7. NUCLEIC ACIDS 7.1 DNA structure and replication 7.2
advertisement
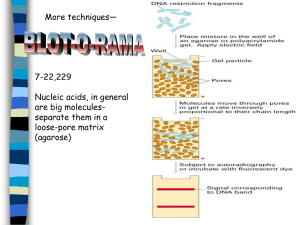
7.2 Transcription and gene expression Information stored as a code in DNA is copied onto mRNA. Diana Carvajal September 2014 HOMEWORK for next class: Define the following terms…. Gene expression is regulated by proteins that bind to specific base sequences in DNA - Prokaryotic cells: ex. lactose vs. repressor protein. - Eukaryotic cells: enhancers, silencers and promoter-proximal elements (proteins). Each cell of a multicellular eukaryotic organisms expresses only a fraction of its genes. Gene regulation is critical in the process of development. Promoter: example of non-coding DNA with a function. The environment of a cell and of an organism has an impact on gene expression Production of skin pigmentation in humans: Exposure to sunlight affects it. Gene “C” codifies for a precursor of the pigment. A mutant, cs produces normal pigmentation only in temperatures below body temperature. At higher temperatures, less pigment is produced. Nucleosomes help to regulate transcription in eukaryotes http://cerch.org/wp-content/uploads/2011/02/DNA-methylation-image.jpg Analysis of changes in the DNA methylation patterns. Expression of genes is regulated by: • 1. Proteins that bind to DNA (enhancers, silencer, promoter-proximal elements) and some non-coding regions (promoters). • 2. Environmental signals • 3. Nucleosomes, together with methylation. Looking for patterns, trends and discrepancies—there is mounting evidence that the environment can trigger heritable changes in epigenetic factors ANIMATION: http://www.wiley.com/college/test/0471787 159/biology_basics/animations/fromGeneTo Protein.swf Transcription occurs in a 5’ to 3’ direction. Eukaryotic cells modify mRNA after transcription. Different ways: 1. RNA splicing (noncoding regions will be taken out, called introns-intervening sequences), only exons codify for a protein. 2. Addition of poly-A tail (works as a message saying it is mature mRNA). mRNA splicing Splicing of mRNA increases the number of different proteins an organism can produce Alternative splicing: process in gene expression where a sigle gene codifies for multiple proteins (different structure and even different biological function). TOK • The nature versus nurture debate concerning the relative importance of an individual’s innate qualities versus those acquired through experiences is still under discussion. Is it important for science to attempt to answer this question?