Ch. 11 Handout
Chapter 11
11.1 Fiscal Policy
What is Fiscal Policy?
- government stabilization policy that uses taxes and government purchases as its tools
- also known as: _______________
Fiscal Year
- the 12-month period to which a budget applies
Stabilization Policy
- government policy designed to lessen the effects of the business cycle
2 categories of Stabilization Policy
● __________________- government policies designed to reduce unemployment and stimulate output
● __________________- government policies designed to stabilize prices and reduce output
The Business Cycle
Four Parts to the Business Cycle
1. ____________
2. ____________
3. ____________
4. ____________
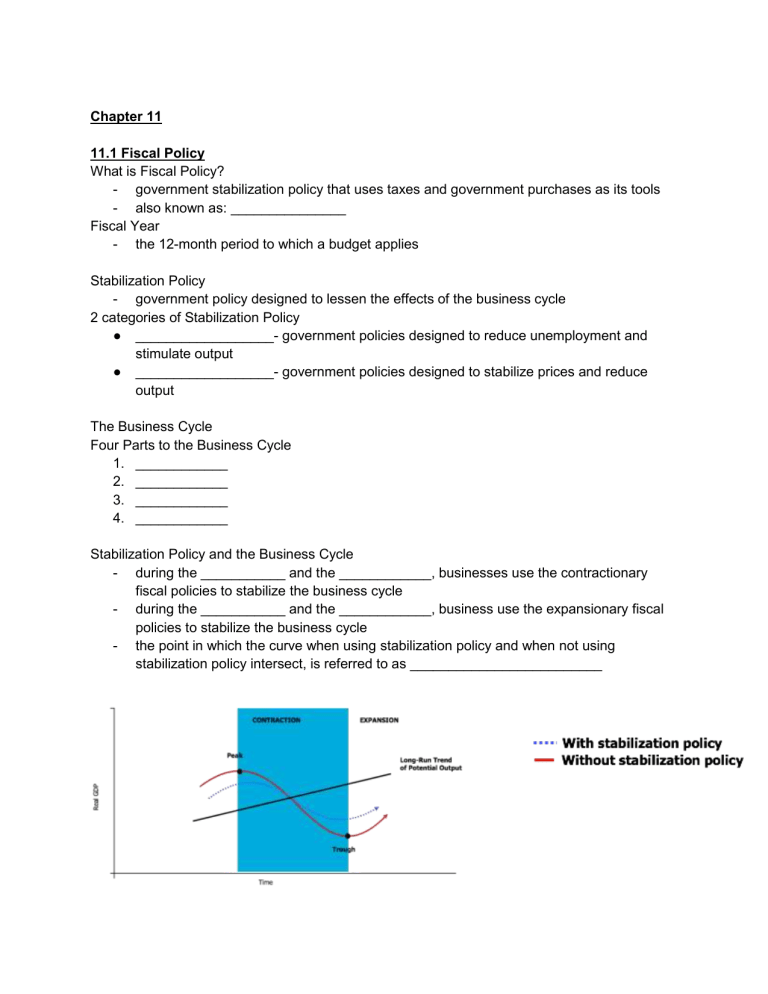
Stabilization Policy and the Business Cycle
- during the ___________ and the ____________, businesses use the contractionary fiscal policies to stabilize the business cycle
- during the ___________ and the ____________, business use the expansionary fiscal policies to stabilize the business cycle
- the point in which the curve when using stabilization policy and when not using stabilization policy intersect, is referred to as _________________________
Stabilization Policy and Aggregate Demand
- stabilization policies can be in a form of fiscal policy and monetary policy
- fiscal policy uses taxes and government purchases:
- Expansionary fiscal policy involves more government purchases and/or lower taxes, shifts AD to the _______
- Contractionary fiscal policy involves less government purchases and/or higher taxes, shifts AD to the _______
Expansionary Policy Contractionary Policy
Expansionary and Contractionary Fiscal Policy
- when showing the AD shift in the expansionary fiscal policy graph, the gap between real
GDP at AD0 and AD1, is known as _____________________
- when showing the AD shift in the contractionary fiscal policy graph, the gap between real
GDP at AD0 and AD1, is known as_____________________
Discretionary Policies vs. Automatic Stabilizers
- discretionary policy is intentional government intervention in the economy
- automatic stabilizers are built-in measures such as taxes and transfer payments to lessen the effects of the business cycle
A _______________ decreases net tax revenues which increases spending and incomes
A _______________ increases net tax revenues which decreases spending and incomes
11.2 Spending Multiplier
Multiplier Effect:
● The multiplier effect is the magnified impact of a spending change on AD:
○ Any given purchase made by government has an initial effect, a secondary effect and son on.
