The Metric System
advertisement

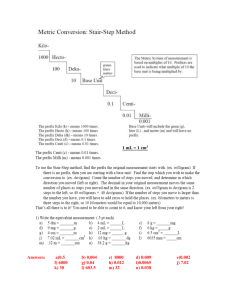
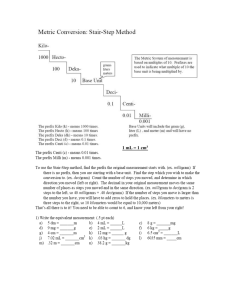
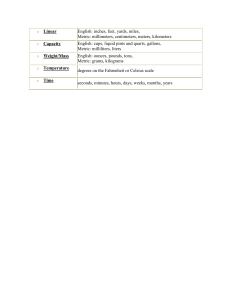
Topic: The Metric System Do Now: Calculate the volume of Fe. What element is Fe? mass of Fe(s) = 15.9 g density of Fe(s) = 7.87 g/cm3 Measurement up to 1790: Not a pretty picture! Measurement requires standard and until 1790’s every region had own standard Systeme International (SI) • French Academy of Sciences created the metric system in 1790* – Originally, earth-based standards – Volume & mass linked to length – Larger & smaller multiples of each unit related by powers of 10 = metric system *updated every few years (particularly in in 1960 and 1991) Standards • “standard: something used as comparison for measuring” – standard must: • be available for everyone to use to check measurements • be something in nature that is same everywhere • never vary What is a second? defined in terms of electron transitions in Cs-133 (Caesium – an element) What is a meter? distance light travels in vacuum in 1/299,792,458 th of second What is a Liter? • defined as cube measuring 10 centimeters on each side (1000 cm3) 10 cm • Liter based on meter, which is based on Earth 10 cm What is a kilogram? defined as mass 1 Liter water at 4°C Why water? 10 cm kilogram is based on liter, which is based on meter, which is based on Earth 10 cm For Water only: Prototype kilogram stored in vault in France Smaller Units • 1/10 of a meter = decimeter (dm) • 1/100 of a meter = centimeter (cm) • 1/1000 of a meter = millimeter (mm) Larger Units • 10 meters = dekameter (dam) • 100 meters = hectometer (hm) • 1000 meters = kilometer (km) Don’t copy…. where can you find? Prefixes in the SI System Prefix Symbol Value Power Use Giga G 1,000,000,000 109 Gigabyte Mega M 1,000,000 106 Megamillion Kilo k 1,000 103 kilometer deci d 0.1 10-1 decimeter centi c 0.01 10-2 centimeter milli m 0.001 10-3 millimeter micro 0.000001 10-6 micrometer nano n 0.000000001 10-9 nanometer Fundamental or Base Units • Based on object or event in nature • The SI system has 7 fundamental units *label on Ref table 7 Fundamental Quantities of SI Quantity Length Name Abbreviation meter m kilogram second kg s Temperature kelvin K Amount of Substance Mole mol Luminous Intensity candela cd Electric Current ampere A Mass Time Derived Units • Combinations of fundamental units • Examples: – – – – Speed (meters/second) Area (Length x Width) Volume (Length x Width x Height) Density (Mass / Volume) Prefixes • prefixes can be used with all 7 fundamental units! – Kilometer – Milliliter – Centigram – Microsecond – Nanokelvin 1790 - Jefferson • Proposed decimal-based measurement system for United States • Didn’t have prefix idea and system had too many names….and so we are stuck using feet, inches, cups, ounces, etc… Kids Have Dropped Dead Converting Metric Ladder Method 1 2 KILO 1000 Units 3 HECTO 100 Units DEKA 10 Units DECI 0.1 Unit Meters Liters Grams How do you use the “ladder” method? CENTI 0.01 Unit MILLI 0.001 Unit 4 km = _________ m 1st – Determine your starting point. Starting Point 2nd – Count the “jumps” to your ending point. How many jumps does it take? 3rd – Move the decimal the same number of jumps in the same direction. Ending Point 4. __. __. __. = 4000 m 1 2 3