THE CELL
advertisement

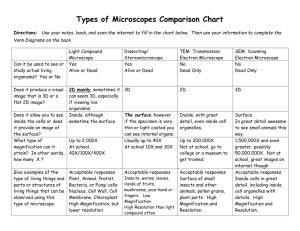
THE CELL Chapter 1 DO NOW 1.1. Do we have eukaryotic or prokaryotic cells? Chapter Objectives • Differentiate unicellular and multicellular organisms. • List the characteristics of life/living things. • Identify the scientists that observed and discovered cells. • List the 3 parts of the cell theory. • Compare light, SEM, and TEM microscopes. • Compare prokaryotic vs. eukaryotic cells AND plant vs. animal cells. • Explain the term specialization and compare to our bodies. DO NOW … • What are cells? • Name different types of cells you know of... • What is a difference between living and non-living things? What is a cell? • Basic structural and functional unit of all living organisms! • They come in different shapes + sizes How were cells discovered? The light microscope helped discover cells! Who discovered the cell? ROBERT HOOKE • Observed dead cork cells • Said boxes looked like tiny rooms or jail “cells”. • Used a microscope at 30x magnification Who else discovered the cell? ANTON VAN LEEUWENHOEK • Observed pond water • 1st to observe “living” cells • Used a microscope at 300x magnification ← Cork cells! *Cork is from tree bark (dead cells) Animalcules ➔ Do you have these recipes at home? People thought organisms grew from non-living materials! Fransisco Redi Experiment • Placed meat in both an open container and a closed container to see what happened. Redi’s Conclusion • Maggots come from flies, NOT the meat! • Life must come from life, which proved that spontaneous generation is not real! • People still did not believe him but he was right. Louis Pasteur Experiment • Showed that bacteria are present in air and do not appear spontaneously. Louis Pasteur Conclusions • Discovered that cells MUST come from other cells • Disproved “Spontaneous Generation” and said life cannot just appear out of no where. • Helped verify Redi’s research! DO NOW 1. Give an example of a multicellular organism and unicellular organism. 2. What type of cells did Robert Hooke observe? Pasteurization • Pasteur came up with the idea of Pasteurization after discovering bacteria could contaminate milk from the air. • This process kills the bacteria so that it does not harm us! • Used in milk, cheese, yogurt, etc. • Cell Theory = • Every living thing is made of one or more cells • Cells carry out the functions needed to support life • Cells come only from other living cells Unicellular vs. Multicellular • Unicellular – a single cell • Multicellular – made up of many cells Characteristics of Life 1. Organization 2. The ability to develop and grow 3. The ability to respond to the environment 4. The ability to reproduce Section 1.2 - Microscopes How small are cells? • Unit used = micrometer (um) One millionth of a meter • Most cells range from 1 um to 1000 um. Types of Microscopes 1. Light Microscope 2. SEM Microscope 3. TEM Microscope Light Microscope • Uses thin light • Looks at thin specimen • Total Magnification = 40x-1000x • Use to see cells, but not detailed organelles SEM vs. TEM SEM • • “Scanning electron microscope” TEM • “Transmission electron microscope” Beams of electrons bounce of • Electrons pass through the the surface of the coated cell. think section. • Images appear 3D • Total Magnification = 100,000x • Must be dead ☹. Specimen coated in metal • Images appear 2D • Total Magnification = 300,000x • Allows us to see organelles inside the cell SEM TEM Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic cells What are the differences you can see? Prokaryotic Cells • Have circular DNA • NO nucleus • Does not have membrane bound organelles ex: snow globe • Most unicellular organisms are prokaryotes Example: Bacteria Eukaryotic Cells • Have linear DNA – double helix shape • Has nucleus • Have membrane bound organelles • Most multicellular organisms are eukaryotic cells. Some are unicellular though. Example: You! Section 1.3 – cell functions • 3 domains of life: • Eukarya – Have a nucleus. Plants, animals, and fungi. • Bacteria – prokaryotics. • Archaea – “ancient”. Genetically different from bacteria. Specialization •Specific cells perform specific functions. Ex: Blood cells can only be blood cells. Muscle cells cannot be turned into blood cells. Tissue and organs • Tissue – group of similar cells that are organized to do a specific job. • Organ – different tissues working together to perform a particular function. Stem Cells to determine specialization • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=evH0I7Coc54 DNA • Rosalind Franklin – used x-rays to produce images of DNA • Watson and Crick – put together a 3D model of DNA and present it to the world in 1953