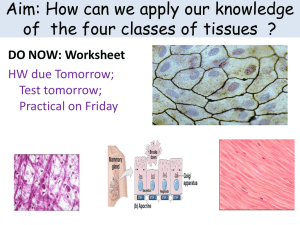
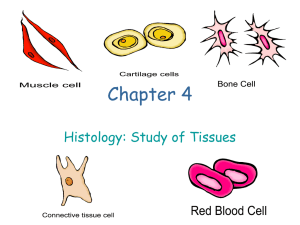
Quiz: Body Tissues
advertisement

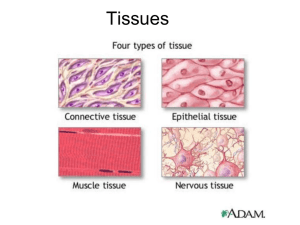
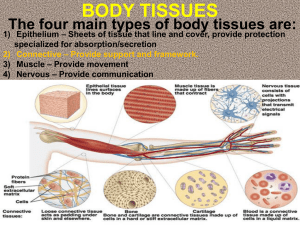
Homework Part 3 1. Which structures in the skin does sweat come from? 2. Which structures in the skin does hair growth come from? 3. Why does the body get goose bumbs? 4. What is the feedback mechanism for the body getting to hot? 5. What type of feedback mechanism is being used when the body is too hot? 6. How many layers of skin must be cut through till one starts to bleed? 7. What does sub-cutaneous mean ? 8. Why is melanin important for the skin? 9. What happens if you do not have any melanin in the skin? 10. What happens to the skin if gets to dry ? Quiz: Body Tissues 1. Which of the following is NOT one of the four main types of tissues? basement epithelial connective muscle 2. Which type of tissue is designed to stretch? stratified squamous transitional epthelial 3. Tissues are groups of similar cells working together to: increase the size and mass of structures in the body perform common functions fight against diseases deliver messages 4. This type of tissue is composed of scattered cells that form a matrix: macrophages cuboidal nervous connective 5. Adipose tissue is also known as: fat cartilage areolar tissue brain matter 6. Smooth muscle is found mainly in: the heart the stomach the brain the skeletal system 7. Chondrocytes are cells found in: the small intestine the heart the brain cartilage 8. What structure connects bones to other bones? tendons hyaline cartilage ligaments fibroblasts 9. Psuedostratified tissue has a distinctive appearance because: the nuclei of individual cells do not line up perfectly cilia is attached to the surface of the cells cells are square and formed in perfect blocks cells are square in the bottom layer and flat at the top 10. Elastic fibers are found where in the body? joints vocal cords ear and nose heart Name: __________________________________ Date: _________ Types of Tissues MAJOR TISSUE TYPE OF TISSUE LOCATION Outer layer of skin, mouth Secretion, absorption, ducts of glands Digestive tract (intestinal wall), absorption EPITHELIAL Air passages (trachea), goblet cells Lining of air sacs in the lungs Stretchable tissue, urinary bladder Binds skin to internal organs Found between vertebrae Dense, tendons & ligaments Covers ends of bones at joints CONNECTIVE TISSUE Osseus, structural tissue of the skeleton Circulates, delivers oxygen Insulation, protection, also called fat Muscles connected to bones MUSCLE TISSUE Walls of many internal organs Walls of the heart NERVE TISSUE Transmits signals, nerve impulses Support cells