Judaism
advertisement

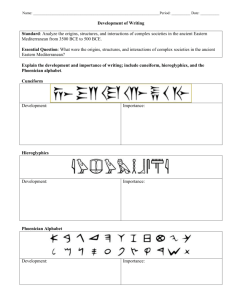
Bellringer: 10/5 and 10/6 Pick up the paper on the desk by the door. Take out a piece of notebook paper. Write a 3-4 sentence reflection on the Unit 1 and 2 Test you took last class. Consider what you think went well on the test, what you think you could have done better, and any concerns you have about the test. Agenda: 10/5 and 10/6 1. Bellringer 2. Timeline: Civilizations in the Mediterranean/Middle East 3. Notes/Lecture: Peoples of the Mediterranean and the Middle East 4. Activity: Mapping Video Worksheet: Hanging Gardens of Nebuchadnezzar 300 BCE 330 BCE 550 BCE 585 BCE 600 BCE 690 BCE 1100 BCE 1200 BCE 1550BCE 1600 BCE 1800 BCE 2000 BCE 2300 -2100 BCE People of the Mediterranean and The Middle East Ms. Allen World History I – 2015-16 People of the Mediterranean: Phoenicians Ms. Allen World History I – 2015-16 Background on Phoenicians Began in modern-day Lebanon City-states develop by 1200 BCE Famous for…. Commerce Dyes Spreading alphabet Colonies Phoenician Geography Phoenicia was located between the eastern Mediterranean coast and the Lebanon Mountains Phoenicians Territory Politics/Government in Phoenicia Not a unified nation Consisted of independent city-states Phoenician Economy/Commerce •Trade = dominates Phoenician economy •Where is commerce centered? •Major city states (Byblos, Sidon, Tyre) •How far did they trade? •All across the Mediterranean coast Phoenician Economy/Commerce Phoenician Commerce Known as the “purple merchants” Exports? Royal purple dye from murex sea snail Found only in the waters of eastern Mediterranean Eventually exploited to extinction Wood (cedar) Slaves Glass Wine/olive oil Imports? Silver from Iberia Ivory, gold Even tin from Britain Phoenician Advancements Purple dye Ship design/building Galleys made of cedar wood Sails & oars Phoenician alphabet Leads us towards more modern-day languages/alphabets Beginning of the Semitic language family Semitic Language Family Phoenician Alphabet Comparison of Alphabets Phoenician Colonies Sailed and colonized throughout the Mediterranean beginning circa 1000 B.C.E. EXAMPLES: Gades (modern-day Spain) Carthage = most important Phoenician colony. Located in northern Africa Phoenician Colonies Phoenician Colony of Carthage Founded in 814 BC Location? Modern-day Tunisia First colonization Eventually becomes a great empire Fights rivals for power, territory Greeks in 400s-300s BCE Romans in 200s-100s BCE Summarizing the Phoenicians: What did they become? They became expert traders. 2. Trade routes to the east were blocked by mountains and hostile neighbors. 3. They used the Mediterranean Sea and became expert sailors 4. They had an abundance of cedar, purple dye, silverwork, ivory carvings and slaves 1. People of the Middle East: Hittites, Assyrians, and Chaldeans Ms. Allen World History I – 2015-16 1. THE Hittites Geography of the Hittites Little known about them until archaeological discoveries of early 20th century Migrated to Asia Minor (modern Turkey) from northern Europe circa 3000 B.C.E. Evolution of the Hittites: First Hittite Empire Begins in 1900 B.C.E. Empire stretched from Aegean Sea to Euphrates River Second Hittite Empire Dates: 1500-1200 B.C.E. Included Asia Minor, Palestine, and Syria Decline and fall Continuous warfare with Egypt 1200 B.C.E. – conquered by northern barbarians Eventually absorbed by Assyria Hittite Economy: Link between Mesopotamia and western Asia Had monopoly on Armenian and European metals for hundreds of years Developed iron for tools and weapons Wealth from trade of gold, iron, lead, and silver Trade shown in numerous excavated clay tablets (tracked trade, transactions) Hittite Politics/Government Ruled by a king Heavily fortified city walls Written laws show Babylonian influence Hittite Advancements: Fortified city walls Art Crude carvings Stone lions at city entrances Carvings of animals and warriors Assyrians – An aggressive mountain people who had waged war for years against the Babylonians 2. THE Assyrians Who are the Assyrians? •An aggressive mountain people who had waged war for years against the Babylonians Achievements of Assyrians Used iron Expanded empire through war Conquered Egypt & the Fertile Crescent. Used military innovations Battering ram, siege towers Cavalry/chariots/infantry Conscription (drafting soldiers) Achievements of Assyrians Built roads for troop movement Messenger service to report rebellions. Conquered people were tortured and enslaved Tunneled under walls to attack other civilizations Divided empire into provinces (states ruled by a governor, protected by the military) 3. THE Chaldeans Geography - In modernday Iraq - Built on the territory of what river valley civilization? Parts of Babylon have been rebuilt by Saddam Hussein Rebuilt by Saddam Hussein Mosul on the Tigris River Important Leader: Nebuchadnezzar He rebuilt Babylon Had the Hanging Gardens constructed One of the 7 Wonders of the World Conquers city of Jerusalem Deports Hebrews to Babylon to keep them from rebelling Nebuchadnezzar 630-562BC Hanging Gardens of Babylon Religion: The Star Gazers of Babylon Priests observed and kept records of the heavens Located in ziggurats Believed stars determined human destiny Could be used to foretell the future They observed the Zodiac Zodiac = belt of 12 constellations and the phases of the moon Priests studied the stars. Their study formed the basis for both astronomy & astrology. First Historical Horoscope Chaldean Numerology Believed to be the oldest of the systems of numerology Converts letters to numbers using numbers 1 to 8. Ones = a beginning or genesis Higher numbers = progress through life, Eights = completion. HOMEWORK Read pages 67-76 in your textbook and take notes. Bring a flash drive to class tomorrow if possible. 10/9 (THIS FRIDAY): Quiz on the Peoples of the Mediterranean and Middle East