○
An initial spending change produces income and part of this new income becomes new spending.
○ This process is repeated with each spending round smaller than the last.
○ It also assumes that the price level stays constant
● Each spending round of the multiplier effect is based on:
○ marginal propensity to consume (MPC), which measures the effect of an income change on domestic consumption.
○ marginal propensity to withdraw (MPW), which measures the effect of an income change on withdrawals (with MPC and MPW always summing to one).
Spending Multiplier:
● The spending multiplier is the value by which an initial spending change
(injections) is multiplied to give the total change in real output:
○ It’s the value by which an initial spending change is multiplied to give the total shift in the AD curve
○ equals (1/MPW), also known as the reciprocal of the marginal propensity to withdraw
Equation:
Total Change in output (shift in AD curve) = initial change in spending * spending multiplier
If rearranged to isolate spending multiplier:
Spending multiplier = total change in output (shift in AD curve)
initial change in spending
The multiplier effect can be applied to other stimulus that government use: tax cuts.
Marginal Propensity to Withdraw
● the effect on withdrawals-saving, import, and taxes- of a change in income
Marginal Propensity to Consume
● the effect on domestic consumption of a change in income
● The proportion of an aggregate raise in pay that a consumer spends on the consumption of goods and services, as opposed to saving it.
Example:
Suppose you receive a $500 bonus on top of your normal annual earnings. You suddenly have
$500 more in income than you did before. If you decide to spend $400 of this marginal increase in income on a new business suit and save the remaining $100, your marginal propensity to
consume will be 0.8 ($400 divided by $500). This also means that your marginal propensity to save will be 0.2 ($100 divided by $500).
If you decide to save the entire $500, your marginal propensity to consume will be 0 ($0 divided by 500). The other side of marginal propensity to consume is marginal propensity to save, which shows how much a change in income affects levels of saving. Marginal propensity to consume
+ marginal propensity to save = 1.
Fiscal policy has two main benefits
● It can be focused on particular regions.
● It has a relatively direct impact on spending.
Fiscal policy has three main drawbacks
● It is subject to delays (recognition lag, decision lag, impact lag).
● It is closely related to public debt, which is the total amount owed by the federal government as a result of past borrowing.
Impact
A government is running a: balanced budget when its expenditures and revenues are equal budget surplus when its revenues exceed its expenditures budget deficit when its expenditures exceed its revenues
11.3 - Impact of Fiscal Policy
Budget Surpluses and Deficits
● Balanced budget is where a government’s expenditures and revenues are _________.
● Budget Surplus is where a government’s __________ exceeds its ___________. budget surplus = government revenues - government expenditure
$9.6 billion = $242.4 billion - $232.8 billion
● Budget Deficit is where a government’s __________ exceeds its ___________. budget deficit = government revenues - government expenditure
-$37.3 billion = $238.7 billion - $276.0 billion
● A deficit occurs when ___________________________________________________.
● Debt occurs when _____________________________________________________.
● Surpluses and Deficits have a very large impact on public debt.
When the federal government has a budget deficit, then the public debt ________ by the same amount.
When the federal government has a budget surplus, then public debt is ________ by the same amount.
Ex. If public debt starts at -$100 at the beginning of the fiscal period and there is a surplus of $25, then the public debt becomes _____.
Fiscal Policy Guidelines
● ________ ________ ________ is the principle that government revenues and expenditures should balance each year; although opponents of this principle suggest it is based on ________ ________. It is appropriate for a household but not society as a whole.
● ________ ________ ________ is the principle that government revenues and expenditures should balance over the course of one business cycle. The deficits from periods of contraction should roughly equal the surpluses from periods of expansion.
● _______ _______ is the principle that government budgets should be geared to the yearly needs of the economy. It states that the government should base a year’s fiscal policy on ____________.
Recent Fiscal Policy
● The fiscal policy has undergone profound change since the early 1980s. It moved from
________ finance to _______ balanced budgets.
○ Functional finance was the guiding principle behind the fiscal policy
● Budget deficits were largely due to ___________ and automatic stabilizers.
● Budget surpluses were due to automatic stabilizers, _______ interest rates, and government spending cuts.
● _____________ _____________ are tax structures and government spending programs that lead to larger budget deficits during a recession and larger budget surpluses during expansion
● To find _______ GDP %,
1.
Add the budgets of the __________, _________, and _________ governments to get a sum
Formula
2.
_________ the budget sum by the GDP to find the nominal GDP
3.
_________ the number by 100 to get a percent
Nominal GDP= (Total Budgets/GDP) x100