Trigonometric Functions of Angles

Warm-Up 3/24-25
What are three basic trigonometric functions and the their ratios?
Sine: sin
= 𝑜𝑝𝑝 ℎ𝑦𝑝
Cosine: cos
= 𝑎𝑑𝑗 ℎ𝑦𝑝
Tangent: tan
= 𝑜𝑝𝑝 𝑎𝑑𝑗
Rigor:
You will learn how to solve right triangles, and find the three basic trigonometric ratios.
Relevance:
You will be able to solve real world problems using trigonometric ratios.
Trig 1:
Right Triangle
Trigonometry
Special Right Triangles
45ᵒ- 45ᵒ- 90ᵒ: both legs are congruent and the length of the hypotenuse is 2 times the length of a leg.
𝑠 = 𝑙𝑒𝑔 𝑙𝑒𝑛𝑔𝑡ℎ ℎ = ℎ𝑦𝑝𝑜𝑡𝑒𝑛𝑢𝑠𝑒 = 𝑠 2
30ᵒ- 60ᵒ- 90ᵒ: The length of the hypotenuse is 2 times the shorter leg and the other leg is 3 times the shorter leg.
𝑠 = 𝑠ℎ𝑜𝑟𝑡 𝑙𝑒𝑔 ℎ = ℎ𝑦𝑝𝑜𝑡𝑒𝑛𝑢𝑠𝑒 = 2𝑠 𝑙 = 𝑙𝑜𝑛𝑔 𝑙𝑒𝑔 = 𝑠 3
Example 1: Solve the triangles.
a.
60ᵒ x s
30ᵒ
16 3
16 3 = 𝑠 3
16 = 𝑠 𝑥 = 2𝑠 𝑥 = 2(16) 𝑥 = 32 b.
x
45ᵒ x
2
2
∙
12 = 𝑥 2
12
2
= 𝑥
12 2
= 𝑥
2
6 2 = 𝑥
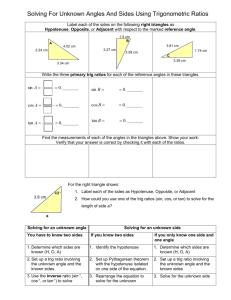
Trigonometric Ratios: ratios of sides of a right triangle.
opposite hypotenuse adj adjacent opp hyp
3 Basic Trigonometric Ratios :
3 basic: sin
opp hyp cos
adj hyp tan
opp adj
Since any two right triangles with angle 𝜃 are similar, side ratios are the same, regardless of the size of the triangle.
3
4
5
30
40
50
Example 2: Find the exact values of the 3 basic
Trigonometric functions of 𝜃.
7 hyp
θ adj 3
2 10 opp s𝑖𝑛 𝜃 = 𝑜𝑝𝑝 ℎ𝑦𝑝
=
2 10
7 𝑎𝑑𝑗 cos 𝜃 = ℎ𝑦𝑝
=
3
7 ta𝑛 𝜃 = 𝑜𝑝𝑝 𝑎𝑑𝑗
=
2 10
3
Example 3: If 𝑠𝑖𝑛 𝜃 =
1
3
, find the exact values of the
2 remaining basic trigonometric functions. s𝑖𝑛 𝜃 =
1
3
= 𝑜𝑝𝑝 ℎ𝑦𝑝
1 2 + 𝑏 2 = 3 2
1 + 𝑏
2
= 9 𝑎𝑑𝑗 cos 𝜃 = ℎ𝑦𝑝
=
2 2
3
3 𝑏 2 = 8 𝑏 = 8
1 ta𝑛 𝜃 = 𝑜𝑝𝑝 𝑎𝑑𝑗
=
1
2 2
=
4
2
2 2
Example 4: Find the value of 𝑥 . Round to the nearest tenth, if necessary.
𝑎𝑑𝑗 cos 𝜃 = ℎ𝑦𝑝
35 °
7 hyp x cos 35° = 𝑥
7
7 ∙ cos 35° = 𝑥
7
∙ 7 adj
7 ∙ cos 35° = 𝑥
Make sure your calculator is in degrees.
𝑥 = 5.73406431
𝑥 ≈ 5.7
Example 5: Use a trigonometric function to find the measure of 𝜃 . Round to the nearest degree. s𝑖𝑛 𝜃 = 𝑜𝑝𝑝 ℎ𝑦𝑝 hyp
15.7
12 opp
12 s𝑖𝑛 𝜃 =
15.7
𝜃 𝜃 = 𝑠𝑖𝑛 −1
12
15.7
𝜃 = 49.84753016° 𝜃 ≈ 50°
Checkpoints:
1. Fill out chart with exact values.
1
2
3
2
3
3
2
2
1
2
2
2
1
2
3
3
2. Find the value of 𝑥 .
sin 53° =
15 𝑥
15 𝑥 = sin 53° 𝑥 = 18.7820
3. Find the measure of 𝜃 .
5 cos 𝜃 =
12 𝜃 = cos
−1
5
12 𝜃 = 65°
Assignment:
Special Right Triangles & Trig
Worksheet, 1-22 all
7 th Warm-Up 3/25
1. Find the value of 𝑥 .
9 tan 21° = 𝑥
9 𝑥 = tan 21° 𝑥 = 23.4458
Assignment:
Special Right Triangles & Trig
Worksheet, 1-22 all