & clean-up…get help from lab table-mates when you need it. Then, lead the discussion of what happened. Run one test at a time with everyone in your group paying attention. What to write down: the number of the station, the title of the station, the data from the station (i.e. what you observe (qualitative data), any quantitative data, & answer any question(s) for that section. Clean-up – it is imperative that you clean up each station so that the next class will be ready to go! Tuesday, Oct. 1st Objective: demonstrate an understanding of the properties of water; Compare the structures and functions of different types of biomolecules, including carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. Agenda: 1. Carbohydrate Notes ( checking today in class) – 25L 2. Finish Properties of Water Lab ( you need TWO stations plus your web-quest finished 3. Clean Up Homework: Study notes for carbohydrate lab tomorrow and you never know when a QUIZ may POP….Also, finish properties of water web-quest. If you DO not have a safety contract on file you will NOT participate in lab. New Grading Scale: 50 ( daily), 10 ( homework), 40( tests/projects) Carbohydrates (polymers) a. provide energy for living cells b. . contains carbon, hydrogen and oxygen in a 1: 2:1 ratio c. Monosaccharides - single sugars that serve as a major fuel for cells and as raw material for building molecules. glucose (C6H12O6) most common=sugar fructose=fruits galactose=milk D. disaccharides- linking two monosaccharide's together E. polysaccharide - many sugars formed by joining monosaccharide -Excess sugars can be stored as starch 1. Glycogen can release glucose from the liver when glucose levels become low. 2. Starch (spaghetti) 3. Plants store excess sugars as plant starch in the chloroplast. 4. Cellulose gives plants their strength and flexibility (wood and paper) 5. Chitin is another structural polysaccharide, is found in the exoskeleton of arthropods Chitin also provides structural support for the cell walls of many fungi monomer polymer polymer ? ? ? ? ? ? Fig. 5-6 Chloroplast Mitochondria Glycogen granules Starch 0.5 µm 1 µm Glycogen Amylose Amylopectin (a) Starch: a plant polysaccharide (b) Glycogen: an animal polysaccharide Fig. 5-10 (a) The structure of the chitin monomer. (b) Chitin forms the exoskeleton of arthropods. (c) Chitin is used to make a strong and flexible surgical thread. CARBOHYDRATES Check your Understanding -Milk contains carbohydrates lactose and galactose. -Fruits contain carbohydrates fructose -Potatoes contain carbohydrates starch 1. What is the source of energy for these carbohydrates? They get energy from sunlight 2. What function do these carbohydrates serve in living things? They provide living organisms with energy STUDY SKILLS LESSON 1 The FRAYER MODEL - artist's delight! • This graphic organizer helps students to learn new vocabulary by not only defining the term in their own words, but contextualizing it through authentic examples and visual representation. ESSENTIAL ACADEMIC VOCABULARY – ALGEBRA or GEOMETRY • • • • • • ALGEBRA STUDENTS Algebraic expression Equation Evaluating an algebraic expression Simplifying an algebraic expression Solving an equation • • • • • • GEOMETRY STUDENTS Congruent transformation Parallel lines Perpendicular lines Non-congruent transformation Slope Wednesday , 10-2-13 Objective: Compare the structures and functions of different types of biomolecules, including carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. Agenda 1. Lab Groups ( 3 min) 2. McMush Lab: Testing for Carbohydrates **complete parts 1 and 2, then 1 and 2 of part 5 only.*** Happy meal includes ( a burger, fries, sprite, and apples) 3. Clean Up Lab Area (5 min) 4. Reflective Questions for Lab ( 25R):- Door Ticket Reflective Questions for Lab ( 25R) Door Ticket Copy the question down then answer in complete sentences. Use the heading Carbohydrate Testing. 1. Which substances are used to test for the presence of monosaccharides and starches? 2. What color indicates the presence of sugar? of starch? Thursday 10-3-13 Objective: Compare the structures and functions of different types of biomolecules, including carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. 1. Lipid’s Pre-Reading ( web based)-26R 2. Lipid Notes (backside)-26R 3. Closure: LIPIDS Check your Understanding Homework: Study daily ( quiz Monday, test, 1015) 2. Lipids contains carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in different ratios than carbohydrates. -The components lipids consist of are a glycerol and fatty acid Glycerol Fatty Acid Chain used for stored energy, insulation, protective coatings, cell membranes and as hormones all are insoluble in water (hydrophobic) steroids are also lipids mainly seen as fats, oils, and waxes. • Can be saturated where all the carbons have a hydrogen attached at every possible spot. No double bonds (usually solid at room temp) • Can be unsaturated carbons are double bonded resulting in a kink in the carbon chain (usually liquid a room temperature) • Polyunsaturated when fatty acids have more than one double bond (peanut oil) Fig. 5-12 Structural formula of a saturated fat molecule Stearic acid, a saturated fatty acid (a) Saturated fat Structural formula of an unsaturated fat molecule Oleic acid, an unsaturated fatty acid (b) Unsaturated fat cis double bond causes bending Lipids in 5 minutes http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JCisFqRtXS4 LIPIDS Check your Understanding 1. 2. What are the elements of a lipid? Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen in diiferent ratios than carbohydrates Would you describe the picture shown to be a saturated or an unsaturated fat? Unsaturated usually liquid at room temperature 3. 4. Is saturated or unsaturated more healthy? Which of these substance stores the most energy? Unsaturated A. One gram of fat B. One gram of alcohol C. One gram of carobohydrate D. One gram of nucliec acid Friday, 10-4-13 Objective: Compare the structures and functions of different types of biomolecules, including carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. 1. Lab Groups (3 min) 2. Mc-Mush Lab: Testing for Lipids and Proteins Happy meal includes ( a burger, fries, sprite, and apples) 3. Clean Up Lab Area 4. Reflective Questions for Lab ( 25R):- Door Ticket Homework: Study for Lipids/Carbohydrate quiz Monday. Lab reports due Tuesday. Reflective Questions for Lab ( 25R) Door Ticket Copy the question down then answer in complete sentences. Use the heading Carbohydrate Testing. 1. Which substances are used to test for the presence of lipids and proteins? 2. What color indicates the presence of a lipid? Or a protein?