Electrocardiography: Chapter 10 Worksheet
advertisement

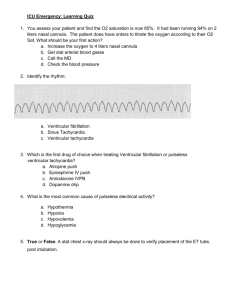
Electrocardiography: Chapter 10 Worksheet Complete the following. 1. Ventricular rhythms often indicate myocardial ischemia and consequently must be diligently assessed and treated aggressively. 2. When the SA node or the AV junctional tissues fail to initiate an electrical impulse, the ventricles will take the responsibility of pacing the heart. 3. PVCs are individual complexes rather than an actual rhythm. 4. Unifocal PVCs are alike in appearance, whereas multifocal PVCs originate from different sites within the ventricles and present with different morphology. 5. PVT is described as a rhythm in which three or more PVCs arise in sequence at a rate greater than 100 bpm. 6. Torsades de pointes rhythm resembles a turning about or a twisting motion along the baseline. 7. Ventricular fibrillation is thought to be the most frequent initial rhythm occurrence in sudden cardiac arrest. 8. Asystole is represented by an isoelectric line on the ECG strip. 9. Pulseless Electrical Activity is not an actual rhythm; rather, it represents a clinical condition wherein the patient is clinically dead, despite the presence of a rhythm on the ECG strip. 10. PVCs characteristically are followed by a compensatory pause. 11. Pacemaker cells found in the Purkinje network in the ventricles have an intrinsic firing rate of 20 – 40 bpm. 12. On the ECG monitor or oscilloscope, ventricular fibrillation can be mimicked by artifact. 13. A PVC that falls between two sinus beats without interfering with the rhythm is an interpolated beat. 14. Another name given to a run or grouping of three or more PVCs in a row is salvos. 15. When an Idioventricular rhythm falls below 20 bpm, the rhythm may be called agonal. 16. A sustained rhythm is generally thought to be a rhythm that lasts for more than 30 seconds and if less than 30 seconds it is a nonsustained rhythm. 17. Patients may report a feeling of “skipped beats” or extra beats called palpitations when PVCs occur. 18. Ventricular asystole is also called cardiac standstill or asystole. 19. VFib is further classified as either fine or coarse VFib. 20. The presence of VFib indicates that the rhythm has been present for an extended period of time.