Rhetorical Triangle.
advertisement

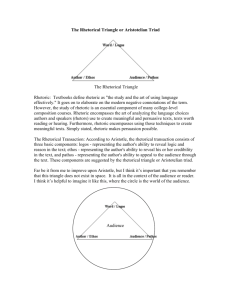
Journal When do you feel that it might be okay to break the law? OR why might you feel that it is never okay to break the law? Self-reliance Review What does “envy is ignorance; imitation suicide” mean? How do the ideas the Declaration of Independence or the constitution relate to some of Emerson’s concepts? What does Emerson think of people who call for consistent in thought and action and who fear being misunderstood? Agree/disagree with Emerson? Rhetoric Review?? This is the Rhetorical Triangle Match the 3 rhetorical appeals to the following terms: Ethos Speaker/Communicator Message Audience Pathos Logos RHETORIC Aristotle was the first to define rhetoric and he came up with the 3 rhetorical appeals: Ethos, Pathos, Logos and how they interact together (the rhetorical triangle) Aristotle defined rhetoric as “the art of using language as a means to persuade” The Merriam Webster Dictionary defines rhetoric as “the art of writing or speaking effectively” Rhetoric has been used since ancient Greece and is considered an ancient art. Rhetoric We are going to use rhetoric to analyze the language choices authors and speakers use to create meaningful and persuasive texts. We will use rhetorical techniques in our own nonfiction writing to create more meaningful texts. Ethos – establishing credibility Pathos -- emotional appeals Logos -- logical appeals These areas form the “Rhetorical Triangle.” The Rhetorical Triangle: What are the arrows for? Logos Pathos Ethos: the speaker Why should we listen to this person’s argument? The author or communicator has to establish a persona (a personality that we trust) and give us a credible reason to want to believe him The author/communicator also needs to establish him/herself as an authority on the subject of their message and someone who is worthy of respect. Pathos: appeal to the audience Persuading by appealing to the reader’s or the AUDIENCE’S emotions. Trying to tap into your audience’s values and beliefs will help your argument. So you must know your audience BEFORE you deliver your message. Your audience will be persuaded when they feel any sort of emotion towards your topic. This is done through anecdotal writing or narratives and “loaded words” words that have emotional meaning This is also done through description and figurative language Logos: the message the logic used to support a claim in the text or MESSAGE Logic is accomplished through the use of facts, data, statistics, details and examples to back up your claims. Also used by citing authority and testimony, establishing causes and effects and using inductive and deductive reasoning Reading for Rhetoric Whenever we read a non-fiction text we should be reading rhetorically, or looking for the hidden persuasion behind the words. The Reader’s Rhetorical Triangle Logos Note the claims the author makes Note the data the author provides to support the claims Note the conclusions draw Ethos Note how the author establishes a persona Note how the author establishes credibility Note any revelation of the author’s credential s or personal history Pathos Note the primary audience for the text Note the emotional appeals the author makes Note the author’s expectations of the audience Pop Quiz Put away your notes, and take out a piece of paper. Draw a triangle on your paper Label the triangle using what you have just learned about the rhetorical triangle. You need to include: ethos, pathos, logos, message, communicator/speaker and audience and write any other words you can around the triangle to represent/describe the different parts Pop Quiz Trade papers with your partner and explain, using your own words, how you have labeled your triangle. Turn this paper into the box Resistance to Civil Government Background In July 1846 Thoreau spent a night in jail because he refused to pay his poll tax (state’s required this tax as a qualification of voting) He refused because he was opposed to the government’s support of slavery and the Mexican American War This poll tax was going to the government, which in turn would probably fund the Mexican American War Many thought the US was involved in the Mexican War only to expand their slave holding territory He only spent one night in jail, his Aunt paid the tax for him and he was set free Ghandi and MLK were inspired by his essay Reading Thoreau’s Civil Disobedience Read as a class While reading, annotate the text: Specifically underline or highlight portions of the article that you think are pertaining to Ethos, Pathos or Logos. You may want to label them as “E”, “P” or “L” or use different colored highlighters. Examples of Rhetoric On a separate sheet of paper: write down Thoreau’s BEST example of each rhetorical appeal: ethos, pathos, logos Explain WHY this is a good example